Studying the Impact of a Nuclear-Powered Naval Ship Severe Accident on Aquatic Biota Using Resrad Code
Received: 13-Dec-2020 / Accepted Date: 22-Mar-2021 / Published Date: 29-Mar-2021 DOI: 10.4172/2155-9910.1000303
Abstract
Naval ships are designed to function under very difficult circumstances. The most common cases of nuclear ship incidents/accidents are collisions, problems with the nuclear power reactor, groundings, fires and explosions as well as leaks in the sea-water systems of submarines. Accidental release to air caused by criticality or core melt is considered a real radiological hazard. This study consists of two parts; first part aims at estimating the core inventory of the suggested accident due to melting of nuclear fuel in the ship's power reactor using a Radiological Assessment System for Consequence Analysis (RASCAL) code.
Keywords: Marine science; Nuclear powered ship incidents/accidents; Biota, Radiation dose assessment; Naval ship; Nuclear accident
Abstract
Naval ships are designed to function under very difficult circumstances. The most common cases of nuclear ship incidents/accidents are collisions, problems with the nuclear power reactor, groundings, fires and explosions as well as leaks in the sea-water systems of submarines. Accidental release to air caused by criticality or core melt is considered a real radiological hazard. This study consists of two parts; first part aims at estimating the core inventory of the suggested accident due to melting of nuclear fuel in the ship's power reactor using a Radiological Assessment System for Consequence Analysis (RASCAL) code. The behaviour control of accidental released radionuclides on surface water body was calculated using mathematical equation. The radionuclides concentrations which have been evaluated in the marine environment are 241Am, 231Pu, 137Cs, 90Sr, and 131I. In the second part: The aquatic biota dose rate was evaluated using the RESRAD-BIOTA code. The radiological impact assessment of accidental releases of 90Sr and 137Cs to marine biota was found to be high. It is higher than International Commission on Radiation Protection (ICRP) dose limit by a factor about 103 for 100 m and by factor ten over the 4 km from the release point. Also, the radiological impact of accidental release of 131I to marine biota increases by factor 104 at 100 m and by factor ten for 4 km from release point.
Keywords
Marine science; Nuclear powered ship incidents/accidents; Biota, Radiation dose assessment; Naval ship; Nuclear accident
Introduction
Nuclear power ships are progressively becoming more popular in advancing ship technology, where those are using reactors have lower fuel costs and last for many years and have almost zero emissions [1]. The accidents related to nuclear ships include; collisions, groundings, sinking, leaks in sea-water systems, fires or explosions problems with the nuclear power reactor, and serious radiation exposures. Regarding accidents involving the nuclear propulsion plant in nuclear naval ship, the Loss of Coolant Accidents (LOCAs) and criticality are of the interest. For Russian nuclear Navy, there have been 6-LOCAs and 5-criticalities. Little radioactivity was detected in Atlantic Ocean water due to LOCA in a Soviet Echo-II class submarine. The exposure of aquatic biota to radiation from accidental releases of radionuclides is considered a real radiological hazard. Radiation from radionuclides released as a result of the Chernobyl accident caused numerous acute adverse effects on the biota located at a distance of a few tens of kilometres from the release point. Researchers found that, organisms in various parts of aquatic environment exposed to radiation from natural radioactivity as well as artificial one by different percentages [2-4]. This work aims at studying the effect of radiological release from a hypothetical nuclear naval ship accident on aquatic biota as a result of core melt. Sever accident scenario was assumed. Core inventory due to the accident calculated using RASCAL code, and the radioisotope distributions in the hydrosphere are calculated using the equation (1). The dose rate for aquatic biota was calculated using RESRAD code [5].
Material And Methods
A postulated core meltdown caused by a loss of coolant accident in a nuclear power ship Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) was considered with power 200 MW. It was assumed that the reactor was operating at full power during passing through a water body “Channel body”. RASCAL code [6] is used to calculate the core inventory due to core melting. RASCAL is a Radiological Assessment System for Consequence Analysis. It is software developed and used by the U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). RASCAL consists of two main tools: The Source Term to Dose model and the Field Measurement to Dose model. RASCAL adjusts the inventory of radionuclides that have a half-life exceeding one year to account for peak rod burn up (U. S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission 2012) [7]. Radionuclide core inventory using RASCAL code was presented in (Table 1). Controlling the behaviour of the longitudinal dispersion of accidental released radionuclides in surface water bodies is determined using the following mathematical equation (NUREG 1983):
| Radionuclide | Inventory (Ci) | Radionuclide | Inventory (Ci) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3H | 3.00x106 | 132I | 4.50x106 |
| 60CO | 9.43x102 | 133I | 6.81x106 |
| 85Kr | 3.78x104 | 135I | 5.81x106 |
| 88Kr | 2.88x106 | 133Xe | 6.83x106 |
| 89Sr | 6.92x106 | 135Xe | 8.30x105 |
| 90Sr | 2.99x105 | 134Cs | 8.31x105 |
| 95Zr | 9.50x106 | 137Cs | 3.12x105 |
| 97Zr | 5.90x106 | 140Ba | 7.35x106 |
| 95Nb | 1.02x107 | 140La | 8.07x106 |
| 97Nb | 6.09x106 | 141Ce | 8.02x106 |
| 99Mo | 6.26x10 6 | 144Ce | 6.13x106 |
| 99Tc | 5.53x106 | 156Eu | 1.91x106 |
| 103Ru | 4.56x106 | 157Eu | 1.91x106 |
| 106Ru | 4.39x105 | 239Np | 1.58x106 |
| 132Te | 4.44x106 | 239Pu | 1.23x10 |
| 131I | 3.01x106 | 241Am | 8.24x10-1 |
Table 1. Radionuclide core inventory using RASCAL code
Mainly radionuclides which have been evaluated in the marine environment are 241Am, 231Pu, 137Cs, 90Sr, and 131I [8]. The calculation obtained at certain time for deferent release distances.
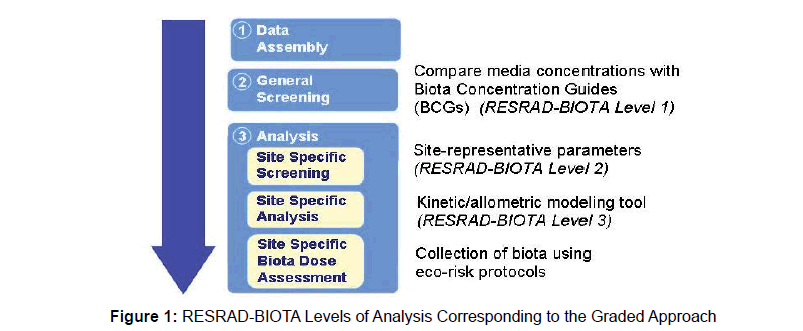
The radionuclide concentration for 131I, 137Cs, 90Sr, 241Am and 239Pu in water at different distances from release point are the input RESRAD-BIOTA code [9-10]. The RESRAD-BIOTA code is a tool for implementing a graded approach to biota dose evaluation. A complete spectrum of biota dose rate evaluation is carried out using RESRADBIOTA code (US Department of Energy 2004). Figure 1 represents RESRAD-BIOTA Levels of Analysis Corresponding to the Graded Approach. Internal and external dose rates due to the input radionuclides for aquatic animal, Riparian animal and fish are the code output.
Results And Discussion
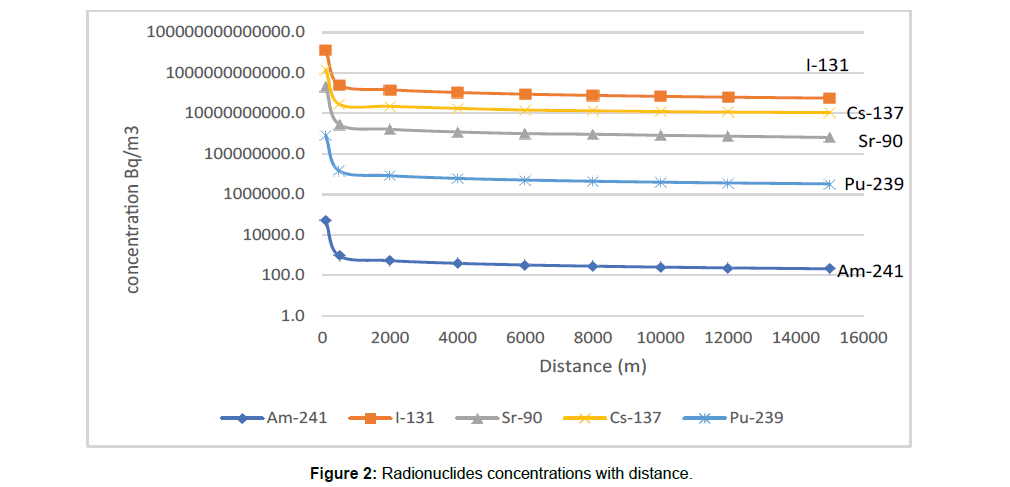
Figure 2 represents the radionuclides concentration in water body at different distances up to 16 Km from the release point. Radionuclides concentrations are decreasing by a factor of approximately 103 over the 16 km from the release point. The highest concentration was the short half-life 131I. In the first 7-days, radiation exposures were essentially acute because of the large quantities of short-lived radionuclide 131I (Its half-life about 8 days), which after one month had been largely disappeared. There is no significant concentration for 241Am, but 137Cs-, 90Sr and 239Pu have been the dominant radionuclides.
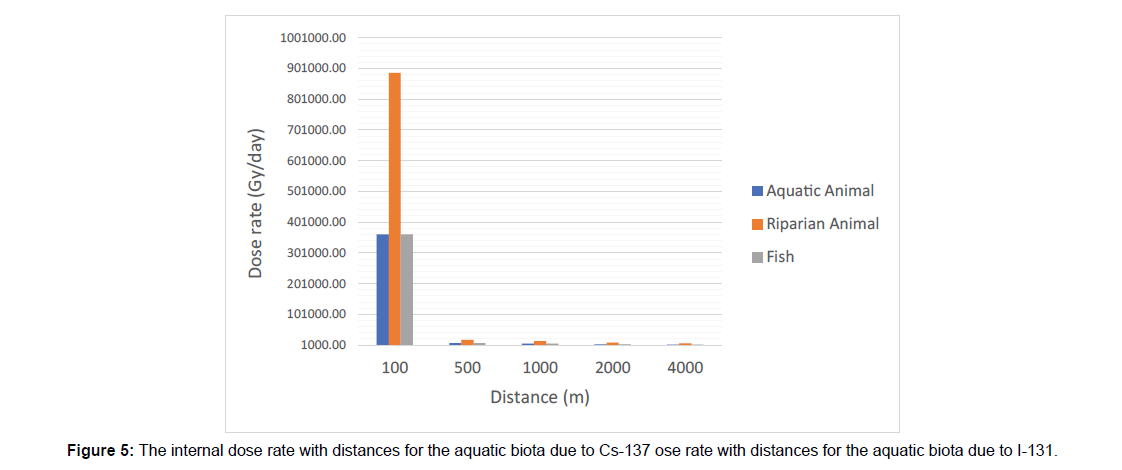
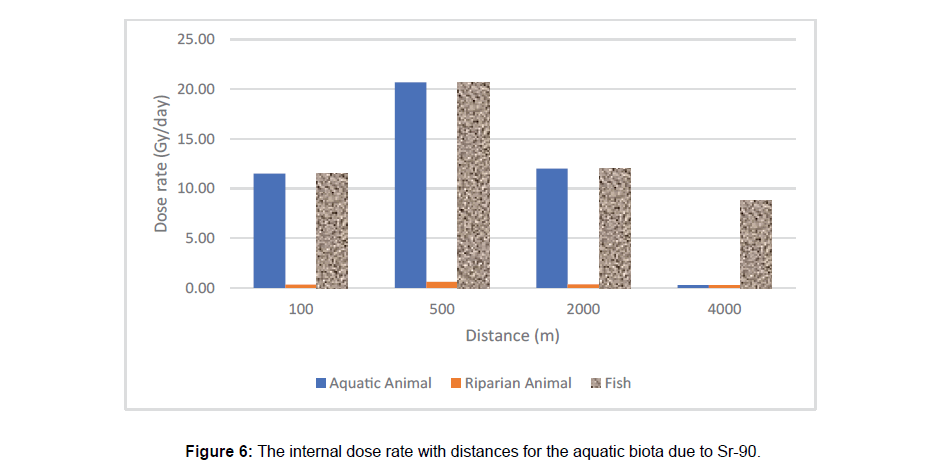
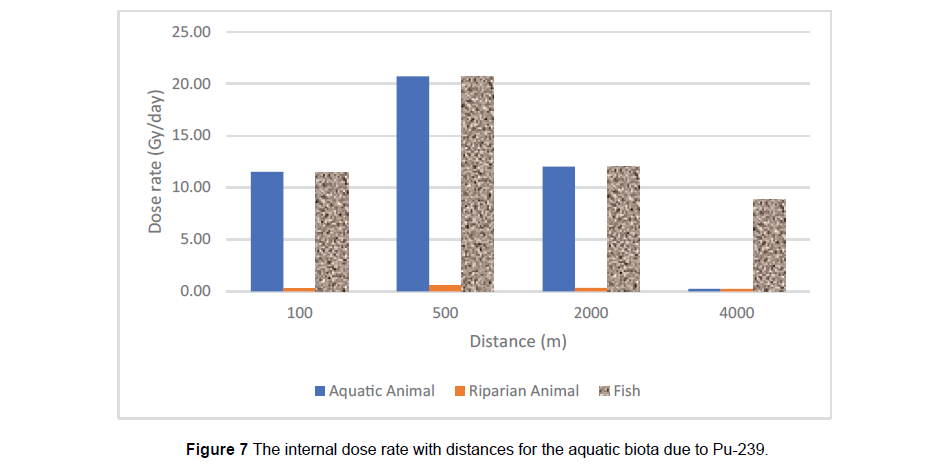
The RESRAD Aquatic Biota (Aquatic animals, Riparian animals and fish) output dose rates (external and internal) are represented in the (Table 2) at different distances up to four kilometres from the release point. It is obvious internal high dose rate from 131I and 137Cs at distance 100m from the release point. This dose rate would cause significant effect in most organisms on a timescale of minutes. It is shown that, the dose rate decreases by about factor 102 for the all radionuclide at distance 4 km from the release point. For external or internal dose, there are no significant effects from 241Am. 241Am released into water from nuclear facilities will tend to stick to particles in the water or the sediment. Ultimately, most americium ends up in soil or sediment. Fish may take up 241Am, the amount that builds up in the flesh is very small. For 131I 4-weeks aftermath the accident there is no significant effect due to its short half live time. The principal focus was for long-lived radionuclides such as 137Cs, 239Pu and 90Sr isotopes.
| Aquatic animal Dose Gy/d | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (m) | Nuclide | Water dose | |
| External | Internal | ||
| 100 | 241Am | 2.01x10-8 | 3.11x10-2 |
| 137Cs | 7.67 | 3.61x105 | |
| 131I | 5.52x10 | 2.41x104 | |
| 239Pu | 3.04x10-7 | 1.15x10 | |
| 90Sr | 1.65 | 1.06x103 | |
| Riparian Animal | |||
| 241Am | 2.01x10-8 | 9.32x10-4 | |
| 137Cs | 7.67x10 | 8.86x105 | |
| 131I | 5.52x10 | 2.73x104 | |
| 239Pu | 3.04x10-7 | 3.44x10-1 | |
| 90Sr | 1.65 | 2.05x104 | |
| Fish | |||
| 241Am | 2.01x10-8 | 3.11x10-2 | |
| 137Cs | 7.67 | 3.61x105 | |
| 131I | 5.52x10 | 2.41x104 | |
| 239Pu | 3.04x10-7 | 1.15x10 | |
| 90Sr | 1.65 | 1.06x103 | |
| Aquatic animal Dose Gy/d | |||
| 241Am | 3.63x10-10 | 5.63x10-4 | |
| 137Cs | 1.56x10-1 | 7.33x103 | |
| 131I | 5.52x10 | 2.41x104 | |
| 239Pu | 5.48x10-7 | 2.07x10 | |
| 90Sr | 1.65x10 | 1.06x103 | |
| Riparian Animal | |||
| 241Am | 3.63x10-10 | 1.69x10-5 | |
| 500 | 137Cs | 1.56x10-1 | 1.80x104 |
| 131I | 5.52x10 | 2.73x104 | |
| 239Pu | 5.48x10-7 | 6.21x10-1 | |
| 90Sr | 1.65 | 2.05x104 | |
| Fish | |||
| 241Am | 3.63x10-10 | 5.63x10-4 | |
| 137Cs | 1.56x10-1 | 7.33x103 | |
| 131I | 5.52x10 | 2.41x104 | |
| 239Pu | 5.48x10-7 | 2.07x10 | |
| 90Sr | 1.65 | 1.06x103 | |
| Aquatic animal Dose Gy/d | |||
| 2,000 | 241Am | 2.11x10-10 | 3.27x10-4 |
| 137Cs | 7.95x10-2 | 3.74x103 | |
| 131I | 5.80x10-1 | 2.53x102 | |
| 239Pu | 3.19x10-7 | 1.20x10 | |
| 90Sr | 1.27x10-2 | 8.16 | |
| Riparian Animal | |||
| 241Am | 2.11x10-10 | 9.78x10-6 | |
| 137Cs | 7.95x10-2 | 9.18x103 | |
| 131I | 5.80x10-1 | 2.86x102 | |
| 239Pu | 3.19x10-7 | 3.61x10-1 | |
| 90Sr | 2.11x10-10 | 1.58x102 | |
| Fish | |||
| 241Am | 2.11x10-10 | 3.27x10-4 | |
| 137Cs | 7.95x10-2 | 3.74x103 | |
| 131I | 5.80x10-1 | 2.53x102 | |
| 239Pu | 3.19x10-7 | 1.20x10 | |
| Aquatic animal Dose Gy/d | |||
| 241Am | 1.55x10-10 | 2.40x10-4 | |
| 137Cs | 5.92x10-2 | 2.79x103 | |
| 131I | 4.25x10-1 | 1.86x102 | |
| 239Pu | 2.34x10-7 | 8.84 | |
| 90Sr | 9.39x10-4 | 6.00x10-1 | |
| Riparian Animal | |||
| 4,000 | 241Am | 1.55x10-10 | 7.20x10-6 |
| 137Cs | 5.92x10-2 | 6.84x103 | |
| 131I | 4.25x10-1 | 2.10x102 | |
| 239Pu | 2.34x10-7 | 2.65x10-1 | |
| 90Sr | 9.39x10-4 | 1.16x10 | |
| Fish | |||
| 241Am | 1.55x10-10 | 2.40x10-4 | |
| 137Cs | 5.92x10-2 | 2.79x103 | |
| 131I | 4.25x10-1 | 1.86x102 | |
| 239Pu | 2.34E-07 | 8.84 | |
| 90Sr | 9.39x10-4 | 6.00x10-1 | |
Table 2. RESRAD aquatic biota output dose rate
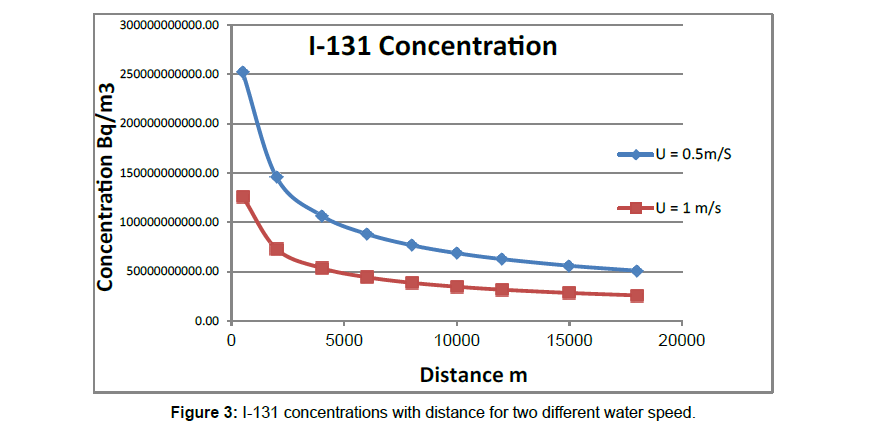
Figure 3 represents the behaviour of 131I concentration for water speed value 0.5 m s-1 and 1m s-1. It is obvious that radionuclide concentration decreases about its half value when the water speed increases to its double value.
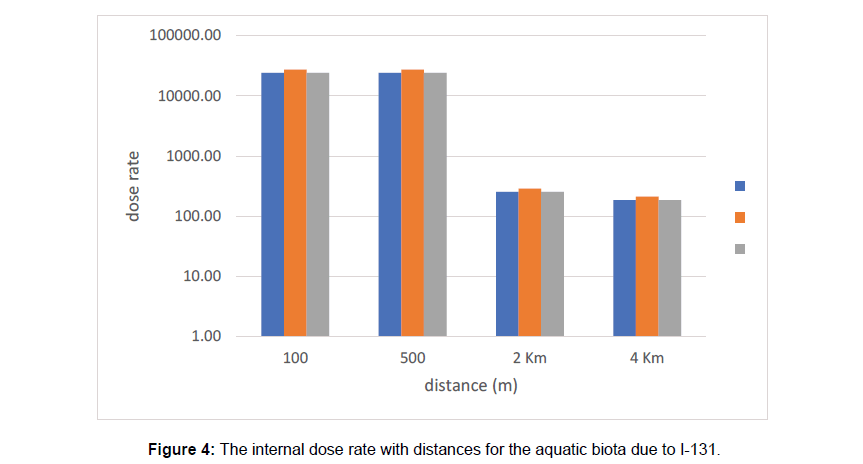
Figure 3 I-131 concentrations with distance for two different water speed (Figures 4-7) illustrate the calculated internal dose rate for different aquatic biota due to each radioisotope. The maximum internal dose rate is 3.6x105 Gy d-1 due to 137Cs. It is eight times greater than generic dose rate according to United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Sources and Effects of ionizing radiation (UNSCEAR), which is 10 mGy d-1/) [11]. Where the external dose rates for fish and aquatic animals from 137Csand 90Sr are about 79 mGy d-1 and 12 mGy d-1 respectively at distance 2 km from the release point. This is due to the complex interaction of radioisotopes chemical properties with the chemical, physical and biological process of aquatic environment. It can also, leading to non-uniform distribution of the radioactivity input to the aquatic environment (Folsom 1957). There is an acute internal dose rate result from contamination with 137Cs, 90Sr and 239Pu greater than generic dose by factor 103. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has proposed a ‘derived consideration reference level’ of (0.1-1m Gyd-1) for the most sensitive Reference Animals and Plants (RAPs) (ICRP 2008b). Fish are more radiosensitive than other aquatic biota and proposed to a reference dose rate of about 1.6 mGy d-1 [3]. The Department of Energy (DOE) adopt a dose rates corresponding to expected safe levels of (populations exposure) of biota based on reviews of the acute and chronic radiation exposure effects. The expected safe levels were a dose rate of 10 mGy d-1 to populations of aquatic animals, 10 m Gy d-1 to populations of terrestrial plants and 1.0 mGy d-1 to populations of terrestrial animals (UNSCEAER 1996). The DOE indicated that, the population should be protected if the dose rate does not exceed the expected safe dose rate to the most individual population exposed [2]. ICRP suggested that, some reductions in reproductive capacity might occur in frogs and possibly in fish species, for a range of 1–10 mGy d-1 dose rates. It had been concluded that significant effects on fish gonads from chronic radiation exposure would be unlikely at dose rates less than 24 mGyd-1 [6]. The dose rates to fish depended on their trophic positions. In general, radionuclide levels in marine water returned to pre-accident values within a few months after the accident. This is mainly due to dilution with non-contaminated water and also to convection processes that have efficiently transported the radionuclide to depth. During fish migration, radioactive caesium will decline when fish leaves contaminated waters. Caesium will gradually be excreted, as it is not bound to the body. The biological half-life of caesium in sea fish is typically between 5 to 100 days (UNSCEAR 2011) [8-12].
Analysis and Recommendation
This study discusses the impact of a nuclear-powered naval ship sever accident on marine biota. The most effects on aquatic biota were found at the 100 m from the release point [13]. The maximum dose rates to aquatic organisms (excluding fish) were found in the first two weeks aftermath the accident [14, 15]. This is due to 131I dose contribution that disappeared largely after one month [16]. No expectation to long-term impact from 131I because of it is rapidly decay and is not expected to be transported over long distances by marine water currents. The longer half - lives 137Cs, 90Sr and 239Pu have been the dominant radionuclides and could be transported over long distances by marine water currents. It is concluded that, based on the water body’s current speed, the diffusion and dilution of radionuclides activity concentrations will be affected, the radiation levels may be returned to the pre-accident levels after few months depending on the contamination levels [17-19]. The great quantity of water, as well as, the increasing of water speed will rapidly disperse and mitigate the existence of radioactive materials to the pre-accident levels. Accident where the water speed is low the pre-accident return will be taken more time. Emergency protective measures are needed for the first 4Km. Regular sampling of seawater at 2, 4 and 16Km must be taken as well as monitoring for the presence of 131I, 137Cs, 239Pu and 90Sr in local seafood. It is important to enhance the preparedness and response to nuclear and radiological emergencies in the coastal ports and sea. When the coastal state which a sea emergency has occurred and has not the enough capabilities to assess the impact of the accident for taking the decisions on protective and other response actions, should request the necessary information, advice and assessments from the Consignor or other IAEA Member States [20].
Conclusion
The radiological impact assessment of accidental releases of 90Sr and 137Cs to marine biota was found to be high. It is higher than International Commission on Radiation Protection (ICRP) dose limit by a factor about 103 for 100 m and by factor ten over the 4 km from the release point. Also, the radiological impact of accidental release of 131I to marine biota increases by factor 104 at 100 m and by factor ten for 4 km from release point.
References
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2004) U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: April.
- Barnthouse LW (1995) Effects of ionizing radiation on terrestrial plans and animals: a workshop report; Oak Ridge, TN (United States); CONF-9506302-SUMM: CONTRACT AC05-84OR21400.
- Fesenko SV, Alexakhin RM, Geras'kin SA, Sanzharova NI, Spirin YV, et al. (2005) Comparative radiation impact on biota and man in the area affected by the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. J Environ Radioact 80:1-25.
- Folsom TR, Harley JH (1957) Comparison of some natural radiations received by selected organisms. Nation Aca Sci 551: 28-33.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2011) Impact on seafood safety of the nuclear accident in Japan 9 May 2011. World health organization.
- International Atomic Energy Agency (2014) Radiation protection after the Fukushima Daiichi accident:Â promoting confidence and understanding. IAEA Report.
- International Atomic Energy Agency (1988) Assessing the impact of deep sea disposal of low-level radioactive waste on living marine resources. Technical Reports Series: No. 288.
- International Atomic Energy Agency (2019) Regional coordination of coastal emergency preparedness and response arrangements for port and maritime radiological emergencies for Member States in the Mediterranean region of Africa and the Middle East.
- International Commission for Radiation Protection. Environmental protection: the Concept and use for reference animals and plants. ICRP Publication 108 Ann ICRP 38: 4-6.
- Juwel MMH, Khondoker MRH, Khan R (2018) Performance Analysis of a Naval Reactor for Nuclear Powered Ship. Int J Res App Sci & Eng Tech: 6 (IV).
- Gussgard K Is spent nuclear fuel at the Kola Coast and dumped in waters a real danger? NO9700072.
- John ET, Robert Meyer H (1983) Radiological Assessment, A Textbook on Environmental Dose Analysis. NUREG/CR-3332.
- Olgaard PL (1996) Accidents in nuclear ships. NKS/RAK-2(96) TR-C3: ISBN 87-550-2266-9.
- US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (2012) RASCAL 4: Description of models and methods. Washington, DC: Office of Nuclear Security and Incident Response: 20555-0001.
- United States Department of Energy (2004) (DOE/EH-0676). User's guide, version 1 RESRAD-BIOTA : a tool for implementing a graded approach to biota dose evaluation: ISCORSs technical report.
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (1996) Sources and Effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly.
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (2013) Sources and Effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly.
- William MA, Joshua H (1989) Naval accidents 1945-1988. Washington DC: Neptune Papers 3.
- Woodhead DS (1984) Contamination due to radioactive materials. Kinne O. (ed.) 1641 p; ISBN 0 471 90216 0 John Wiley Chichester UK: p 1111-1287.
Citation: Salem EF, Bakr WF, Abdien AK, Tawfik FS (2021) Studying the Impact of a Nuclear-Powered Naval Ship Severe Accident on Aquatic Biota Using Resrad Code. J Marine Sci Res Dev 11: 303. DOI: 10.4172/2155-9910.1000303
Copyright: © 2021 Salem EF, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2266
- [From(publication date): 0-2021 - Apr 03, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1525
- PDF downloads: 741