Significance of Maintaining Cause in the Study of Diabetes Mellitus
Received: 01-Oct-2022 / Manuscript No. jomb-22-76790 / Editor assigned: 04-Oct-2022 / PreQC No. jomb-22-76790(PQ) / Reviewed: 19-Oct-2022 / QC No. jomb-22-76790 / Revised: 25-Oct-2022 / Manuscript No. jomb-22-76790 (R) / Published Date: 28-Oct-2022
Abstract
The diabetes is a chronic disease a, fast growing issue with major effect on social, economic aspects. Epidemiologically, there is rise in DM in past 20 years with 177 million cases by 2000 and the figure has estimated to 285 million people in 2010 i.e.,6.4% of the population. More than 360 million people may have DM by 2030.This study supports the importance of maintaining cause in cases of diabetes mellitus. Lifestyle disorders are ice-berg diseases. So, the cause gives an utmost importance while prescribing medicine in Homoeopathy. According to Organon of medicine by Hahnemann, it is clearly stated that the perseverance of health is done only when the causes that deranges and maintains the disease is removed completely. Obstacles that hinder in resolving the derangement of health has to be given importance and should be annihilated. Result: Of 30 patients who completed the study, 15 are the experimental, i.e.; medicine is prescribed and 15 are control group. It is seen that 15 cases where medication is prescribed shows marked to moderate improvement, whereas, control group shows no improvement. Statistically, for all three clinical variables, p-values are very small so, the conclusion of the study shows that the removal of identified maintaining cause produces significant improvement in diabetes mellitus.
Keywords
Diabetes Mellitus; maintaining cause; Randomized control study; Complimentary study; Homoeopathy; Lifestyle Disorder
Introduction
According to Greek language Diabetes means “To pass through”; and according to Latin language Mellitus referred as “Honey”. [2] A Classical classification is done in 1997 by American Diabetes Association as Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. [3] Type 1 is termed as Insulin dependent Diabetes Mellitus which is due to deficiency of insulin because of destruction of β-cells in islets of Langerhans. This type of diabetes mellitus may occur at any age of life. But it usually occurs before 40 years of age and persons affected by this require insulin injection.
Type 2 is termed as Noninsulin dependent Diabetes Mellitus which is due to insulin resistance (failure of insulin receptors to give response to insulin). So, the body is unable to use insulin.
It usually occurs after 40 years. Only some forms of Type II diabetes require insulin. Other types include Gestational Diabetes. [4] The global prevalence in DM in 2013 was 8.3% which may increase to 10.1% by 2035.
Factors: Family history; Obesity; History of vascular disease [4]
OTHER FACTORS WHICH INCREASES GLUCOSE LEVELS:

Diabetes is a chronic lifestyle disoreder which has multiple etiologies and has hyperglycemia. It has clinical features like polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss. DM increases the glucose levels in the blood which leads to complications when left untreated. This is the disorder resulted from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action. [3]
Pathophysiology
Type 2DM is characterized by
a. impaired insulin secretion,
b. insulin resistance,
c. excessive hepatic glucose production,
d. abnormal fat metabolism.
e. Obesity
Homeopathic Approach in Diabetes:
The DM was first noted in 5th Century BC which is called as Madhumeha by ayurvedic physicians. Whereas, insulin was discovered in year 1921. Medications of Ayurveda, Chinese medicines were used at early times [5] Homeopathic medications like syzygium was used since 1880. Alkaloids like quinine and opium were used since 1900. Toxic agents like Arsenic, Uranium Salts are also used since 1892 & 1966 respectively [6] Homoepathy is the science that based on individualization of the person. Cause of the chronic diseases is one of the important factors which could be maintaining cause or fundamental cause in the treatment using Homeopathy. Homoeopathy plays a significant role in dealing with the lifestyle disorders and treats the patient on individualistic manner by considering constitution, mental, physical, emotional, spiritual aspects of the person. [7]
DM has many maintaining causes like Stress, Smoking, Alcohol consumption, Depression, etc; Studies shown that DM has Psychosomatic and Somatopsychic Interrelationship. Fear, anxiety, anger, resentment, sorrow, Physical activity, change of habits are some of the psychosomatic causes. [8] High consumption of alcohol shown increased risk [9] Women who are obese, overweight is seen to have increased risk of DM. Reports shows increased risk in Diabetes at similar rate for all categories of BMI for heavy smokers [10] Sedentary Lifestyle in Type 2 DM patients may leads to increase in Total body & Trunk fat and also decreases Limb Skeletal mass. [11]
Methods
Case definition: Pre-diagnosed and newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus cases are to be taken for study where case will be properly worked out and remedy will be prescribed.
Study setting: This is a Randomized single blind placebo control clinical study on Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 individuals of age group 30- 55 years from outpatient department of Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University Homoeopathic College & Research Centre, Katraj, and Pune.
Inclusion criteria: Patient who fulfilling the case definition, HbA1c level of patient should be above 6.5% - 9%, Patients of both sexes and age group of 30 to 55 years.
Exclusion criteria: Patient having illness other than lifestyle illness such as communicable diseases, Patients needed with emergency medical intervention with complication of systemic diseases, Patients with diabetic complications like diabetic nephropathy and cardiovascular diseases will not be included, Gestational diabetes is excluded from the study.
Selection of remedy: The remedy will be selected and prescribed on the basis of symptom similarity and reference will be taken from various homoeopathic literature wherever its needed.
Statistical test: T-Test; Two sample T-Test.
Experimental Parameters: Total 32 patients of pre diagnosed and newly diagnosed DM are enrolled of which 30 patients (Male & female) are present till the end of the study whereas 2 individuals dropped out from study. The study is done by assessing the Fasting, PBS and HbA1c values and the remedy is prescribed after detailed case taking where the Maintaining cause is given importance as it is the cause which obstructs the path of cure.
Management
Management of the participated individuals is done by assessing their Blood Glucose Levels every 15 days. Diet & Nutrition, Regular Exercise is advised.
Diet includes, lukewarm water with squeezed Lemon Juice, Intake of Fiber foods, fruits (except high sucrose fruits), dairy products, Minimized fatty foods, Cucumber juice, Bitter gourd juice, vegetable Salad. Instructions are given to the patients about the diet.
Exercises like light jogging, yoga Asanas, Walking are advised. They are instructed to perform the activities 15 minutes a day and advised to increase the time to an extra 10 minutes every week.
Result
The cases in the study are included as per the criteria mentioned above and after detailed case taking the repertorization is done using Radar Repertory and medicine is prescribed after referring the Homoeopathic Literature based on the reperterized result. (Table 1)
| Medicine Prescribed | Control(n=15) | Experimental(n=15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | % | f | % | |
| PLACEBO | 15 | 100% | 0 | 0.00% |
| ACID PHOS 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 3 | 20.00% |
| ARSENIC ALB 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 6.67% |
| CALCARIA CARB 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 6.67% |
| IGNITIA 1M | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 6.67% |
| PHOSPHORUS 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 13.33% |
| PULSATILLA 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 6.67% |
| SEPIA 1M | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 13.33% |
| SULPHUR 1M | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 13.33% |
| SULPHUR 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 6.67% |
| URANIUM NITRICUM 200 | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 6.67% |
Table 1: Distribution of patients according to medicine prescribed in the Study
Based on assessing the 30 cases, it is seen that 15 cases where medication is prescribed with importance given to maintaining cause shows marked to moderate improvement, whereas, control group shows change of <0.5% change in HbA1c levels. (Table 2)
| Clinical Variable | Group | Mean ± SD | T-value | p-value | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Change in values after treatment | |||||
| Fasting | Control | 134.87 ± 15.83 | 121.27 ± 16.12 | 13.60 ± 13.58 | -5.48 | 0.000** | Reject H0 |
| Exp. | 145.67 ± 20.94 | 97.33 ± 8.63 | 48.33 ± 20.46 | ||||
| PP | Control | 193.33 ± 34.15 | 159.67 ± 17.47 | 33.67 ± 18.21 | -2.51 | 0.009** | Reject H0 |
| Exp. | 192.00 ± 33.80 | 134.00 ± 9.10 | 58.00 ± 32.89 | ||||
| HbA1c | Control | 7.41 ± 0.51 | 7.22 ± 0.48 | 0.19 ± 0.12 | -9.12 | 0.000** | Reject H0 |
| Exp. | 7.59 ± 0.38 | 6.79 ± 0.20 | 0.80 ± 0.23 | ||||
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of clinical variables before and after intervention in control and experimental group
Statistical Result
In control group before intervention fasting glucose was 134.87±15.83, PP glucose was 193.33±34.15, HbA1c value was 7.41±0.51. after intervention it Fasting glucose decreased to 121.27±16.12, PP Glucose decreased to 159.67±17.47, HbA1c decreased to 7.22±0.48. In experimental group before intervention fasting glucose was 145.67±20.94, PP glucose was 192.00±33.80, HbA1c was 7.59±0.38, after intervention fasting glucose decreased to 97.33±8.63, PP Glucose decreased to 134.00± 9.10. HbA1c decreased to 6.79±0.20. Statistically, for all three clinical variables, p-values are very small so we conclude that the removal of identified maintaining cause produces significant improvement in diabetes mellitus. (Table 3)
MAINTAINING CAUSE |
f | % |
|---|---|---|
| FINANCIAL STRESS | 8 | 26.67 |
| FAMILY STRESS | 6 | 20.00 |
| OCCUPATIONAL STRESS | 6 | 20.00 |
| OBESITY | 6 | 20.00 |
| SEDENTARY LIFESTYLE | 5 | 16.67 |
| SMOKING/TOBACCO | 5 | 16.67 |
| ALCOHOL | 4 | 13.33 |
| STRESS | 4 | 13.33 |
| UNHYGENIC ENVIROMENT | 2 | 6.67 |
| IMPROPER/ UNHEALTHY DIET | 2 | 6.67 |
| GRIEF | 1 | 3.33 |
| MENTAL STRESS | 1 | 3.33 |
Table 3: The above table shows the causes that maintained the disease from the Study.
Discussion
The DM is due to impaired insulin secretion and abnormal fat metabolism in obese person with BMI > 25 Kg/m2. Also, the risk of DM is increased in individuals with familial tendency of DM, in persons whose physical activity is decreased. There are factors which also interfere with the recovery like stress, over alcohol consumption, smoking, improper nutrition etc.; which are elicited by a detailed case taking and the cause which obstruct the prognosis is noted and the Homeopathic Remedy is prescribed based on the totality obtained.
By considering patient as a whole, All the symptoms which alter the state of health needs attention as they may cause the obstruction of cure. The importance of cause is said by
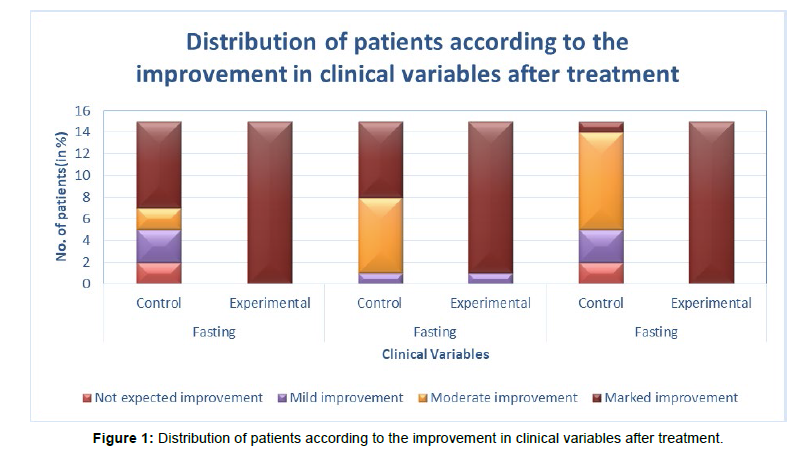
Dr.Hahnemann in §5, which includes details about the persons occupation, intellectual character, habits, one’s social and domestic relations especially in Chronic cases. It should be noted that the cause in a case which interferes the path of cure gives the Totality of a case. It could be stress, Lack of Financial support, Sedentary lifestyle, Improper food habits, etc.; These kinds of causes which maintains and obstruct the disease prognosis should be considered in the case of the individual and appropriate medication is to be prescribed. All the cases that are taken are given management instructions regarding Diet and physical Exercise. Based on assessment of 30 cases, it is seen that 15 cases where medication is prescribed with importance given to maintaining cause shows marked to moderate improvement, whereas, the control group shows change of <0.5% change in HbA1c levels. Statistically, for all three clinical variables, p-values are very small so we reject H0 and accept H1 and conclude that the removal of identified maintaining cause produces significant improvement in diabetes mellitus. (Table 4 and Figure 1)
Clinical variable |
Group | Improvement in the patients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not expected improvement | Mild improvement | Moderate improvement | Marked improvement | |||
| Fasting | Control | F | 2 | 3 | 2 | 8 |
| % | 13.33% | 20.00% | 13.33% | 53.33% | ||
| Exp. | F | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | |
| % | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100.00% | ||
| PP | Control | F | 0 | 1 | 7 | 7 |
| % | 0.00% | 6.67% | 46.67% | 46.67% | ||
| Exp. | F | 0 | 1 | 0 | 14 | |
| % | 0.00% | 6.67% | 0.00% | 93.33% | ||
| HbA1c | Control | F | 2 | 3 | 9 | 1 |
| % | 13.33% | 20.00% | 60.00% | 6.67% | ||
| Exp. | F | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | |
| % | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100.00% | ||
Table 4: Distribution of patients according to the improvement in clinical variables after treatment
Conclusion
By the end of the study, it can be concluded that the Homoeopathic Constitutional Medicines are helpful in treating DM. This study also shows that Maintaining causes are like stuck which are the key factor that obstacles the way of treatment and become a hindrance to the treatment. The above-mentioned maintaining causes not only obstructs the treatment but also may lead to over production of insulin and which in turn cause increased glucose levels. Homoeopathy as a progressive medicine has shown its whole capability of satisfying the therapeutic demands in DM with respectable results. So, Homeopathy a Holistic approach which is safe to use and is economical and which also shows the best required results.
Acknowledgement:
With blessings and inspirations of my ideal and respected Father Mr. Nedumaran Natesan and Mother Mrs. Sundhari Nedumaran, I achieved all this in my life.
I take this opportunity to express my deep sense of gratitude to my guide,
Prof. Dr. Sushma.S.Manhas M.D. (Hom), for her expert guidance, valuable suggestions and kind support during the period of study. A very big thanks and special gratitude towards my friends who helped in the study.
Conflict of Interest
None declared
References
- Kaveeshwar SA, Cornwall J (2014) The current state of diabetes mellitus in India. The Australasian medical journal 7(1): 45.
- Kaul K, Tarr JM, Ahmad SI, Kohner EM, Chibber R (2013) Introduction to diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1-1.
- Kharroubi AT, Darwish HM (2015) Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World journal of diabetes 6(6):850.
- Sainani GS & Association of Physicians of India (1992) A.P.I. textbook of medicine. Bombay: Association of Physicians of India. Chapter:9 Epidemiology and Basic Considerations of Diabetes. 33: 321-327.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_diabetes
- Helmstädter A (2007) Antidiabetic drugs used in Europe prior to the discovery of insulin. Die Pharmazie-An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 62(9): 717-720.
- Robert HA (2004-6) The principles and art of cure by Homoeopathy. Reprint ed. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
- Wasserman LI, Trifonova EA (2006) Diabetes mellitus as a model of psychosomatic and somatopsychic interrelationships. The Spanish journal of psychology 9(1): 75-85.
- Carlsson S, Hammar N, Grill V (2005) Alcohol consumption and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 48(6):1051–1054.
- Will JC, Galuska DA, Ford ES, Mokdad A, Calle EE (2001) Cigarette smoking and diabetes mellitus: Evidence of a positive association from a large prospective cohort study. International Journal of Epidemiology 30(3):540–546.
- Yang Y, Gao Z-yi, Zhao L-hua, Yang X, Xu F, et al. (2022) Sedentary lifestyle and body composition in type 2 diabetes. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome 14(1): 8.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Vinoth N, Manhas SS (2022) Significance of Maintaining Cause in the Study of Diabetes Mellitus. J Obes Metab 5: 131.
Copyright: © 2022 Vinoth N, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Usage
- Total views: 1615
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Apr 07, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1287
- PDF downloads: 328