Mini Review Open Access
Study on the Prevalence of Bovine Demodecosis and its Associated Risk Factors in and Around Bahir Dar, Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia
Melessew Wubante2 and Mulat Asrat1*1Bahir Dare Veterinary Regional Laboratory, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
2School of veterinary medicine, Wollo University, Ethiopia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Asrat M
Assistant professor of Veterinary Surgery and Radiology
Bahir Dare Veterinary Regional Laboratory, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
Tel: +251912923170; E-mail: mullur1974@gmail.com
Received date: May 16, 2017; Accepted date: May 29, 2017; Published date: June 05, 2017
Citation: Wubante M, Asrat M (2017) Study on the Prevalence of Bovine Demodecosis and its Associated Risk Factors in and Around Bahir Dar, Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia. J Marine Sci Res Dev 7:1000231. doi:10.4172/2155-9910.1000231
Copyright: © 2017 Wubante M, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Marine Science: Research & Development
Abstract
A cross-sectional study was conducted from October 2014 to April 2015 in Bahir Dar, Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia to determine prevalence of bovine demodicosis. A total of 384 cattle of different groups of age, sex and breed were examined by taking deep skin scrapings. There was no statistically significant difference observed between two categories of breeds (p=0.938), though prevalence was lower in cross breeds (4.8%) than local breeds (5%). There was no statistically significant difference among three categories of age (P=0.430), with prevalence rate of 3.0%, 2.9% and 6.0% in less than one year, one to three year and greater than three years, respectively. The prevalence of demodicosis in female and male was, 5.9% and 3.9%, respectively, with statistically insignificant difference between them (P=0.369).Statically insignificant difference was also found between the two management systems (P=0.096), higher prevalence was observed on cattle managed under semi-intensive management system 7.5% than extensive ones 3.6% management systems. There was statistical significant variation detected among different site of infestation (P=0.027), the highest prevalence was found on shoulder 3.4% followed by neck, (0.8%), dew lap, fore limb and generalized (0.3%). In conclusion the overall prevalence (4.9%) of Demodex bovis infestation was recorded.
Introduction
Domesticated animals is a critical segment of almost all cultivating frameworks in Ethiopia and give draft control, drain, meat, excrement, conceals, skins and different items. As of now, the number of inhabitants in animals observed in Ethiopia is assessed to be 53.4 million dairy cattle, 25.5 million sheep and 22.78 million goats [1]. Animals contribute 15-17% of GDP and 35-49% of horticultural GDP, and 37-87% of the family salary [2]. The presence of different skin ailments (dermatophilosis, demodicosis, sarcoptic and psoroptic mange, ticks and lice pervasions) influencing cows is as often as possible detailed from various parts of Ethiopia. These skin maladies are responsible for extensive monetary misfortunes especially to the skin and shroud trade. Aside from quality debasement of skin and conceals skin illnesses actuate related monetary misfortunes due to decrease of fleece quality, meat and drain yield, misfortunes thus of separating and periodic mortalities and related with cost of treatment and avoidance of the maladie [3]. Demodex species parasites have a place with the request Prostigmata clogged pore rashes and family Demodicidae. Demodicosis in cows is brought on by a tiny parasite, D. bovis . The illness is very much portrayed and very normal in tropical zones, however uncommon and in all probability belittled in calm locales [4]. Injuries comprise of papules and little knobs loaded with a velvety shading gaseous material perhaps connected with hair misfortune primarily seen in the periocular district, on the neck, and on the shoulders. Under certain conditions, similar to push, nutritious inadequacies, simultaneous illnesses and hot and damp climate, the condition can stretch out to most parts of the body and prompt lost body condition [5]. Determination is affirmed by finding the bug amid infinitesimal examination of profound skin scrapings of the influenced range. However, bovine demodicosis are pervasive in Ethiopia yet the dispersion of the ailment in and around Bahir Dar were not considered. In this way, the present review was made to decide the commonness and related hazard components of cow-like demodicosis in and around Bahir Dar area.
Materials and Methods
The review was led in Bahir Dar city, from November 2014 to April 2015. Bahir Dar is situated in the North Western piece of Ethiopia at a physical separation of 567 kilometers from Addis Ababa, the capital city of Ethiopia. The coordinates of the study area are 11°29’ –11°41' N and 37°16' –37°27’ E. The scene is level with some little slopes toward the East and West. The normal rise in the town is around 1795 meters above sea level. The review zone encounters normal yearly precipitation that extends from 1200-1600 mm and it has mean yearly temperature of 26°C [1]. Ponder populace. The review populaces subjected to this review were cows of various breed, age, sex and kept under Semi-concentrated and broad administration frameworks. The example size were ascertained utilizing the recipe given by Thrusfield [6] by taking an expected pervasiveness of half and the review considered 95% of certainty interim with 5% total exactness.
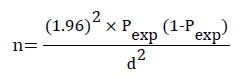
Where, n=sample size;
Pexp=expected prevalence
d=desired absolute precision=5%
Further history was taken from the animal owners about previous treatment, management, feeding and occurrence of skin diseases. Samples of deep skin scraping were collected and proper labelling of necessary information after recorded and then transported to the laboratory under aseptic procedure. After adding of 10% KOH and then a direct smear of skin scraping were examined under low power microscope. All collected data were entered and managed in Microsoft Excel worksheet and analysed using statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) software version 20. The prevalence of demodicosis was expressed as percentage by dividing the total number of cattle positive to demodicosis to total number of cattle examined; Chi- Square test (X2) used to test the association between variables. At p<0.05 was considered as statically significant.
Results
Out of the 384 cattle examined in and around Bahir Dar, 19(4.9%) were found to be positive for D. bovis. Traumatic damage what's more, kick by furrowing instruments which encourage the parasite to nourish effortlessly by puncturing the host cell what's more, sucking out the cell substance of the harmed region gatherings (P 0.05). The pervasiveness of demodicosis in cows under various age classes watched were most noteworthy in age aggregate 3 years 6.0% while the least predominance 2.9% was seen in age bunch between1 -3 years. In any case, measurably noteworthy distinction was not seen among the three age classes (P 0.05). The commonness of cow-like demodicosis found to be5% and 4.8% in nearby and cross breeds, individually. There was no factually critical contrast between the two breeds ((P 0.05) There was no factually critical variety distinguished between the two administration frameworks (P 0.05); however moderately higher commonness of oxlike demodicosis (7.5%) was recorded in creatures kept under semiescalated administration framework than broad administration framework (3.6%).The site of pervasion was recorded most noteworthy on shoulder (3.4%) and least on rear appendage, back and ear (0%).The site commonness was factually noteworthy (P 0.05).
Discussion
In the present review, the general commonness of demodicosis on dairy cattle in the review region was 4.9%. Nearly comparative outcomes have prior been accounted for by Yacob [7], with commonness of 5.9%, in and around [8], with commonness of 4.19% in Debrezeit. These distinctions may be because of the distinctions in climatic condition, season, creature administration framework, and the exertion applied towards the control of the parasites [9].The variety could likewise be because of time of testing and strategies taken after to recognize the parasites in examined creatures. A noteworthy variety was seen in sex astute pervasiveness rates. The conceivable clarification for this could be both male and female creatures was similarly presented to demodex. The nonappearance of noteworthy sex related contrast was likewise detailed by Mersha et al. [10] and Tewodros et al. [11]. On opposite, Yacob et al. [10] announced 2.22% in male and 1.67% in female creatures in Adama and Bogale [8] announced 4.57 and 3.17% in male and female creatures in Debre-Zeit separately. In view of the present discoveries, the predominance's of D. bovis was higher in more noteworthy than three years of age. In any case, this variety was not statically noteworthy (p 0.05). Comparable predominance rates have too been accounted for by Tewodros et al. [11] Yacob et al [7]. In complexity Bogale [8] detailed 7.95% commonness in youthful and 2.40% predominance in grown-up in Debre-Zeit. The predominance rate of cow-like demodicosis in neighborhood breeds (8.8%) was discovered higher than cross reared breeds (2.2%). Again this distinction was not statically noteworthy (p 0.05). This finding is in [40] concurrence with the past work of Yacob et al. [7] and Mersha et al. [10] The predominance rate of demodicosis was discovered higher in semi escalated (7.5%) than broad (3.6%) administration framework with non-noteworthy varieties. These outcomes are as per Mersha et al. [10] and Tewodros et al. [11]. However, Yacob et al. [7] higher predominance rates in broad frameworks than for semi-serious framework. The most elevated frequencies of event of demodicosis were identified on shoulder (3.4%) as thought about to dewlap, fore limp and summed up (0.3%). The distinction was statically critical (p 0.05). This result is in concurrence with Tewodros et al. [11,12] and Mersha et al. [10] and Ademe i expressed that the dissemination of knobs of D. bovis on the host's body has run of the mill design with shoulder as significant inclination destinations. The minor departure from different site of invasion may be because of the living style of the parasite as commensalism that leads for abruptly pathogenic states or due to the continuous introduction of neck and shoulder for different anxiety conditions like burden sore, traumatic damage what's more, kick by furrowing instruments which encourage the parasite to nourish effortlessly by puncturing the host cell what's more, sucking out the cell substance of the harmed region.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Demodex bovis impact is huge that decrease numerous creature items whether straight forwardly or in a roundabout way. Demodex bovis bugs were observed to be strong ailments in dairy cattle. This suggested the parasite is financially critical for its being stow away harming nature. The female cows which are over three a long time old, nearby breed that overseen at the semi-concentrated creation framework were watched the most helpless to D. bovis . Consequently, mindfulness creation in domesticated animals proprietors about the control and avoidance of demodicosis and further epidemiological examination in the review territory are prescribed.
References
- Central Statistical Authority (CSA) (2011) Agricultural sample survey. Report on livestock and livestock characteristics.
- Gebre Mariam S, Amare S, Baker D, Solomon A (2010) Diagnostic study of live cattle and beef production and marketing, Constraints and opportunities for enhancing the system p: 10.
- Yacob H (2013) Ectoparasitism: Threat to Ethiopian small ruminant population and tanning industry. Ethiopia J Vet Med Anim Hlth 6: 25-33.
- Turton J (2007) External parasites of cattle. Animal Health for Developing Farmers p: 5.
- Wall R, Shearer D (2001) Veterinary ectoparasites: Biology, pathology and control (2nd edn.) pp: 191-192.
- Thrusfield M (2005) Veterinary Epidemiology (3rd edn.). Blackwell Science, Great Britain pp: 253-259.
- Yacob H, Netsanet B, Dinka A (2008) Prevalence of major skin diseases in cattle. Ethiopia J Vet Med Anim Hlth 159: 455-461.
- Bogale A (1991) Epidemiological study of major skin diseases of cattle: Southern rang elands.
- Urquhart M, Armour J, Duncan L, Dunn M, Jennings W (1996) Veterinary parasitology (2nd edn.) UK: Blackwell science Ltd p: 196.
- Mersha C, Solomon T, Basaznew B (2013) Prevalence of Bovine Demodicosis in Gondar Zuria District, Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia. Gondar Ethiopia Glob Vet Res 11: 30-35.
- Tewodros F, Tsegiedingle Y, Mersha C (2012) Bovine Demodecosis: Treat to leather industry in Ethiopia. Asian J Agri Sci 4: 314-318.
- Youssefi M, Pour R, Rahimi M (2012) Prevalence of Demodex Mites (Acari: Demodicidae). Iran Acad J Entom 5: 62-64.
Relevant Topics
- Algal Blooms
- Blue Carbon Sequestration
- Brackish Water
- Catfish
- Coral Bleaching
- Coral Reefs
- Deep Sea Fish
- Deep Sea Mining
- Ichthyoplankton
- Mangrove Ecosystem
- Marine Engineering
- Marine Fisheries
- Marine Mammal Research
- Marine Microbiome Analysis
- Marine Pollution
- Marine Reptiles
- Marine Science
- Ocean Currents
- Photoendosymbiosis
- Reef Biology
- Sea Food
- Sea Grass
- Sea Transportation
- Seaweed
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 3933
- [From(publication date):
June-2017 - Mar 31, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 3088
- PDF downloads : 845
