Make the best use of Scientific Research and information from our 700+ peer reviewed, Open Access Journals that operates with the help of 50,000+ Editorial Board Members and esteemed reviewers and 1000+ Scientific associations in Medical, Clinical, Pharmaceutical, Engineering, Technology and Management Fields.
Meet Inspiring Speakers and Experts at our 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events with over 600+ Conferences, 1200+ Symposiums and 1200+ Workshops on Medical, Pharma, Engineering, Science, Technology and Business
Editorial Open Access
Sinorhizobium meliloti Bacteria Contributing to Rehabilitate the Toxic Environment
| Ashish Chauhan* | |
| National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Mohali, Punjab, India | |
| Corresponding Author : | Ashish Chauhan National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Mohali, Punjab, India Tel: +91-9464616773 E-mail: aashishchauhan26@gmail.com |
| Received February 15, 2015; Accepted February 24, 2015; Published February 27, 2015 | |
| Citation: Chauhan A (2015) Sinorhizobium meliloti Bacteria Contributing to Rehabilitate the Toxic Environment. J Bioremed Biodeg 6:e164. doi:10.4172/2155-6199.1000e164 | |
| Copyright: © 2015 Chauhan A. This is an open-a ccess article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |
Related article at Pubmed Pubmed  Scholar Google Scholar Google |
|
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation
Abstract
Nitrogen fixing microorganisms play a vital role in the rejuvenating the environment. A Sinorhizobium meliloti
bacterium is one such microbe and has immense potential to rehabilitate the toxic environment that lies unexplored.
The review highlights some of its uses in agriculture and environment.
| Introduction |
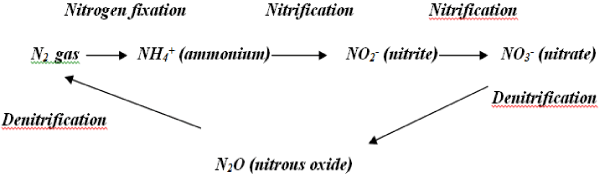
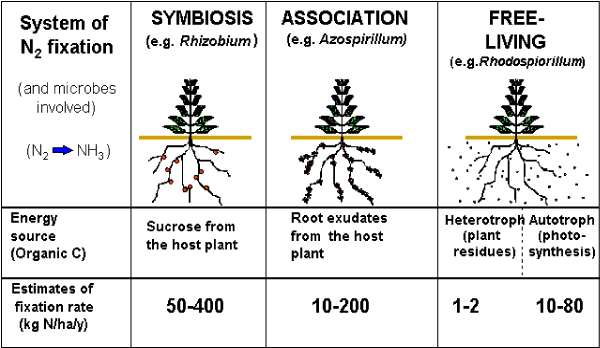
| Production of nitrogenous fertilizers has stagnated in recent years because of high costs and pollution. Estimated 90% of applied fertilizers never reach roots and contaminate groundwater. Hence, the importance of nitrogen fixing organisms has emerged as key issue. The nitrogen fixation by organisms occurs by a symbiotic relationship, association or free living organisms (Figures 1-3) that plays an important role in maintaining the nitrogen cycle in the environment. The biological fixation in brief that could be depicted as follows: |
| Nitrogenase |
| N2 + 8 flavodoxin- + 8H + + MgATP2- + 18 H2O → 2NH4+ + 2OH- + 8 flavodoxin + 16 MgADP- + 16H2PO4 - + H2 |
| It is a rare, extremely energy consuming conversion because of stability of triply bonded N2. The fixed Nitrogen which can be directly assimilated into Nitrogen containing bio-molecules. Some of the host plant and bacterial symbiont are shown in the Table 1. |
| The nitrogen can be fixed by non-symbiotic nitrogen fixation by Cyano bacteria Anabaena nostoc. It can be fixed by terrestrial and rhizosphere associated microorganisms like Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Acetobacter, Klebsiella and Clostridium [1,2]. |
| Sinorhizobium meliloti and its uses to the environment |
| Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum: Proteobacteria Class: Alpha Proteobacteria Order: Rhizobiales Family: Rhizobiaceae Genus: Sinorhizobium Species: S.meliloti |
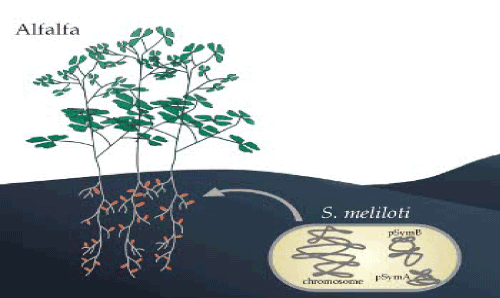
| Sinorhizobium meliloti is a soil bacterium of Rhizobiales group of the Alpha proteobacteria sub-division. S. meliloti forms nitrogen-fixing nodules on the roots of leguminous plants of the genera Medicago, Melilotus and Trigonella and it is the best studied model system for the rhizobium legume symbiosis. S. meliloti is distributed all over the world and is present in many soil types, both in association with legumes and in free-living form. The occurrence of this species reveals a wide metabolic capability that allows its adaptation to very different environmental and nutritional conditions. S. meliloti has been the subject of extensive genetic, biochemical and metabolic research. The sequencing of the strain Rm1021 genome provided a solid foundation for a number of molecular studies of the genetic basis of plant-bacterium interactions and of the response of S. meliloti to environmental stimuli. Strains of S. meliloti, as for other rhizobial species, are known to show different nodulation capabilities and phenotypic characteristics, such as salt and stress tolerance and exo-polysaccharide production. Despite the large number of genetic and molecular biology studies of the sequenced Rm1021 strain and its natural populations, little is known about the overall extent of metabolic diversity of Rm1021 and environmental strains. Consequently, clear evidence on possible functional and metabolic roles of the observed genomic polymorphism is still lacking. In past years, more attention has been focused on that part of bacterial genetic variation which is directly related to the phenotype. |
| Sinorhizobium meliloti cells serve a significant role in the survival of many plant species and they also largely contribute to the environment. The atmosphere is composed of approximately 85% nitrogen and it is an essential element to most living organisms and their metabolic activities. But, nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as dinitrogen (N2) that is unusable by most plants and animals. S. meliloti cells in the environment form symbiotic relationships with leguminous plants and convert N2 into organic nitrogen. S. meliloti also serves as denitrifying agent that reduces nitrate and nitrite into free N2 in the environment (Figure 2). S. meliloti is unique and one of the first organisms to have a cluster of all four nitrogen oxide reductases (nap, nir, nor, nos) on the same chromosome. Denitrification can have hazardous effects such as a loss of biologically useful nitrogen, a buildup of N2O as a byproduct which contributes to acidic rain and a depletion of the ozone layer. However, denitrification conducted by S. meliloti cells can have positive effects as well if it is harnessed properly. For example, the N2O produced by denitrification can serve as a green-house gas that traps heat. The microbial denitrification can contribute significantly to the purification of waste water. Nitrogen-rich fertilizers have contributed to the pollution of ground water. This water is potentially hazardous to pregnant women and infants and thus scientists are considering using microbial denitrification in water treatment facilities to remove excess NO3. A bacterium isolated from soil (designated 9702-M4) synthesizes an extracellular polymer that facilitates the transport of such hydrophobic pollutants as polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, as well as the toxic metals lead and cadmium in soil [3-9]. This property of the organism if expedited can play a crucial role to purify the toxic soil and inhibit the health hazards. |
| Conclusion |
| S. meliloti has huge potential to reduce the toxicity from the environment so; there is need of enhancing the survival of nodule forming bacterium by improving competitiveness of inoculant strains there is need to extend host range of crops that can benefit from biological nitrogen fixation. We should engineer microbes with high nitrogen fixing capacity for a healthy environment. |
References
|
Tables and Figures at a glance
| Table 1 |
Figures at a glance
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
Post your comment
Relevant Topics
- Anaerobic Biodegradation
- Biodegradable Balloons
- Biodegradable Confetti
- Biodegradable Diapers
- Biodegradable Plastics
- Biodegradable Sunscreen
- Biodegradation
- Bioremediation Bacteria
- Bioremediation Oil Spills
- Bioremediation Plants
- Bioremediation Products
- Ex Situ Bioremediation
- Heavy Metal Bioremediation
- In Situ Bioremediation
- Mycoremediation
- Non Biodegradable
- Phytoremediation
- Sewage Water Treatment
- Soil Bioremediation
- Types of Upwelling
- Waste Degredation
- Xenobiotics
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 15427
- [From(publication date):
March-2015 - Apr 03, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 10828
- PDF downloads : 4599
