SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test: Laboratory Validation of the Performance of POCT Antigen Test Kits of COVID-19
Received: 10-May-2022 / Manuscript No. JIDT-22-63337 / Editor assigned: 16-May-2022 / PreQC No. JIDT-22-63337 (PQ) / Reviewed: 30-May-2022 / QC No. JIDT-22-63337 / Revised: 06-Jun-2022 / Manuscript No. JIDT-22-63337 (R) / Published Date: 13-Jun-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877.1000501
Abstract
With the advent of deadly SARS-CoV-2, public health organizations and researchers emphasized the timely detection and identification of the virus to limit the spread. Different tests were designed to detect coronaviruses for timely and rapid identification, including Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) that detects the organism's genetic material. This research aims to validate the performance of Point-of-care testingantigen test kits of COVID-19, including the Lateral Flow Test (LFT) and the lateral Flow Immunofluorescent Assay (FIA) is intended for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen. This evaluation involved six different rapid test kits, including Fia Test ATFNCG21040001, All Test ATNCP21060014, All Test ATNCP21060015, All Test ATNCP21060012, Abbott Panbio Cov-19 Ag Rapid Test, and Siemens Rapid COVID-19 Antigen Test. In addition, another study also compare the SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test (COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test) (Swab) manufactured by Hangzhou All Test Biotech Co., Ltd.; 2019-nCoV Antigen Test, manufactured by Guangzhou Wondfo Biotech Co., Ltd.; SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test, manufactured by Roche, the molecular SARS-COV-2 assay (nucleic acid extraction using the automatic system Versant, followed by RT-PCR using the FDT SARS-CoV-2 kit) manufactured by Siemens from Germany that meets EU CE standards, to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of candidate kit. The Nasopharyngeal Swab (NPS) samples were collected and analysed by RT-PCR method. The specificity of all rapid test kits was greater than 99.9%, whereas the sensitivity ranged from 91 to >99%, which is also significant. The finding suggests the rapid antigen test can be used as an effective tool in controlling COVID-19 promptly. Moreover, these tests can also be conducted by a layman or at home for primary identification of COVID-19, which would limit the transmission of disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Rapid antigen test; POCT Antigen test kit; Laboratory validation; Immunological assays; PCR; Lateral flow test; All Test
Introduction
The first case of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was reported in Wuhan, China in late 2019 [1], and caused the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic all around the world since then. The pandemic has cost at least 6 million lives in last two years [2], and have inflicted huge socioeconomic losses worldwide. Many efforts have been put to control the disease and prevent its further spread. One of the most effective ways to curb the spread of SARSCoV- 2 is early detection followed by effective isolation and treatment of patients. The result of an earlier study showed that a country had a lower overall mortality rate when adopting more extensive early testing on COVID-19 [3], highlighting the importance of accurate and fast diagnosis to contain the virus.
At present, the method based on Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (NAAT), as Real-Time reverse transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), is considered the gold standard for detecting SARS-CoV-2. The RT-PCR could detect the SARS-CoV-2 genetic materials in many types of samples, including sputum, nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs, and respiratory secretions, with a high sensitivity and specificity [4]. However, a RT-PCR test is expensive, takes at least 2-3 hours to obtain the result, and requires well-equipped facilities and experienced laboratory workers. These disadvantages limit its use for fast and massive diagnostics in controlling the virus spread. Alternative methods, such as rapid antigen test, with the ability to identify the virus in a fast, cheap way is needed.
Rapid Antigen Diagnostic tests (RAD) detect viral antigen in samples by the immobilized coated SARS-CoV-2 antibody on the device [5]. The test can provide a result in 15-20 minutes and can be operated and interpreted by individuals without specialized instrument and knowledge. The RADs assays have been used for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Point-Of-Care (POC) settings worldwide [6-9]. After two years of COVID-19 pandemic, many countries chose to lift or remove the pandemic restrictions, and the PCR test was only given to the groups that need it the most, such as patients, and health care and elderly care staff. Some countries, such as Sweden, recommended that you take self-antigen tests if you develop symptoms of COVID-19 [10], which underlined that there is growing importance of the utilization of SARS-CoV-2 RAD tests to combat the pandemic.
With the progression of COVID-19, many new SARS-CoV-2 variants with increased transmissibility, disease severity are emerging [11]. These new variants will bring additional challenges to current diagnosis methods, including the RAD test. There are more than 300 RAD kits that have been certified in European Union (EU) as of April 2022 [12]. The EU Technical Working Group is continuously monitoring the performance of current RAD tests, especially in the context of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and potential breakthrough infections among vaccinated individuals [13]. To address these concerns, there is a need to update the evaluation of the clinical performance of commercial RAD kits for COVID-19 diagnosis. In this work, two independent studies were carried out to evaluate the filed performance of the All Test SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test (COVID- 19 Antigen Rapid Test) (Swab). Its efficacy was compared with that of the Fia Test, Abbott Panbio, and Siemens COVID-19 antigen rapid test kits, and with RTPCR results in Sweden. Another set of comparative trials to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of the candidate kits was conducted in Rome.
Materials and Methods
Ethical considerations
The samples were collected from routine examinations of SARSCoV- 2 in authentic health care settings. The researcher evaluated the clinical samples without disclosing any personal information of the participants. Moreover, the information of the participants is not traceable.
Study cohort of 214 samples from Sweden
For this study, 214 samples were collected from healthcare settings in Sweden from July 2021 to September 23, 2021. All samples were collected by nasopharyngeal swabs and they were tested both by RTPCR and by antigen test on the same day. Both the antigen test kits and the RT-PCR kits were at least 6 months away from their expiration dates. The RNA was extracted with Viral RNA extraction kit from Norgen Biotek (Canada) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, for which 250 μl of each sample was collected by nasopharyngeal swabs into a viral transport medium. For each batch of the tested samples, an extraction control (EC) was included. The samples and spiked EC were processed and extracted. The extracted RNA was eluted in 50 μl RNasefree water, and 5 μl of which was used for the PCR reaction per test. Using the TaqPath 1-Step RT-qPCR MasterMix kit from ThermoFisher on the Roche 480 Light Cycle II platform, the detection was performed by RT-PCR. The probe used in the test are Light-Mix Modular SARSCoV- 2 (COVID19) RdRp that targets the ORF1ab genes. The targets were predefined, and the criteria were based on analytical Limit of Detection (LOD), corresponding to an RT-PCR Cycle threshold (Ct) of approximately 25 (~100,000 RNA copies/ml); an analytical specificity of ≥ 97%, an analytical sensitivity of ≥ 85%; and a kit failure rate <10%. This experiment was conducted by iLAB Medical AB.
Study cohort of 452 samples from Rome
The evaluation included: 452 specimens, including 152 nasal swab samples from RT-PCR confirmed SARS-CoV-2 positive cases, and 300 nasal swab samples from RT-PCR confirmed SARS-CoV-2 negative cases. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test assay kits of Wondfo, All test, Roche. The rapid antigen test was performed according to manufacturer’s instruction.
Tests have been performed in the Laboratory of Biochemical Chemistry of the Sant'Andrea Hospital of Rome, which can execute molecular testing for SARS-COV-2 by real-time PCR for 1500 samples/ day. All clinical specimens have been taken from patients by trained laboratory staff and the whole procedure (sampling to reporting) is according to ISO 15189 standards (The Accreditation Certificate No. 621-4, to ELOT EN ISO 15189:2012). Unselected Participants with symptomatic and asymptomatic suspects of COVID-19 under investigation were candidates for the evaluation. Swab specimen to be used in Rapid test, Nasopharyngeal specimen of same patient to be used in PCR test.
Statistics
After four months, on April 30 (day 120), the numbers of the current symptomatic infected individuals, the current asymptomatic infected individuals charged in observations, the cumulative recovered symptomatic individuals, the cumulative recovered asymptomatic individuals discharged in observations increased to 24002, 92792, 179772, and 402199, respectively. During the last two weeks, 424 death cases were reported. From December 31, 2021 to April 30, 2022, 114496 symptomatic infected cases were reported.
Results
Limit of Detection (LoD)
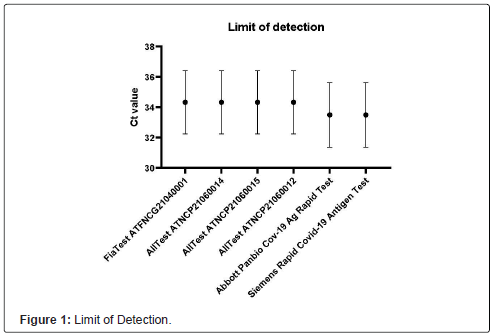
The limit of Detection (LoD) is the minor concentration of the sample analyte, which can be constantly identified with statistical significance and precise probability, usually 95 percent. The LoD is calculated based on standard deviation and calibration curve slope. The Ct Value was 36 for Fia Test ATFNCG21040001, All Test ATNCP21060014, All Test ATNCP21060015, and All Test ATNCP21060012. What’s more, Abbott Panbio Cov-19 Ag Rapid Test and Siemens Rapid COVID-19 Antigen Test showed the Ct value of 35(Figure 1).
Validation of SAR-CoV-2 rapid antigen test kit performance on a study cohort of 214 samples
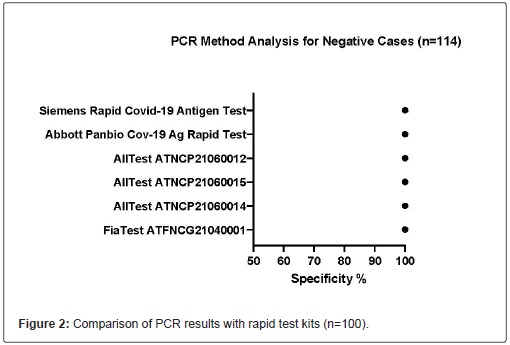
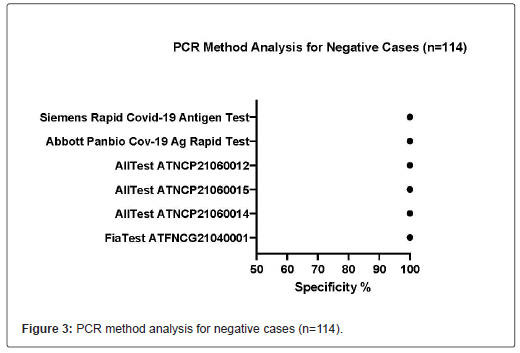
214 samples were obtained from healthcare settings in Sweden, dated from July 2021 to September 23, 2021. Among these 214 samples, 114 were tested SARS-CoV-2 negative and 100 were tested SARS-CoV-2 positive (CT<37) by RT-PCR. The performance of all rapid antigen test kits is listed in Table 1. All kits displayed >99.9% specificity. All Test ATNCP21060014, All Test ATNCP21060015, and All Test ATNCP21060012 displayed >99.9% sensitivity, whereas Fia Test ATFNCG21040001, Abbott Panbio Cov-19 Ag Rapid Test Device and Siemens Rapid COVID-19 Antigen Test displayed the sensitivity of 96.0%, 91.0% and 94.0% respectively. In this experiment, almost all kits provided adequate results, except one test failed in Fia Test ATFNCG21040001(Table 2) (Figures 2-4).
| Sacace SARS-CoV-2-Real-TM | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
| All Test SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test(COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test) (Swab) | Positive | 141 | 0 | 141 |
| Negative | 11 | 300 | 311 | |
| Total | 152 | 300 | 452 | |
Note: Sensitivity=92.76% (95%CI:87.42%~96.33%); Specificity=100% (95%CI:98.78%~100%); Accuracy=97.57% (95%CI:95.69%~98.78%)
Table 1: Test results of the All test.
| Sacace SARS-CoV-2-Real-TM | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
| Roche SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test | Positive | 145 | 0 | 145 |
| Negative | 7 | 300 | 307 | |
| Total | 152 | 300 | 452 | |
Note: Sensitivity=95.39% (95%CI:87.42%~96.33%); Specificity=100% (95%CI:98.78%~100%); Accuracy=98.45% (95%CI:95.69%~98.78%)
Table 2: Test results of the Roche.
Comparative trials to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid test
In the clinical evaluation test, there was 452 × 3 samples were tested, Every different brand tested 152 positive and 300 were negative according to RT-PCR. Analysis the reason of false negative samples, it seemed to need pay attention to the sample with high Ct value, it may appear an false negative result. The candidate kit show negative result, all the results conform to the RT-PCR results. Negative results of candidate kit are presumptive, do not rule out COVID-19 infection and it may be necessary to obtain additional testing with a molecular assay, if needed for patient management. Details of the results of the comparative trials are shown in Table 3.
| Sacace SARS-CoV- 2-Real-TM | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
| Wondfo SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test | Positive | 114 | 0 | 114 |
| Negative | 38 | 300 | 338 | |
| Total | 152 | 300 | 452 | |
Note: Sensitivity=75.00% (95%CI:87.42%~96.33%); Specificity=100% (95%CI:98.78%~100%); Accuracy=91.59% (95%CI:95.69%~98.78%)
Table 3: Test results of Sacace.
(1) 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases and 300 non-infected individuals of all test SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid test (COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test) (Swab):
In 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases, the candidate kit reported 141 positive results, and 11 negative results. In 300 non-infected individuals, the candidate kit reported 300 negative results. Test results of the All Test are summarized in Table 4 below:
| Study cohort of 214 samples | SARS-CoV-2 positive (n=100) | SARS-CoV-2 negative (n=114) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid antigen test kits | Limit of Detection (Ct) | Positive (Ct<37) | Negative | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Kit failure rate |
| Fia Test ATFNCG21040001 | 36 | 95 | 114 | 96 | >99.9* | 1/214 |
| All Test ATNCP21060014 | 36 | 100 | 114 | >99.9* | >99.9* | 0/214 |
| All Test ATNCP21060015 | 36 | 100 | 114 | >99.9* | >99.9* | 0/214 |
| All Test ATNCP21060012 | 36 | 100 | 114 | >99.9* | >99.9* | 0/214 |
| Abbott Panbio Cov-19 Ag Rapid Test Device | 35 | 91 | 114 | 91 | >99.9* | 0/214 |
| Siemens Rapid Covid-19 Antigen Test | 35 | 94 | 114 | 94 | >99.9* | 0/214 |
Note: Limit of Detection was determined by RT-PCR with Roche 480 detection kit; *:The marked sensitivity and specificity are witnessed in the lab to be 100% for the samples tested
Table 4: Performance characteristics of SAR-CoV-2 rapid antigen test kit.
(2) 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Cases and 300 non-infected individuals of Roche rapid test kit
In 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases, the candidate kit reported 145 positive results, and 7 negative results. In 300 non-infected individuals, the candidate kit reported 300 negative results. Test results of the Roche are summarized in Table 5 below:
| Sample Groups | CT Values of ORF Gene | Estimated Viral RNA Copy Numbers | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| High positive | CT ≤ 20 | >10^6 copies/reaction | 179 |
| High/Medium Positive | 21<CT ≤ 25 | 10^6~10^7 copies/reaction | 14 |
| Medium/Low Positive | 25<CT ≤ 30 | 10^4~10^5 copies/reaction | 10 |
| Low Positive | CT>30 | 10^4 copies/reaction | 20 |
| Negative | Not detected | Not detected | 302 |
Table 5: Samples included in the present evaluation grouped by Ct values.
(3) 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Cases and 300 non-infected individuals of Wondfo rapid test kit
In 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases, the candidate kit reported 114 positive results, and 38 negative results. In 300 non-infected individuals, the candidate kit reported 300 negative results (Table 6).
| Study cohort of 452 samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | All Test | Roche | Wondfo |
| CT<26 | 96.45% | 97.87% | 80.85% |
| 26 ≤ CT<28 | 66.67% | 83.33% | 0% |
| CT ≥ 28 | 20.00% | 40.00% | 0% |
| Total sensitivity | 92.76% | 95.39% | 75.00% |
| Total specificity | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Table 6: Test results of comparative trials.
Discussion
Limit of Detection (LoD)
This study evaluated four different antigen test kits for COVID-19 using clinical nasopharyngeal samples that were screened for SARSCoV- 2 RNA with RT-PCR on the same day. The result showed that FiaTest and All Test kit have a better detection limit than Abbott and Siemens kit, but not significantly. All four antigen test kits have passed the initial analytical LOD corresponding to RT-PCR Cycle Threshold (CT) of 25.
Validation of SAR-CoV-2 rapid antigen test kit performance on a study cohort of 214 samples
With a wide range of POCT antigen test kits available on the market, comparative laboratory evaluation of POCT antigen test kits is vital to validate performance features and to ensure batch-to-batch consistency. In the study, we addressed different batches of the same product, All Test test kits (All Test ATNCP21060014, All Test ATNCP21060015, and All Test ATNCP21060012), to evaluate the clinical performance of All Test antigen test kits. We included three other antigen test kits that is made widely available on the market, Fia Test test, Abbott Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test, and Siemens Rapid COVID-19 Antigen Test for comparison and evaluation on performance of different test kits.
Four POCT antigen test kits were evaluated by testing on 100 positive samples and 114 negative samples in compare with PCR results. The results of kit failure rate have superseded our initial target of less than 10%. None of the kits has failed throughout different batches of All Test, Abbott, and Siemens. Only one of the FiaTest tests did not provide adequate results. The reliability of the kits can be regarded as a safe and effective tool to detect SARS-CoV-2.
The specificity of all rapid test kits was greater than 99.9%, whereas the sensitivity ranged from 91% to >99% across different test kid. All test kits have passed the initial targets set of analytical specificity of ≥ 97% and analytical sensitivity of ≥ 85% on the laboratory validation of the performance of POCT antigen test kits of COVID-19.
There is convincing evidence that high viral loads in the samples correlate with increased transmission of SARS-CoV-2 [14]. These individuals are most infections during the time of symptom onset. According to the demographic analysis, both the Abbott and Siemens test kits are capable in detecting all positive samples from symptomatic individuals. The rapid spread of coronavirus has quickly followed by several cases reporting false negative in antigen test kits [15]. This is consistent in our analysis showing false negative in Abbott and Siemens test kits, resulting a sensitivity of 91.0% and 94.0% respectively. All false negative cases were obtained from asymptomatic individuals. The accuracy of test kits improved significantly when asymptomatic individuals and cases above CT of 32 were excluded. However, individuals in pre-symptomatic or early asymptomatic phase of infection remain to constitute a transmission risk. A false negative result delivered during infection could offer false security to individuals, missing the opportunity to make an early decision about patient management.
The safety and compliance of antigen test kits in the market are crucial for capturing and containing the transmission of COVID-19. The performance of All Test antigen test kit was further evaluated to ascertain the test kits’ comparability and consistency. Herein our study, we verify the performance features and batch-to-batch consistency of All Test antigen test kit. Our result showed that the clinical performance of three batches of All Test has shown consistent results in sensitivity and specificity of >99.99%. Based on our evaluation in approximately 200 samples, All Test shows a better consistency and sensitivity than Fia Test, Abbott, and Siemens, even with asymptomatic individuals with low viral loads.
Evaluation of clinical performance of the SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid test by Hangzhou all test biotech Co., Ltd.
Regular PCR-based methods are sensitive and specific in detecting SARS-CoV-2. However, the timely identification process of PCR routine is less suitable for regular screening in leisure, education, workplace, and health-care settings. Realistically, cost-effective test of lateral flow devices, such as rapid antigen test, can be used to make early, rapid decisions in accordance with regional and national health authorities’ protocols. Evaluating the performance of rapid antigen test available on the market is crucial in providing reliable reference for both public and private individuals.
The clinical performance of All Test test kit was evaluated on another independent laboratory. Comparatively larger study pool of 452 samples, divided into 152 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 positive cases and 300 confirmed SARS-CoV-2 negative cases was conducted. This second laboratory evaluation continues to provide similar results. The results showed a wide range of varying sensitivity, which is dependent on the CT value within sample population. The kit has highest sensitivity of 100% for samples with high viral loads (CT value lower than 25), and the sensitivity gradually reduced decrease in viral loads samples. All Test test kit shows significant sensitivity to detect early symptomatic case with high positive individuals, which is more likely to account for a considerable proportion of transmission. With recent studies showing association between increased transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in high viral load [16], this early detection of positive cases aid in rapid patient management decision and rapid initiation of contact tracing [17].
Several failed cases with asymptomatic individuals with low and very low viral loads were reported. As compared to symptomatic individuals which presented their symptoms in their early stage with higher viral load, asymptomatic individuals presented only for onetime screening test could be in any stage of infections including those who tested positive with PCR but viable virus is rapidly decreasing. The reduced sensitivity of All Test test kit relative to increased CT value is less of a concern in terms of risk of onward transmission [17].
This multi-centre accuracy study conducted in Sweden and Rome reveals a clearer overview on the multiwave pandemic dynamic at the respective times. The studies performed in various centre are likely to reflect phase of pandemic in each country. The variation in patient population, health care systems’ guidelines and recommendations mimic the real-world challenges of patient testing. According to our evaluation, individuals showing COVID-19 related symptoms were detected successfully across all range of viral loads.
The multi-centre accuracy study is limited by samples and individuals involved in different countries. The stages of pandemic phase, patient population with different viral load distribution, and prevalence of positive cases are differed between laboratory centres and countries. Another limitation of this study is the reference method used in Sweden and Poland. The variation in reagents used in PCR reference standard in different countries may affect actual CT values.
Conclusion
To conclude, from our evaluation in different country, the clinical performance of rapid antigen test demonstrates high sensitivity particularly in infectious individuals with high viral load. All antigen rapid tests included in our study have shown sufficient sensitivity to meet the current recommendations of Health Security Committee by the EU which request a sensitivity of >90% for individuals with aReferences CT<25 and specificity over 98%. The All Test Antigen rapid test that provides fast, effective results in a timeframe of 20 to 30 minutes can thereby act as an alternative tool to detect coronavirus in individuals. The cost-effectiveness of rapid antigen tests included in this study can act as a useful screening tool and contribute to pandemic control.
Our results thus indicate that the All Test’s RAD may be a valuable tool for diagnosing contagious individuals and con- trolling disease transmission in the ongoing pandemic. The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to gratefully acknowledge the collaboration of all laboratory and patients.
Declaration of Figures’ Authenticity
All figures submitted have been created by the authors, who confirm that the images are original with no duplication and have not been previously published in whole or in part.
References
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, et al. (2020) A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382:727-733.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019
- Pokhrel P, Hu C, Mao H (2020) Detecting the coronavirus (COVID-19). ACS Sens 5:2283-2296.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afzal A (2020) Molecular diagnostic technologies for COVID-19: Limitations and challenges. J Adv Res 26:149-159.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mak GC, Cheng PK, Lau SS, Wong KK, Lau CS, et al. (2020) Evaluation of rapid antigen test for detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus. J Clin Virol 129:104500.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carbonell-Sahuquillo S, Lázaro-Carreño MI, Camacho J, Barrés-Fernández A, Albert E, et al. (2021) Evaluation of a rapid antigen detection test (PanbioTM COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) as a point-of-care diagnostic tool for COVID-19 in a pediatric emergency department. J Med Virol 93:6803-6807.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krüger LJ, Gaeddert M, Tobian F, Lainati F, Gottschalk C, et al. (2021) The Abbott PanBio WHO emergency use listed, rapid, antigen-detecting point-of-care diagnostic test for SARS-CoV-2-Evaluation of the accuracy and ease-of-use. PLoS One 16:e0247918.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouassa RSM, Veyer D, Péré H, Bélec L (2021) Analytical performances of the point-of-care SIENNA COVID-19 antigen rapid test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in nasopharyngeal swabs: A prospective evaluation during the COVID-19 second wave in France. Int J Infect Dis 106:8-12.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torres I, Poujois S, Albert E, Álvarez G, Colomina J, et al. (2021) Point-of-care evaluation of a rapid antigen test (CLINITEST® Rapid COVID-19 antigen test) for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals. J Infect 82:e11-e12.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Testing for COVID-19, Folkhälsomyndigheten Public Health Agency of Sweden, 2022.
- Tao K, Tzou PL, Nouhin J, Gupta RK, de Oliveira T, et al. (2021) The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Rev Genet 22:757-773.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 in vitro diagnostic medical devices, European Commission, 2022.
- EU health preparedness: A common list of COVID-19 rapid antigen tests, European Commission, 2022.
- Marks M, Millat-Martinez P, Ouchi D, Roberts CH, Alemany A, et al. (2021) Transmission of COVID-19 in 282 clusters in Catalonia, Spain: A cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 21:629-636.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adamson BJ, Sikka R, Wyllie AL, Premsrirut PK (2022) Discordant SARS-CoV-2 PCR and rapid antigen test results when infectious: A December 2021 occupational case series. medRxiv 1:1-14.
- Alqahtani M, Abdulrahman A, Mustafa F, Alawadhi AI, Alalawi B, et al. (2022) Evaluation of rapid antigen tests using nasal samples to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 in symptomatic patients. Front Public Health 9:728969.
- Turner F, Vandenberg A, Slepnev VI, Car S, Starritt RE, et al. (2021) Post-disease divergence in SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection between nasopharyngeal, anterior nares and saliva/oral fluid specimens—significant implications for policy & public health. medRxiv 2:1-19.
Citation: Lie Z, Feng Y, Junzhe Z (2022) SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test: Laboratory Validation of the Performance of POCT Antigen Test Kits of COVID-19. J Infect Dis Ther 10: 501. DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877.1000501
Copyright: © 2022 Lie Z, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 1747
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Nov 21, 2024]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1496
- PDF downloads: 251