Remodelled Water Adjusted Both Proportion of Intestinal Flora and Peripheral Leukocyte Subset
Received: 24-Jan-2018 / Accepted Date: 02-Feb-2018 / Published Date: 08-Feb-2018 DOI: 10.4172/2573-4555.1000263
Abstract
Around 60% of the body weight consisted with water. So we tried to characterize the quality of the water for human physical factors. Lots of fundamental and clinical studies reported that many kind of water plays an important role in the physiological maintenance of humans as well as animals. This report was design to assess the influence of administration by remodeled water (RMW) on the development of physiological functions in human and experimental animal model. RMW was different from many other water, different from molecule itsself. RMW was proved to absorbed human odor molecule in vitro and in vivo. The animal model of experiment by immune-suppressive agent, RMW recovered the function of phagocytic cell in diabetes meritus (DM) model. In a human trial for intestinal model were shown to increased lactobacillus group other than anaerobic bacillus. More about odor factor, RMW decreased main odor elements, ammonia and hydrosulfate to decrease the odor in the exhaustive faces even after 7 days. In case of combat against infectious agent such as foreign microorganism, an active oxygen is most important in phagocytic cell. However excess level of oxygen is some time harmful for self-tissue, requiring to regulate at minimum level. Therefore, digital reliable assessment is necessary in phagocytic cells, not in in vitro system. In this report, we reported such trial by employing RMW.
Keywords: Quality of life; Digital presentation; Constitution; Remodeled water; Leukocyte subset; Macrophage; Granulocyte; Lymphocyte Antioxidative activity; Diabetes meritus
Introduction
Fork medicines were found elsewhere in the world where native peoples started to live. According to the report from WHO, traditional medicine counted as 65~85% within a medical science. In fact, when these percentage of medicine is regarded as complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) after when these medicines introduced [1]. Japan located in Far East, therefore substyle of medicine generated along with century and geographical condition, such in acupuncture in TCM [2]. Therefore, fine assessment and reviewing is necessary to estimation between the subtype as well as main type of traditional medicine [3-13]. In this article, we tried to present the effect of RMW [14], as a digital presentation of Japanese new CAM style reported as digital methodology and issue modeling. Hence over 60% of the body weight consisted with water. So we tried to characterize the quality of the water for human physical factors together with mice model.
Method
Preparation of remodeled water
Commercially available remodeled water (RMW) labeled SOSEI SUI was purchased with (Sosei World Co. Ltd. Ueda/Tokyo, Japan). Conventionally available purified water that prepared with reverse dialyzed by the laboratory in Kanazawa Medical University was set up as control (Figure 1) [14].
Absorbance/Solvent test
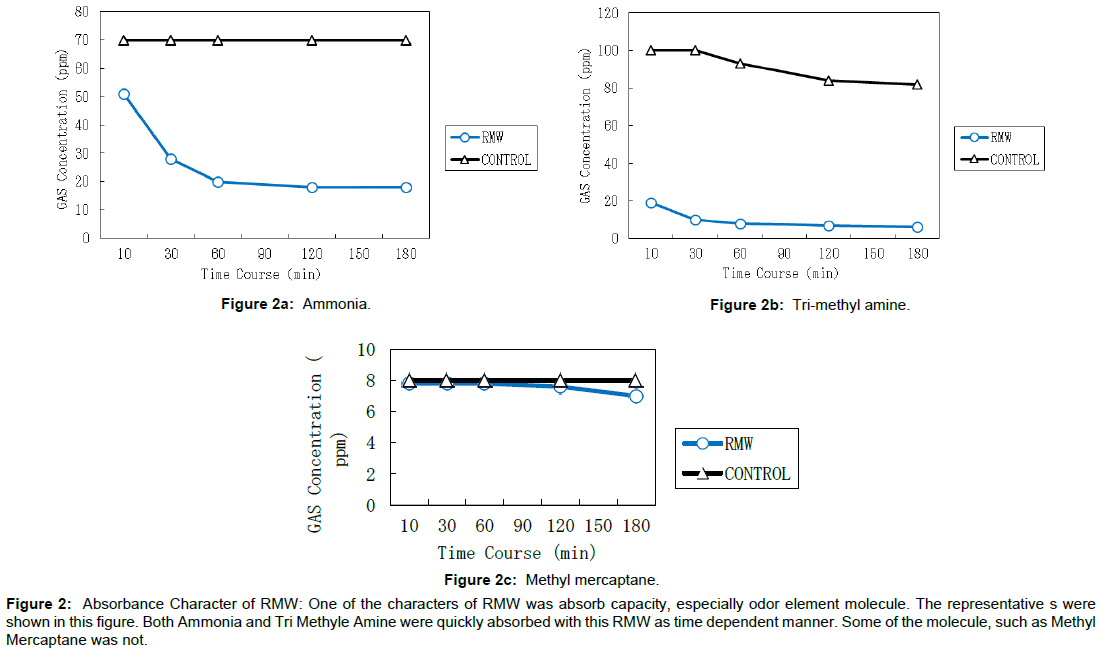
RMW have many character in the molecule its self, exhibiting one eminent effect of RMW. The routine experiment were made for absorption test for odor factor gas elements, ammonia, Tri-Methyle Amine, Methyl Mercaptan, xylem, toluene etc. As shown in Figure 2, ammonia (Figure 2a) and Tri-Methyle Amine (Figure 2b) were immediately absorbed by RMW but not for Methyl Mercaptan (Figure 2c). Beside the material in the figure, Hydro Sulfate, Acetaldehyde, Formaldehyde were could absorbed by RMW but not xylem and Methyl Mercaptan (assayed and reported by Japanese Food Analysis Center, Foundation, Tokyo).
Figure 2: Absorbance Character of RMW: One of the characters of RMW was absorb capacity, especially odor element molecule. The representative s were shown in this figure. Both Ammonia and Tri Methyle Amine were quickly absorbed with this RMW as time dependent manner. Some of the molecule, such as Methyl Mercaptane was not.
Animal experiment
An acute and chronical toxicity study was set up with ten female mice (7 week old ddY). The toxicity study was performed according to Ethics of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Test Guideline 401. All the animals were kept in SPF cleaned animal room at 24 ± 1ºC, 50% humidity.
Streptzotosin was selected as experimental dm model plus immune-deficient one
For preparing experimental diabetes mice, ddY mice, aged 7-8 weeks, were injected with Streptzootosin (5 mg/kg). For the control group of water, sterilized laboratory water as supplied to the control mice. Four week later, their blood were withdrawn from their tail vain. Peripheral blood were collected via tail vain and macrophage were corrected from their peritoneal cavity. The cell number and population assay were done by the dye solution, Bürker-Türk [15-34].
Estimation of anti-oxidative level, mice model
C57BL/6 SPF female mice (8wo) prepared by Animal Laboratory Service Corporation (Shizuoka, Japan. All mice were kept under specific pathogen-free conditions. Animal facility was controlled as specific pathogen free: SPF condition, controlled 24˚C ± 1˚C and 50%). The food and water supply were set up freely until the end of observation [35-37].
Preparing reagent
HEPES buffer (HEPES 17 mM, NaCl 120 mM, Glucose 5 mM, KCl 5 mM, CaCl2 1 mM, MgCl2 1 mM) was set up as basical solutions. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, Sigma, USA) was diluted to 10−6 M by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma, USA) Cytochromec (Sigma, USA) and employed as stimulant medium for mice. For measuring the amount of super oxide anion, cytochrome-c was selected, being reduced by super oxide showed maximum absorbance at 550 nm. In order to collect macrophage from mice peritoneal, Oyster Glycogen (Type II, Sigma, USA) was diluted in the purified water (10% w/v, Wako, Japan) was selected for this purpose.
Test system for phagocytic cell activity
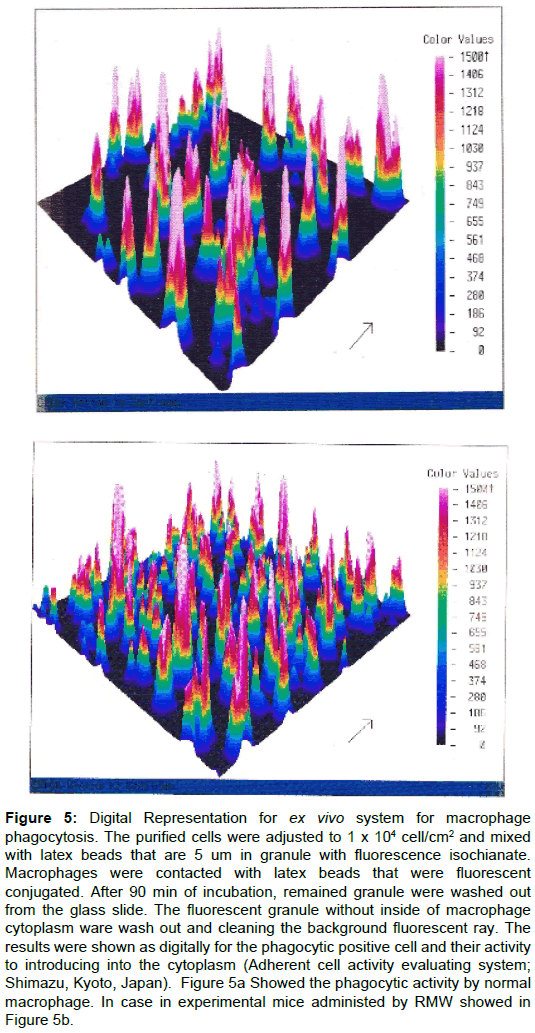
Peritoneal exhausted cell were collected from Streptozotosinn treated mice. Phagocytes were purified using adherent technique to get cell suspensions which contained more than 95% of phagocytes. Macrophages were purified by grass adherent technic and 95% of purity population. The purified cells were adjusted to 1 x 104 cell/cm2 and mixed with latex beads that are 5 um in granule with fluorescence isochianate. Macrophages were contacted with latex beads that were fluorescent conjugated. After 90 min of incubation, remained granule were washed out from the glass slide. The fluorescent granule without inside of macrophage cytoplasm ware wash out and cleaning the background fluorescent ray. The results were shown as digitally for the phagocytic positive cell and their activity to introducing into the cytoplasm (Adherent cell activity evaluating system; Shimazu, Kyoto, Japan).
Trial by human volunteer
Volunteers aged 65 ± 6.7 were nominated as this trial. Prior to the final step, all the applier were given self-questionnaires. At the final stage of this trial, volunteer were selected according their medical history. To confirm their condition, each participant gave written informed and consented in this trial.
Statistical considerations
The data were expressed as mean +/− standard deviation. The WBC is number of cells, granulocytes and lymphocytes were shown as % of total leukocytes and adrenalin content was expressed by pg (picogram/ ml). Group comparison of data was performed by ANOVA and post hoc multiple test.
Results
Animal safety test by RMW
Nine female seven-week-old ddY mice were used for the acute oral toxicity study. No incidence to ddY mice about food and water consumption by RMW the clinical observation were also made at once a day and all the mice ware no sign about medical incidence. Necropsy was tried to all mice on eight days after administration. No animal died or abnormalities of body weight, water and food consumption, or coat condition were seen in both group of mice. There was no significant problem in both control and RMW group from necropsy observation in thymus, spleen, kidney, liver, ovary, abdominal lymph node.
The comparison of generated super oxide anion in RMW
The temporal disappearance in human blood plasma of endogenous antioxidants in relation to the appearance of various classes of lipid hydro peroxides measured by HPLC post column chemiluminescence detection has been investigated under two types of oxidizing conditions. Exposure of plasma to aqueous peroxyl radicals generated at a constant rate leads immediately to oxidation of endogenous ascorbate and sulfhydryl groups, followed by sequential depletion of bilirubin, urate, and alpha-tocopherol. Stimulating polymorph nuclear leukocytes in plasma initiates very rapid oxidation of ascorbate, followed by partial depletion of urate. Once ascorbate is consumed completely, micromolar concentrations of hydro peroxides of plasma phospholipids, triglycerides, and cholesterol esters appear simultaneously, even though sulfhydryl groups, bilirubin, urate, and alpha-tocopherol are still present at high concentrations. None-sterified fatty acids, the only lipid class in plasma not transported in lipoproteins but bound to albumin, are preserved from per oxidative damage even after complete oxidation of ascorbate, most likely due to site-specific antioxidant protection by albumin-bound bilirubin and possibly by albumin itself. Thus, in plasma ascorbate and, in a site-specific manner, bilirubin appear to be much more effective in protecting lipids from per oxidative damage by aqueous oxidants than all the other endogenous antioxidants. Hydro peroxides of linoleic acid, phosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol added to plasma in the absence of added reducing substrates are degraded, in contrast to hydro peroxides of trilinolein and cholesterol linoleate. These findings indicate the presence of a selective peroxidase activity operative under physiological conditions. Our data suggest that in states of leukocyte activation and other types of acute or chronic oxidative stress such a simple regimen as controlled ascorbate supplementation could prove helpful in preventing formation of lipid hydro-peroxides, some of which cannot be detoxified by endogenous plasma activities and thus might cause damage to critical targets. Extracellular release of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide during the respiratory burst of porcine neutrophil/phagocyte was studied by using diacetyldeuteroheme-substituted horseradish peroxidase as a trapping agent for these oxygen derivatives. The method permitted simultaneous measurement of oxygen consumption and formation of both O2 and H2O2 in a single reaction mixture. When neutrophils/phagocytes were stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate in the presence of the home-substituted peroxidase, a rapid accumulation of compound, a complex of the enzyme with O2, was observed accompanying an increase in oxygen consumption. During the process, amounts of compound formed and oxygen consumed were stoichiometric, and no compound II, an indicator of H2O2 formation, was observed. These results establish that neutrophil/ phagocyte stimulated with the phorbol ester produce exclusively O2 as the primary oxygen metabolite and release it into the extracellular medium.
In case of combat against infectious agent such as foreign microorganism, an active oxygen is most important in phagocytic cell. However excess level of oxygen is some time harmful for self-tissue, required to regulate at minimum level [37-39]. Therefore, digital reliable assessment is necessary in phagocytic cells, not in in vitro system. The digital approach In case of activated water SOSEISUI (Sosei World, Co. Ltd, Nagano, Japan), anti-oxidative activity was exhibited compared than conventional water.
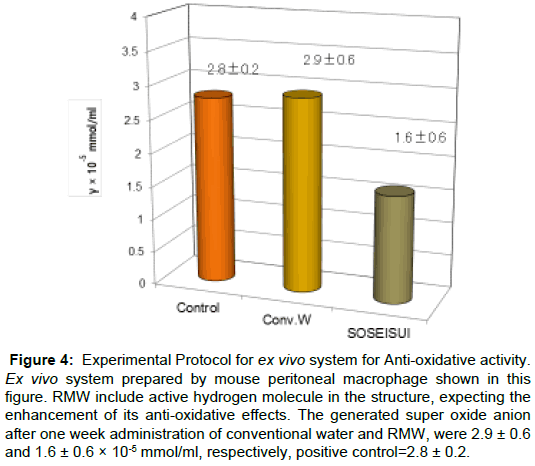
Since the anti-oxidative effects of herbal medicine were reported by us, stressing to employ animal phagocytic cell other than in vitro system [15]. We investigated the significance of this way to confirm by animal cell, phagocyte. Since RMW include active hydrogen molecule in the structure, expecting the enhancement of its antioxidative effects. The generated super oxide anion after one week administration of conventional water and RMW, were 2.9 ± 0.6 and 1.6 ± 0.6 × 10-5 mmol/ml, respectively, positive control =2.8 ± 0.2. The value obtained by RMW was a half level of control is required level of active oxygen level in the phagocyte, minimally need for the phagocyte against foreign micro organism against infection (Figures 3 and 4).
Figure 3: Experimental protocol for ex vivo system for Anti-oxidative activity.
These findings indicate the presence of a selective peroxidase activity operative under physiological conditions. Our data suggest that in states of leukocyte activation and other types of acute or chronic oxidative stress such a simple regimen as controlled ascorbate supplementation could prove helpful in preventing formation of lipid hydro-peroxides, some of which cannot be detoxified by endogenous plasma activities and thus might cause damage to critical targets. Extracellular release of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide during the respiratory burst of porcine neutrophil/phagocyte was studied by using diacetyl deuteroheme-substituted horseradish peroxidase as a trapping agent for these oxygen derivatives. The method permitted simultaneous measurement of oxygen consumption and formation of both O2 and H2O2 in a single reaction mixture. When neutrophils/phagocytes were stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate in the presence of the home-substituted peroxidase, a rapid accumulation of compound, a complex of the enzyme with O2, was observed accompanying an increase in oxygen consumption.
Figure 4: Experimental Protocol for ex vivo system for Anti-oxidative activity. Ex vivo system prepared by mouse peritoneal macrophage shown in this figure. RMW include active hydrogen molecule in the structure, expecting the enhancement of its anti-oxidative effects. The generated super oxide anion after one week administration of conventional water and RMW, were 2.9 ± 0.6 and 1.6 ± 0.6 × 10-5 mmol/ml, respectively, positive control=2.8 ± 0.2.
Chemotaxis, phagocytosis and intracellular killing
Our data, Figure 5 showed that Streptozotosin clearly suppressed the phagocytic activity of mice both in number and function (Figure 5a). After the treatment of RMW, the mice recovered their phagocytic activity to normal range. With a precise observation, the recovery activity of RMW was almost normal level among the four formulae as to augmentation in number and function of phagocytes (Figure 5b).
Figure 5: Digital Representation for ex vivo system for macrophage phagocytosis. The purified cells were adjusted to 1 x 104 cell/cm2 and mixed with latex beads that are 5 um in granule with fluorescence isochianate. Macrophages were contacted with latex beads that were fluorescent conjugated. After 90 min of incubation, remained granule were washed out from the glass slide. The fluorescent granule without inside of macrophage cytoplasm ware wash out and cleaning the background fluorescent ray. The results were shown as digitally for the phagocytic positive cell and their activity to introducing into the cytoplasm (Adherent cell activity evaluating system; Shimazu, Kyoto, Japan). Figure 5a Showed the phagocytic activity by normal macrophage. In case in experimental mice administed by RMW showed in Figure 5b.
So as to against an invasion by microorganism, macrophage have to work out, chemotaxis, phagocytosis and intracellular degradation of foreign organism. In this report, we picked up main activity phagocytosis. Streptozotosin. One of cancer chemotherapeutic agent, depressed macrophage function, phagocytosis (Figure 5a). After the treatment of RMW, the mice recovered their phagocytic activity to normal range. With a precise observation, the recovery activity of RMW was almost normal level among the four formulae as to augmentation in number and function of phagocytes.
Recovery of lymphocyte subset by RMW in cancer chemotherapeutic agent in mice
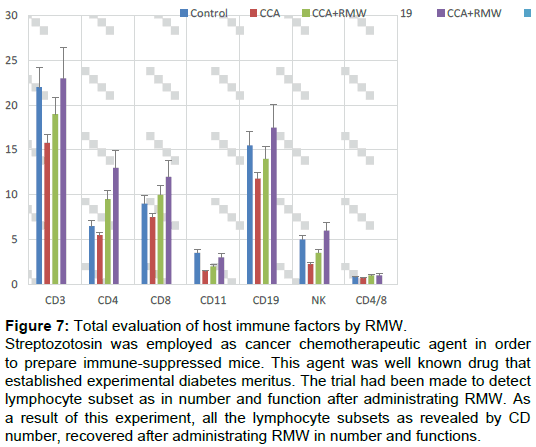
It had been well known that severe immune depressive status had accompanied by injection of cancer chemotherapeutic agent. In this script, Streptozotosin was employed as cancer chemotherapeutic agent. This was well known drug that established experimental diabetes meritus. The trial had been made to detect lymphocyte subset as in number and function after administrating RMW. From this experiment, all the lymphocyte subsets as revealed by CD number, recovered after administrating RMW in number and functions quantitatively and qualitatively (Figure 6).
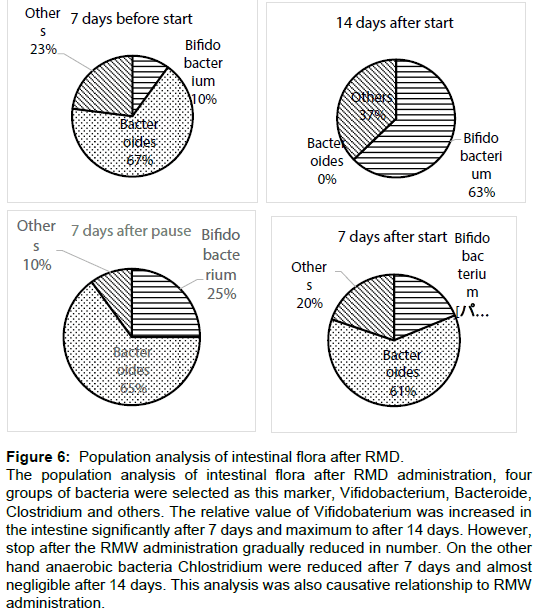
Figure 6: Population analysis of intestinal flora after RMD.
The population analysis of intestinal flora after RMD administration, four groups of bacteria were selected as this marker, Vifidobacterium, Bacteroide, Clostridium and others. The relative value of Vifidobaterium was increased in the intestine significantly after 7 days and maximum to after 14 days. However, stop after the RMW administration gradually reduced in number. On the other hand anaerobic bacteria Chlostridium were reduced after 7 days and almost negligible after 14 days. This analysis was also causative relationship to RMW administration.
Clinical Findings
Accessing bio chemical agent, ammonia and sulfide in the feces after RMW
First, we asked our volunteer as healthy one by written questionably. After informed and consented by the Ethics Committee in Kanazawa Medical University, they were administered RMW 3 weeks. Every one week after the start, the amount of both ammonia and sulfide were detected. As shown in Figure 7, From 7 days after the start, both ammonia and sulfide were significantly reduced in their feces. However, stop after the administration both level were up to the level at start, indicating close causal relationship to RMW administration (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Total evaluation of host immune factors by RMW.
Streptozotosin was employed as cancer chemotherapeutic agent in order to prepare immune-suppressed mice. This agent was well known drug that established experimental diabetes meritus. The trial had been made to detect lymphocyte subset as in number and function after administrating RMW. As a result of this experiment, all the lymphocyte subsets as revealed by CD number, recovered after administrating RMW in number and functions.
Effect on population of both goody bacillus and villainous bacillus
The volunteers were healthy subject, with no drastic change for health problem. After informed and consented by the Ethics Committee in Kanazawa Medical University, they were administered RMW 3 weeks. Every one week after the start, the amount of both ammonia and sulfide were detected. As shown in Table 1. 7 days after the start, both ammonia and sulfide were significantly reduced in their feces. As a representative of intestinal flora, Bifidobacterium, bacteroides, Escherichia coli and Streptococcus were selected for this tracing. RMW was compared to the health promoting standard, yogurt, Chitosan, Oligosaccharide and Lactulose. The results were shown in Table 1a-d respectively. From the result of this trial, RMW was the best material to up-regulating goody bacillus. On the same trend was evident that RMW was the best one for down-regulation of villainous bacillus number in the intestine.
| Comparative to Bifidobacterium | (Unit: x10000) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Before | 14 days after | Subtraction |
| RM Water | 6,45,654 | 18,19,800 | (+)1,174,046(181.8%) |
| Yogurt | 7,76,247 | 12,88,249 | (+)512,002(65.9%) |
| ※Chitosan | 10,96,478 | 3,89,045 | (+)707,433(64.5%) |
| Oligosaccharide | 7,41,310 | 27,54,228 | (+)2,012,918(271.5%) |
| Lactulose | 4,87,778 | 24,54,708 | (+)1,964,930(401.1%) |
Table 1a: Comparison of goody bacillus after administration of RMW.
| Combative to Bacteroides | (Unit: x10000) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Before | 14 days after | Subtraction |
| RM Water | 4,168,693 | 3,890,451 | (-)378,232(149.8%) |
| Yogurt | 3,981,071 | 3,891,071 | - |
| ※Chitosan | 6,760,829 | 5,754,399 | (-)1,006,430(14.8%) |
| Oligosaccharide | 2,398,832 | 3,162,277 | (+)763,445(31.8%) |
| Lactulose | 4,897,778 | 2,454,708 | (-)2,443,070(49.8%) |
Table 1b: Comparison of villainous bacillus after administration.
| Combative to E. coli | (Unit: x10000) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Before | 14 days after | Subtraction |
| RM Water | 6,025 | 5,623 | (-)402(6.6%) |
| Yogurt | 19,952 | 6,165 | (-)13,787(69.1%) |
| ※Chitosan | 58,884 | 97,723 | (+)38,839(65.9%) |
| Oligosaccharide | 16,982 | 11,748 | (+)5,234(30.8%) |
| Lactulose | 24,547 | 6,165 | (-)18,381(74.8%) |
Table 1c: Comparative to E. coli.
| Comparative to Streptococcus | (Unit: x10000) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Before | 14 days after | Subtraction |
| RM Water | 300,199 | 1,380 | (-)38,819(95.4%) |
| Yogurt | 19,952 | 31,622 | (-)11,670(58.4%) |
| ※Chitosan | 24,547 | 97,723 | (-)33,176(298.1%) |
| Oligosaccharide | - | - | - |
| Lactulose | 6,165 | 119 | (-)5,066(82.1%) |
Table 1d: Comparative to Streptococcus.
Dynamics of intestinal flora after RMW
As was the same trend of trial for the analysis of intestinal flora, four groups of bacteria were selected as this marker, Vifidobacterium, Bacteroides, Clostridium and others. The relative value of Vifidobaterium was increased in the intestine significantly after 7 days and maximum to after 14 days. However, stop after the RMW administration gradually reduced in number. On the other hand anaerobic bacteria Chlostridium were reduced after 7 days and almost negligible after 14 days. This analysis was also causative relationship to RMW administration (Figure 6).
Dividing subjects according to constitution into G-rich type and L-rich type
For the total evaluation by administrating RMW, 10 volunteer were informed and contented had written informed and consented to join atrial for this observation. The volunteer they were collected blood from fore arm vein before and 30 days after the trial pre and post this trial. Peripheral leukocyte subset and lymphocyte subsets were estimated by authorized institution on the county (Ishikawa Institute for Preventive Medicine, Foundation, Kanazawa, Japan). In Tables 2 and 3, volunteer were divided as G-rich type or L-rich type [15-17] As a results, G-rich type tend to decrease granulocyte yet, lymphocyte were increased. On the other hand, L-rich type However, L-type were shown as vice versa.
| G type individual | L type individual | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMW | RMW | |||
| Before | After | Before | After | |
| Total WBC (x 103 μl) | 6.37 | 5.97 | 3.65 | 5.76 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 23.6 | 27.9 | 42.5 | 39.2 |
| Granulocyte (%) | 68.3 | 66.7 | 55.2 | 59.6 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 63.2 | 63.3 | 45.1 | 54.2 |
| Eosinophil (%) | 1.8 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 4.6 |
| Basophil (%) | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
Table 2: The constitution/condition dependent regulation of leukocyte subsets by RMW.
| CD | G type individual | L type individual | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMW | RMW | |||
| Before (%) | After (%) | Before (%) | After (%) | |
| CD2 | 73.6 | 75.66 | 62.43 | 75.35 |
| CD4 | 17.64 | 20.34 | 30.44 | 41.22 |
| CD8 | 36.45 | 41.33 | 28.67 | 29.33 |
| CD11 | 72.45 | 74.32 | 62.11 | 68.94 |
| CD14 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| CD16 | 63.66 | 59.59 | 53.67 | 49.34 |
| CD19 | 8.11 | 8.35 | 8.65 | 7.41 |
| CD56 | 1.44 | 1.65 | 1.43 | 2.57 |
Table 3: The constitution/condition dependent regulation of CD positive lymphocyte by RMW.
The constitution/condition dependent regulation and presentation for CD positive lymphocyte. Constitution dependent regulation of leukocyte by RMW, Volunteer were divide according to their constitution base on their granulocyte/Lymphocyte Ratio. The data represented the value obtained 30 days after RMW administration. Variations in leukocyte subpopulations in the peripheral blood before and after each CAM therapy. A Variations in lymphocyte subpopulations in the peripheral blood before and after RMW administration.
Volunteer were dividing G-rich type and L-rich type by Lymphocyte Subset Proportion For the total evaluation by administrating RMW, 10 volunteer were written informed and contented to join atrial for this observation. The volunteer were collected blood from fore arm vein before and 30 days after the trial. Peripheral lymphocyte subsets were estimated by authorized institution on the county (Ishikawa Institute for Preventive Medicine, Foundation, Kanazawa, Japan). In Table 3, volunteer were divided as G-rich type or L-rich type. As a results, G-rich type tend to T-cell series of lymphocyte, yet, lymphocyte were decreased. On the other hand, L-rich type were shown as vice versa.
Discussion
The World Health Organization classifies 65~85% of the world health control business into the “traditional medicine”. In other words, if these traditional medicines are practiced in the West, it is classified into the alternative medicine. In this article, we select one of the simple compound remodeled water [14], hence the over 60% of body weight. This specialized water was eminent molecule that autonomally activated within a water molecule. This water was as safe by animal safety test. Moreover, the regulatoional effect was obtained in peripheral leukocyte that we propose that this facto is the best scale for access the physiological condition not by analog but digital one, preclinical and bedside test In order to compare the each traditional medicine in the each country, a common digital evaluation system is necessary. We propose that the best way for the sale is an immunological factor and compare the results as constitution dependent manner [15-17]. As a results of CAM sample exhibiting efficacy through immunological factor by hot spring hydro therapy, light exercise, floor heating and TCM etc. [37-40]. In this report we confirmed that RMW was also regulated immunological factor through life related complains, especially in senile [41-44].
References
- Yu F, Takahashi T, Kawamura K, Yamakawa J, Kusaka K, et al. (2006) Traditional Chinese Medicineand Kampo: a review from the distant past for the future. J Int Med Res 34: 231-239
- Kawakita K, Shichidou T, Inoue E, Nabeta T, Kitakoji H, et al. (2008) Do Japanese Style Acupuncture and Moxibustion Reduce Symptoms of the Common Cold? Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 5: 481-489.
- Wang XX, Katoh S, Liu BX (1998) Effect of Physical Exercise on Leukocyte and Lymphocyte Subpopulations in Human Peripheral Blood. Cytometry Res 8: 53-61.
- Kitada Y, Wan W, Matsui K, Shimizu S, Yamaguchi N (2000) Regulation of Peripheral White Blood Cells in Numbers and Functions through Hot-Spring Bathing during a Short Term Studies in Control Experiments. J Japanese Society Balneology Climatology Physiological Med 63: 151-164.
- Yamaguchi N, Nurmuhammad A, Zhao J, Jia X, Jian J, et al. (2014) Quantitative & Qualitative Regulation of Peripheral Leukocyte Subsets plus Emotional Hormones by Floor Heating. Open J Rheumatol Autoimmune Dis 4: 97-105.
- Yamaguchi N, Takahashi T, Sugita T, Ichikawa K, Sakaihara S, et al. (2007) Acupuncture Regulates Leukocyte Subpopulations in Human Peripheral Blood. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 4: 447-453.
- Yamaguchi N, Shimizu S, Izumi H (2004) Hydrotherapy Can Modulate Peripheral Leukocytes: An Approach to Alternative Medicine. Complementary and Alternative Approaches to Biomed Ishikawa 239-251.
- Yamaguchi N, Wan W, Sakamoto D, Nurmuhammad A, Matsumoto K, et al. (2013) Regulative Effect for Natural Killer Cell by Hot Spring Hydrotherapy—Quantitative and Qualitative Discussion. Open J Immunol 3: 201-209.
- Wang XX, Kitada K, Matsui S, Ohkawa T, Sugiyama H, et al. (1999) Variation of Cell Populations Taking Charge of Immunity in Human Peripheral Blood Following Hot Spring Hydrotherapy Quantitative Discussion. The Journal of Japanese Association of Physical Medicine, Balneologyand Climatology 62: 129-134.
- Yamaguchi N, Hashimoto H, Arai M, Takada S, Kawada N, et al. (2002) Effect of Acupuncture on Leukocyte and Lymphocyte Subpopulation in Human Peripheral Blood-Quantitative Discussion. The J Japanese Association of Physical Medicine, Balneology and Climat 65: 199-206.
- Wan W, Li AL, Izumi H, Kawada N, Arai M, et al. (2002) Effect of Acupuncture on Leukocyte and Lymphocyte Sub-Population in Human Peripheral Blood Qualitative Discussion. The J Japanese Association of Physical Medicine, Balneology and Climatology 65: 207-211.
- Yamaguchi N, Chen R, Okamoto K, Takei T, Tsubokawa M, et al. (2013) Quantitative Regulation of Peripheral Leukocyte by Light Exercise and Tailored Scale for Assessment. Open J Immunol 3: 175-183.
- Mark D, Tukerman ME, Hutton J, Parrinello M (1999) The nature of the hydrated proton in water. Nature 397: 601-604.
- Abo T, Kawate T, Itoh K, Kumagai K (1981) Studies on the Bioperiodicity of the Immune Response. 1. Circadian Rhythms of Human T, B and K Cell Traffic in the Peripheral Blood. J Immunol 126: 1360-1363.
- Abo T, Kumagai T (1978) Studies of Surface Immunoglobulins on Human B Lymphocytes. III Physiological Variations of Sig+ Cells in Peripheral Blood. Clin Exp Immunol 33: 441-452.
- Suzuki S, Toyabe S, Moroda T, Tada T, Tsukahara, et al. (1997) Circadian Rhythm of Leukocytes and Lymphocytes Subsets and Its Possible Correlation with the Function of the Autonomic Nervous System. Clin Exp Immunol 110: 500-508.
- Bylund DB, Eikenberg DC, Hieble JP, Langer SZ, Lefkowitz RJ, et al. (1994) Intenational Union of Pharmacology Nomenclature of Adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev 46: 121-136.
- Dulis BH, Wilson IB (1980) The β-Adrenergic Receptor of Live Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes. J Biol Chem 255: 1043-1048.
- Maisel AS, Harris T, Rearden CA, Michel MC (1990) Beta-adrenergic receptors in lymphocyte subsets after exercise. Alterations in normal individuals and patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 82: 2003-2010.
- Sanders VM, Baker RA, Ramer-Quinn DS, Kasprowicz DJ, Fuchs BA, et al. (1997) Differential Expression of the β2-Adrenaergic Receptor by Th1 and Th2 Clones. J Immunol 158: 4200-4210
- Eguchi Y, Yamaguchi N, Amat N, Yimit D, Hoxur P, et al. (2015) A New ActivatedWater Charged by Electrophoresis, Effect on the Experimentally Immuno-Suppressed Animal and Their Anti-Oxidative Activity. Open J Immunol 5: 122-132.
- Miyazaki S (1977) Immunodificiency in Clinical Origin. Clin Pediatr 1: 1001-1006.
- Kishida K, Miyazaki S, Take H, Fujimoto T, Shi H, et al. (1978) Cranial Irradiation and Lymphocyte Subpopulation in Acute Lymphatic Leukemia. J Neveral Pedi 92: 785-786.
- Yamaguchi N, Takei T, Chen R, Wushuer P, Wu WH (2013) Maternal Bias of Immunity to Her Offspring: Possibility of an Autoimmunity Twist out from Maternal Immunity to Her Young Open J Rheum Autoimmune Dis 3: 40-55.
- Murgita RA, Tomasi TB (1975) Suppression of the Immune Response by Alpha-Fetoprotein. J Exp Med 141: 269-286.
- Garside P, Steel M, Liew FY, Mowat AM (1995) CD4+ but Not CD8+ T Cells Are Required for the Induction of Oral Tolerance. Int Immunol 7: 501-504.
- Koshimo H, Miyazawa Y, Shimizu Y, Yamaguchi N (1989) Maternal Antigenic Stimulation Actively Produces Suppressor Activity in Offspring. Dev Comp Immunol 13: 79-85.
- Zoeller M (1988) Tolerization during Pregnancy: Impact on the Development of Antigen-Specific Help and Suppression. Eur J Immunol 18: 1937-1943.
- Auerback R, Clark S (1975) Immunological Tolerance: Transmission from Mother to Offspring. Science 189: 811-813.
- Shinka S, Dohi Y, Komatsu T, Natarajan R, Amano T (1974) Immunological Unresponsiveness in Mice. I. Immunological Unresponsiveness Induced in Embryonic Mice by Maternofetal Transfer of Human-Globulin. Biken J 17: 59-72.
- Aase JM, Noren GR, Reddy DV, Geme Jr JW (1972) Mumps-Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and the Immunologic Response of Their Offspring. N Engl J Med 286: 1379-1382.
- Cramer DV, Kunz HW, Gill III TJ (1974) Immunologic Sensitization Prior to Birth. Am J Obstetric Gynec 120: 431-439.
- Stoika RS, Lutsik MD, Barska ML, Tsyrulnyk A, Kashchak NI (2002) In Vitro Studies of Activation of Phagocytic Cells by Bioactive Peptides. J Physiol Pharmacol 53: 675-688.
- Yamaguchi N, Matsuba K, Okamoto K, Ueyama T, Matsuba Y, et al. (2014) Rodent Macrophage Select Vin Blank Together with Vin Rouge According to SO Level in Situ. Open J Rheumatol Autoimmune Dis 4: 240-247.
- Yamaguchi N, Kawada K, Jia X, Okamoto K, Okuzumi K, et al. (2014) Overall Estimation of Anti-Oxidant Activity by Mammal Macrophage. Open J Immunol 4: 13-21
- Elbim C, Pillet S, Prevost MH, Preir A, Girard PM, et al. (2001) The Role of Phagocytes in HIV-Related Oxidative Stress. J Clin Virol 20: 99-109.
- Speer CP, Gahr M, Pabst MJ (1986) Phagocytosis Associated Oxidative Metabolism in Human Milk Macrophages. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 75: 444-451.
- Yamaguchi N, Arai M, Murayama T (2015) Aspect of QOL Assessment and Proposed New Scale for Evaluation. Aspect of QOL Assessment and Proposed New Scale for Evaluation. Open J Immunology 5: 147-182
- Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi N, Horiuch I, Murayama T (2015) Fermented Black Turmeric Designed by Lactobacillus Rearranged Leukocyte Subsets and Anti-Oxidative Activity. Open J Immunol 5: 199-214.
- Yamaguchi N, Hiruma W, Suruga K, Amat N, Yimit D, et al. (2015) Hemopoietic Formulae Rearranged Leukocyte Subsets and Implication for Use against the Type of Constitution and Infectious Agent for Further Modification to Future. Open J Immun 5: 183-98.
- Yamaguchi N, Kawada N, Jia X, Okamoto K, Okuzumi K, et al. (2014) Overall Estimation of Anti-Oxidant Activity by Mammal Macrophage. Open J Rheumatology and Autoimmune Dis 4: 13-21.
- Nobuo YN, Matsuba K, Okamoto K, Ueyama T, Matsuba Y, et al. (2014) Rodent Macrophage Select Vin Blank Together with Vin Rouge According to SO Level in Situ. Open J Rheumatology and Autoimmune Dis 4: 240-47.
- Yamaguchi N, Nurmuhammad A, Zhao J, Jia X, Jian J, et al. (2014) Quantitative & Qualitative Regulation of Peripheral Leukocyte Subsets plus Emotional Hormones by Floor Heating. Open J Rheumatology and Autoimmune Dis 4: 97-105.
Citation: Fukai T, Yamaguchi N (2018) Remodelled Water Adjusted Both Proportion of Intestinal Flora and Peripheral Leukocyte Subset. J Tradit Med Clin Natur 7:263. DOI: 10.4172/2573-4555.1000263
Copyright: © 2018 Fukai T, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 4687
- [From(publication date): 0-2018 - Nov 10, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 3722
- PDF downloads: 965