Research Article Open Access
Short-term Effects of Supplementation with a Multi-ingredient Weight-loss Product on Weight Maintenance and Fat Oxidation in Obese Female with Weight Reduction: Preliminary Results
| Naoki Sakane1*, Kazuhiko Kotani1,2, Kokoro Tsuzaki1, Kaoru Takahashi1,3, Taku Hamada1,4, Narumi Nagai5, Toshio Moritani6, Kahori Egawa7, Makiko Yoshimura8, Yoshinori Kitagawa9 and Hiroshi Shibata7 | |
| 1Division of Preventive Medicine, Clinical Research Institute, National Hospital Organization Kyoto Medical Center, Kyoto, Japan | |
| 2Department of Clinical Laboratory Medicine, Jichi Medical School, Tochigi, Japan | |
| 3Hyogo Preventive Medical Center, Hyogo, Japan | |
| 4Graduate School of Sport and Exercise Science, Osaka University of Health and Sport Sciences, Osaka, Japan | |
| 5Department of Food Science and Nutrition, School of Human Science and Environment, University of Hyogo, Hyogo, Japan | |
| 6Laboratory of Applied Physiology, Graduate School of Human and Environmental Studies, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan | |
| 7Institute for Health Care Science, Health Care Science Center, Suntory Wellness Limited, Osaka, Japan | |
| 8Research Institute, Suntory Global Innovation Center Limited, Osaka, Japan | |
| 9Safety Science Institute, Quality Assurance Division, Suntory Business Expert Limited, Osaka, Japan | |
| Corresponding Author : | Naoki Sakane M.D., Ph. D., Division of Preventive Medicine, Clinical Research Institute National Hospital Organization Kyoto Medical Center 1-1 Mukaihata-cho, Fushimi-ku, Kyoto 612-8555, Japan Tel: 075-641-9161 Fax: 075-645-2781 E-mail: nsakane@kyotolan.hosp.go.jp |
| Received September 01, 2014; Accepted October 04, 2014; Published October 11, 2014 | |
| Citation: Sakane N, Kotani K, Tsuzaki K, Takahashi K, Hamada T, et al. (2014) Short-term Effects of Supplementation with a Multi-ingredient Weight-loss Product on Weight Maintenance and Fat Oxidation in Obese Female with Weight Reduction: Preliminary Results. J Obes Weight Loss Ther 4:231. doi:10.4172/2165-7904.1000231 | |
| Copyright: © 2014 Sakane N, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Obesity & Weight Loss Therapy
Abstract
Background: Numerous multi-ingredient weight-loss supplementation products are marketed, whereas the effects of these supplements on weight maintenance have rarely been studied. This study aimed to investigate preliminarily whether a 4-week supplementation of a multi-ingredient weight-loss product (named ‘diet’s BB’), containing L-carnitine, banaba, caffeine, capsaicin, Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract and sesamin, could contribute to weight maintenance and its related parameters among obese women with weight reduction following a Low-calorie Diet (LCD). Methods: In a prospective, randomized, double-blind intervention design, subjects with ≥5% of weight reduction following LCD were randomized to the group who used the diet’s BB (Group A) or tablet containing six types of vitamins (Group B) for four weeks. Their body weight and related parameters, including Respiratory Quotient (RQ) and fat oxidation, were measured pre- and post-intervention. Results: The changes in body weight and related parameters were not significantly different between the groups. Group A showed significantly reduced RQ and increased fat oxidation more than the Group B. Conclusion: The short-term multi-ingredient weight-loss supplementation product did not yield further weightloss for obese women with weight reduction, while it could potentially lead to favorable changes of fat oxidation levels. The effects of the supplementation on weight traits merit large-scale and long-term investigations.
Methods: In a prospective, randomized, double-blind intervention design, subjects with =5% of weight reduction following LCD were randomized to the group who used the diet’s BB (Group A) or tablet containing six types of vitamins (Group B) for four weeks. Their body weight and related parameters, including Respiratory Quotient (RQ) and fat oxidation, were measured pre- and post-intervention.
Results: The changes in body weight and related parameters were not significantly different between the groups. Group A showed significantly reduced RQ and increased fat oxidation more than the Group B.
Conclusion: The short-term multi-ingredient weight-loss supplementation product did not yield further weight-loss for obese women with weight reduction, while it could potentially lead to favorable changes of fat oxidation levels. The effects of the supplementation on weight traits merit large-scale and long-term investigations.
Very many dietary supplementation products are currently available for weight-loss [8]. Despite this situation, evidence using the supplementation for weight-loss has not yet been established, and moreover, trials on the effects of the supplementation on weight maintenance following successful weight-loss are limited.
There have been several dietary components that are used as the supplementation products for weight-loss and its maintenance. For instance, Carnitine plays an essential role in the integration of fat and carbohydrate oxidation in skeletal muscle, which is impaired in obesity [9]. L-carnitine (L-C) transports fatty acids into mitochondria for oxidation; therefore, L-C itself is applicable to control body weight [10,11]. However, there has been a report that the supplementation of L-C failed to reduce body weight in obese women [12]. The effects of such supplementations of single dietary component are lately thought to be restricted for weight management [13]. Various supplementation products can, thus, be mixed by several dietary components for weight management.
A multi-ingredient supplementation product (called ‘diet’s BB’), containing anti-obesity and thermogenic dietary components (L-C, banaba, Nelumbo nucifera extract, caffeine, capsaicin and sesamin), was recently developed to manage body weight (Tables 1 and 2). The aim of this study was to investigate preliminarily whether a 4-week supplementation of the multi-ingredient product (diet’s BB) could contribute to weight maintenance and its related parameters among obese women with weight reduction following a Low-calorie Diet (LCD), based on a prospective, randomized, double-blind intervention study design.
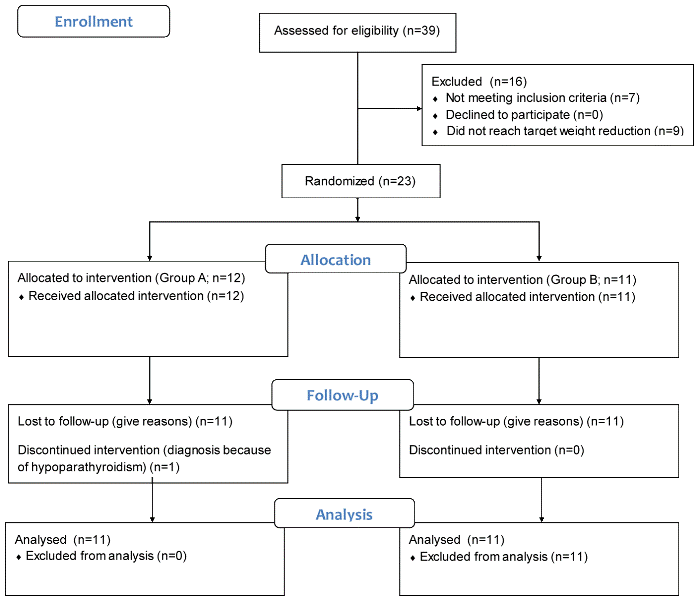
As shown in Figure 1, subjects who showed =5% of their weight reduction following the LCD were randomized into groups by an independent statistician using sequentially numbered sealed envelopes to the group who received the diet’s BB (Group A) or received tablets containing six types of vitamins (Group B).
In the metabolic measurements, the coffee, tea and alcohol consumption was not allowed, and vigorous sports activities were not permitted. The subject was equipped with electrocardiogram electrodes, and then rested for at least 30-minutes in a temperature- and humidity-controlled environment [17,18]. After the subject had received an explanation of the procedure and adjusted the mask, gas exchange parameters were recorded using an open-circuit computerized indirect calorimeter (Aero monitor AE 280; Minato Medical Science Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) while the subject is seated in a comfortable chair. The calorimeter was calibrated before each test with a reference gas mixture (15% O2 and 5% CO2). Continuous ventilator volumes, VO2 (oxygen consumption) and VCO2 (carbon dioxide production) were monitored on a computer at 15-second intervals, and the mean value for each minute was recorded. The Respiratory Quotient (RQ) is defined by the ratio of c VCO2/VO2, and a high RQ indicates a relatively low level of fat (lipid) oxidation, which is known to be a risk for weight gain [19-22].
As shown in Table 3, in the pre-intervention, characteristics of all variables measured did not significantly differ between the groups. Between pre- and post-intervention, non-significant differences in changes of most variables measured were observed between the groups. However, in the metabolic measurements, RQ was significantly reduced and fat oxidation was significantly increased in Group A than in Group B.
In the nutritional analysis, total intake energy from the pre- to post-post-intervention, was from 1266 (259) to 1546 (271) kcal in Group A and from 1423 (274) to 1611 (680) kcal in Group B (P>0.05 in the pre-intervention, P>0.05 in the post-intervention).Overall, the nutritional analysis did not find significant differences in any variables between the groups (Table 4). The analysis of exercise habits did not find significant differences between the groups (data not shown).
One of the major components of the diet’s BB is L-C (300 mg). There have been several studies that examined the associations between RQ, fat oxidation and the supplementation of L-C. For instance, Iwami et al. have previously reported that the RQ was reduced after a continuous supplementation of L-C alone in rats fed a high-fat diet [23]. Wutzke et al. have also reported that the supplementation of L-C (3g/day for 10-days) increased in fat oxidation in overweight human subjects [22]. Vecchiet et al. have reported that the supplementation of L-C (2 g) significantly increased maximal oxygen uptake before exercise in trained men [25]. Gorostiaga et al. have reported that, RQ was reduced during submaximal exercise with a high-dose supplementation of L-C (2 g for 28 days) than with a placebo in endurance-trained people [25]. The dosage of L-C used in our current study was considerably lower than in these previous studies, while the results observed in our study seems to be in line with the previous studies.
Besides L-C, caffeine [26,27] and capsaicin [28-30] have been known as potent themogenic and obesity-alleviating components. Banaba has also been used as a log-term folk medicine especially among patients with diabetes mellitus in the Philippines, and it can be effective for phenotypic improvements in diabetic mice [31]. Ashakumary et al. have reported that sesamin induces hepatic fatty acid oxidation in rats [32]. Ono et al. have reported that Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract suppresses an increase in body weight, parametrial adipose tissue weight and liver triacylglycerol levels in mice with obesity caused by a high-fat diet [33]. These data are suggestive of the positive effects on not only fat oxidation levels but weight traits. Future interest is the remaining possibility that the changes of on RQ and fat oxidation by the supplementation of the diet’s BB may affect body weight in a long-term period.
NS, the project leader, was involved in all aspects of the study. TH, KE, MY, YK and SH designed the study and prepared the intervention. Kokoro Tsuzaki, NN and TM designed the study and coordination of the intervention. KK prepared the draft and coordination of the intervention. Kaoru Takahashi performed the statistical analyses. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
References
- Sakamoto M (2006) The situation of the epidemiology and management of obesity in Japan. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 76: 253-256.
- Elfhag K, Rössner S (2005) Who succeeds in maintaining weight loss? A conceptual review of factors associated with weight loss maintenance and weight regain. Obes Rev 6: 67-85.
- Vogels N, Diepvens K, Westerterp-Plantenga MS (2005) Predictors of long-term weight maintenance. Obes Res 13: 2162-2168.
- Anderson JW, Konz EC, Frederich RC, Wood CL (2001) Long-term weight-loss maintenance: a meta-analysis of US studies. Am J Clin Nutr 74: 579-584.
- Leermakers EA, Perri MG, Shigaki CL, Fuller PR (1999) Effects of exercise-focused versus weight-focused maintenance programs on the management of obesity. Addict Behav 24: 219-227.
- Ewbank PP, Darga LL, Lucas CP (1995) Physical activity as a predictor of weight maintenance in previously obese subjects. Obes Res 3: 257-263.
- Sumithran P, Proietto J (2013) The defence of body weight: a physiological basis for weight regain after weight loss. Clin Sci (Lond) 124: 231-241.
- Saper RB, Eisenberg DM, Phillips RS (2004) Common dietary supplements for weight loss. Am Fam Physician 70: 1731-1738.
- Foster DW (2004) The role of the carnitine system in human metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1033: 1-16.
- Lee MS, Lee HJ, Lee HS, Kim Y (2006) L-carnitine stimulates lipolysis via induction of the lipolytic gene expression and suppression of the adipogenic gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Med Food 9: 468-473.
- Winter BK, Fiskum G, Gallo LL (1995) Effects of L-carnitine on serum triglyceride and cytokine levels in rat models of cachexia and septic shock. Br J Cancer 72: 1173-1179.
- Villani RG, Gannon J, Self M, Rich PA (2000) L-Carnitine supplementation combined with aerobic training does not promote weight loss in moderately obese women. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 10: 199-207.
- Johansson K, Neovius M, Hemmingsson E (2014) Effects of anti-obesity drugs, diet, and exercise on weight-loss maintenance after a very-low-calorie diet or low-calorie diet: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 99: 14-23.
- Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D (2010) CONSORT Group: CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 340: c332.
- Anuurad E, Shiwaku K, Nogi A, Kitajima K, Enkhmaa B, et al. (2003) The new BMI criteria for asians by the regional office for the western pacific region of WHO are suitable for screening of overweight to prevent metabolic syndrome in elder Japanese workers. J Occup Health 45: 335-343.
- Pan WH, Yeh WT (2008) How to define obesity? Evidence-based multiple action points for public awareness, screening, and treatment: an extension of Asian-Pacific recommendations. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 17: 370-374.
- Nagai N, Sakane N, Ueno LM, Hamada T, Moritani T (2003) The -3826 A-->G variant of the uncoupling protein-1 gene diminishes postprandial thermogenesis after a high fat meal in healthy boys. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 5661-5667.
- Nagai N, Sakane N, Hamada T, Kimura T, Moritani T (2005) The effect of a high-carbohydrate meal on postprandial thermogenesis and sympathetic nervous system activity in boys with a recent onset of obesity. Metabolism 54: 430-438.
- Snitker S, Tataranni PA, Ravussin E (1998) Respiratory quotient is inversely associated with muscle sympathetic nerve activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 3977-3979.
- Zurlo F, Lillioja S, Esposito-Del Puente A, Nyomba BL, Raz I, et al. (1990) Low ratio of fat to carbohydrate oxidation as predictor of weight gain: study of 24-h RQ. Am J Physiol 259: E650-657.
- Seidell JC, Muller DC, Sorkin JD, Andres R (1992) Fasting respiratory exchange ratio and resting metabolic rate as predictors of weight gain: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study on Aging. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 16: 667-674.
- Wutzke KD, Lorenz H (2004) The effect of l-carnitine on fat oxidation, protein turnover, and body composition in slightly overweight subjects. Metabolism 53: 1002-1006.
- Iwami M, Shimooka R, Shimazu T (2006) Effects of L-carnitine on energy metabolism in rats. J Jpn Soc Nutr Food Sci 59: 107-113.
- Vecchiet L, Di Lisa F, Pieralisi G, Ripari P, Menabò R, et al. (1990) Influence of L-carnitine administration on maximal physical exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 61: 486-490.
- Gorostiaga EM, Maurer CA, Eclache JP (1989) Decrease in respiratory quotient during exercise following L-carnitine supplementation. Int J Sports Med 10: 169-174.
- Kogure A, Sakane N, Takakura Y, Umekawa T, Yoshioka K, et al. (2002) Effects of caffeine on the uncoupling protein family in obese yellow KK mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29: 391-394.
- Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Lejeune MP, Kovacs EM (2005) Body weight loss and weight maintenance in relation to habitual caffeine intake and green tea supplementation. Obes Res 13: 1195-1204.
- Hsu CL, Yen GC (2007) Effects of capsaicin on induction of apoptosis and inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Agric Food Chem 55: 1730-1736.
- Shin KO, Moritani T (2007) Alterations of autonomic nervous activity and energy metabolism by capsaicin ingestion during aerobic exercise in healthy men. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 53: 124-132.
- Belza A, Frandsen E, Kondrup J (2007) Body fat loss achieved by stimulation of thermogenesis by a combination of bioactive food ingredients: a placebo-controlled, double-blind 8-week intervention in obese subjects. Int J Obes (Lond) 31: 121-130.
- Suzuki Y, Unno T, Ushitani M, Hayashi K, Kakuda T (1999) Antiobesity activity of extracts from Lagerstroemia speciosa L. leaves on female KK-Ay mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 45: 791-795.
- Ashakumary L, Rouyer I, Takahashi Y, Ide T, Fukuda N, et al. (1999) Sesamin, a sesame lignan, is a potent inducer of hepatic fatty acid oxidation in the rat. Metabolism 48: 1303-1313.
- Ono Y, Hattori E, Fukaya Y, Imai S, Ohizumi Y (2006) Anti-obesity effect of Nelumbo nucifera leaves extract in mice and rats. J Ethnopharmacol 106: 238-244.
Tables and Figures at a glance
| Table 1 | Table 2 |
Figures at a glance
 |
| Figure 1 |
Relevant Topics
- Android Obesity
- Anti Obesity Medication
- Bariatric Surgery
- Best Ways to Lose Weight
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Child Obesity Statistics
- Comorbidities of Obesity
- Diabetes and Obesity
- Diabetic Diet
- Diet
- Etiology of Obesity
- Exogenous Obesity
- Fat Burning Foods
- Gastric By-pass Surgery
- Genetics of Obesity
- Global Obesity Statistics
- Gynoid Obesity
- Junk Food and Childhood Obesity
- Obesity
- Obesity and Cancer
- Obesity and Nutrition
- Obesity and Sleep Apnea
- Obesity Complications
- Obesity in Pregnancy
- Obesity in United States
- Visceral Obesity
- Weight Loss
- Weight Loss Clinics
- Weight Loss Supplements
- Weight Management Programs
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 13934
- [From(publication date):
December-2014 - Apr 02, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 9385
- PDF downloads : 4549
