Research Article Open Access
Primary Helicobacter pylori Eradication Rates of Lansoprazole, Amoxicillin, and Metronidazole Therapy is Much Higher than Lansoprazole, Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin Therapy in Chiba Prefecture, Japan
So Sakamoto1,3, Shunji Fujimori2* and Fumio Sakamoto2,3
1Emergency Intensive Care, Juntendo University Nerima Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
2Department of Gastroenterology, Nippon Medical School, Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
3Sakamoto Clinic, Chiba, Japan
- *Corresponding Author:
- Shunji Fujimori
Department of Gastroenterology
Graduate School of Medicine
Nippon Medical School 1-1-5
Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8603, Japan
Tel: 81-3-3822-2131
Fax: 81-3-5685-1793
E-mail: s-fujimori@nms.ac.jp
Received date: October 22, 2014; Accepted date: November 11, 2014; Published date: November 17, 2014
Citation: Sakamoto S, Fujimori S, Sakamoto F (2014) Primary Helicobacter pylori Eradication Rates of Lansoprazole, Amoxicillin, and Metronidazole Therapy is Much Higher than Lansoprazole, Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin Therapy in Chiba Prefecture, Japan. J Gastrointest Dig Syst 4:242. doi: 10.4172/2161-069X.1000242
Copyright: © 2014 Sakamoto S, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Gastrointestinal & Digestive System
Abstract
Aim: To compare the efficacy of primary Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy between PPI/AC therapy (proton-pump inhibitor; lansoprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin) and PPI/AM therapy (lansoprazole, amoxicillin, and metronidazole).
Methods: The subjects were patients with Helicobacter pylori infection who received initial eradication treatment at a family doctor in Katori City, Japan. Infection of Helicobacter pylori was initially evaluated pathologically using gastric mucosal specimens obtained by biopsy through upper endoscopy. Ninety-two patients underwent PPI/AC therapy and 28 patients underwent PPI/AM for primary eradication. Success or failure of eradication was determined by a urea breath test, and the primary eradication rates were compared between the two therapies. Patients who underwent PPI/AC but failed to achieve eradication were recommended to undergo secondary eradication treatment with PPI/AM, and the secondary eradication rate was assessed.
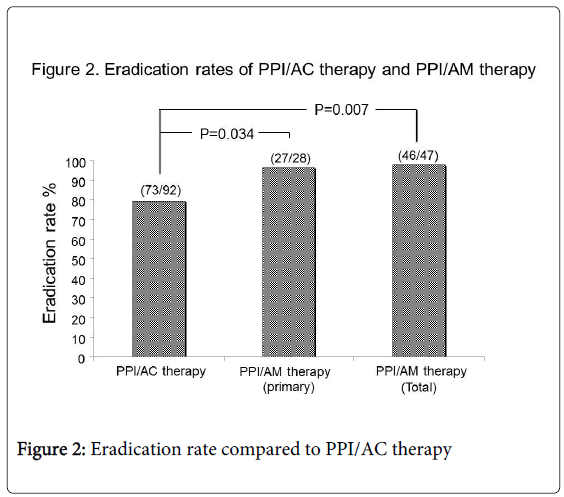
Results: In primary eradication therapy, successful eradication rates were 79.3% (73/92) in PPI/AC and 96.4% in PPI/AM, indicating that PPI/AM had a significantly higher eradication success rate (P=0.034). The 19 patients who failed to achieve eradication by PPI/AC underwent secondary eradication by PPI/AM. All 19 cases showed effective eradication (100%). Ultimately, eradication was successful in 99.2% (119/120) patients. Successful eradication rate in the total of primary and secondary PPI/AM treatments was also significantly higher than primary PPI/AC (46/47 vs. 73/92: P=0.007). Neither therapy was associated with any notable side effects.
Conclusion: In this regional study, PPI/AM therapy showed a favorable eradication rate, significantly higher than PPI/AC therapy. Thus, PPI/AM therapy is recommended as the primary eradication therapy in the region.
Keywords
Helicobacter pylori; Eradication; Clarithromycin; Metronidazole
Introduction
In Japan, Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication therapy has been indicated under Japanese national health insurance since November 2000 for patients with H. pylori-positive gastric/duodenal ulcers including ulcer scars. Since then, the use of eradication therapy has also been included in the treatment of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma, idiopathic thrombocytopenia, and early gastric cancer [1]. Since February 2013, H. pylori-positive gastritis was added to the list of diseases amenable to eradication therapy. Currently, eradication treatment is widely performed, and the number of patients receiving eradication therapy has significantly increased.
However, the eradication success rate has decreased recently due to the occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, due to the three-drug combination therapy of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), and two antibiotic drugs; amoxicillin (AMPC) and clarithromycin (CAM) namely PPI/AC therapy, which comprise the primary eradication regimen [2]. Recently, about 30% of patients with H. pylori infection are failed to eradicate by primary PPI/AC therapy by CAM-resistant H. pylori increasing [3]. In 2007, a three-drug combination therapy using antibiotic metronidazole (MNZ) instead of CAM, namely PPI/AM therapy, was indicated under national health insurance as a secondary eradication regimen, whereas the use of a primary eradication scheme was excluded as an insurance-based indication [4,5].
Under the established Japanese insurance-based H. pylori eradication therapy such as PPI/AC for primary eradication and PPI/AM for secondary eradication, it is difficult to compare primary H. pylori eradication capability between PPI/AC therapy and PPI/AM therapy. Thus, no reports were published to compare primary PPI/AC therapy and primary PPI/AM therapy for H. pylori eradication in Japan.
Before national approval of using insurance for H. pylori eradication in patients with only gastritis, some H. pylori infected patients with gastritis wanted to undergo H. pylori eradication at their own expense. H. pylori infected patients without ulcers who wanted to eradicate H. pylori at their own expense were able to undergo primary PPI/AM H. pylori eradication therapy if they desired. The aim of the study was to compare the primary H. pylori eradication capability between PPI/AC therapy and PPI/AM therapy in Japan.
Subjects and Methods
Study patients
The study was performed retrospectively to check the medical records of consecutive patients infected with H. pylori who desired to undergo initial H. pylori eradication treatment in Katori City, Chiba Prefecture, Japan, between 2008 and 2011. A total of 120 patients with H. pylori infection were eligible for inclusion: 62 were male (51.7%) and 58 were female, with a mean age of 62.6 years. The study patients were outpatients. Inclusion criteria were: 1) patients were over 18 years old; 2) patients had positive H. pylori infection at the primary eradication therapy; 3) patients suffered a controlled adult disease such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes mellitus to visit a family doctor at regular intervals; and 4) patients gave informed consent to each eradication therapy. Exclusion criteria were: 1) patients receiving any H. pylori infection therapy before the study; 2) patients with severe anemia and/or active bleeding due to active gastroduodenal ulcer, because they were referred to a specialized hospital.
H. pylori infection was diagnosed pathologically by gastric mucosal specimen obtained by biopsy through upper endoscopy in all study patients.
H. pylori eradication therapy
Patients with gastric / duodenal ulcers including ulcer scars were given seven days of insurance-indicated PPI/AC therapy: PPI (lansoprazole 30 mg twice daily), AMPC (750 mg twice daily), and CAM (200 mg twice daily). Patients who received PPI/AC therapy but failed to achieve primary successful eradication were recommended to undergo insurance-indicated secondary eradication with PPI/AM therapy.
Patients without ulcers who desired H. pylori eradication were provided with adequate information and independently selected to undergo PPI/AC therapy or PPI/AM therapy: PPI (lansoprazole 30 mg twice daily), AMPC (750 mg twice daily), and MNZ (250 mg twice daily), and underwent primary eradication at their own expense. Information provided to patients without ulcers included the fact of the recent decreasing H. pylori eradication success rate of PPI/AC therapy compared to PPI/AM therapy.
Eradication efficacy was determined using a 13C-urea breath test administered eight weeks after eradication treatment; successful eradication was identified when the result of the 13C-urea breath test was less than 2.5‰. All eradication therapies and all 13C-urea breath tests were conducted in the Sakamoto clinic.
Primary and secondary analysis
Primary analysis was evaluated as the primary H. pylori eradication rate comparing PPI/AC therapy with PPI/AM therapy. Patients who received PPI/AC therapy but failed to achieve primary eradication underwent secondary eradication with PPI/AM therapy, to additionally assess the secondary eradication rate. Thus, secondary analysis compared H. pylori eradication rate between primary PPI/AC therapy and primary plus secondary PPI/AM therapy.
Statistical analysis
Age and gender were compared between patients with ulcers and patients without ulcers by student’s t test and chi-square test. The difference in H. pylori eradication rate between PPI/AC therapy and PPI/AM therapy at primary analysis was compared by Cochran test. The difference in H. pylori eradication rate between PPI/AC therapy and PPI/AM therapy at secondary analyses were compared by Mantel-Haenszel test. Data were expressed as mean value ± SD. P-values <0.05 were considered significant.
Results
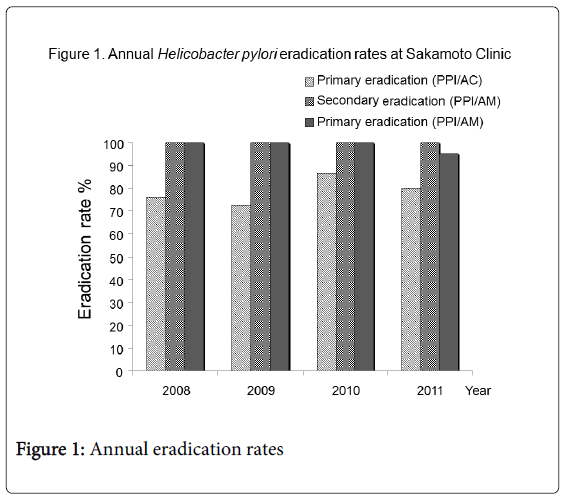
A total of 120 patients receiving H. pylori eradication therapy were divided into two groups: patients with gastroduodenal ulcers (92 cases: 50 males (54%), mean 61.5 ± 13.2 years) and patients without ulcers who desired H. pylori eradication (28 cases: 12 males (43%), 66.1±10.2 years). There were no statistical differences between the two groups in terms of age and gender. All 92 patients with ulcers were treated with PPI/AC therapy for primary eradication using Japanese national health insurance. In addition, all 28 patients without ulcers were treated with PPI/AM therapy according to their own will, and at their own expense. All study patients had sufficient drug compliance. Neither therapy resulted in any notable side effects. The detailed annual data of H. pylori eradication rate in each therapy are shown in Table 1 and the annual eradication rates are shown in Figure 1. There were no notable tendencies in annual eradication rates for each therapy.
| Year | No. (Male/Female) | H.pylori eradiation (success/total number) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPI/AC (primary) | PPI/AM (secondary) | PPI/AM (primary) | ||
| 2008 | 27 (12/15) | 19/25 | 6/6 | 2/2 |
| 2009 | 25 (13/12) | 16/22 | 6/6 | 3/3 |
| 2010 | 32 (20/12) | 26/30 | 4/4 | 2/2 |
| 2011 | 36 (17/19) | 12/15 | 3/3 | 20/21 |
| Total | 120 (62/58) | 73/92 (79.3%) | 19/19 (100%) | 27/28 (96.4%) |
Table 1: Annual data of H. pylori eradication rates
Primary analysis
Of the 92 patients who underwent PPI/AC therapy for primary eradication, 73 showed successful eradication (79.3%); of the 28 patients who underwent PPI/AM therapy, 27 patients showed successful eradication (96.4%). PPI/AM therapy showed a significantly higher primary eradication rate compared to PPI/AC therapy (27/28 vs. 73/92: P=0.034) (Figure 2).
Secondary analysis
All 19 patients who initially underwent PPI/AC therapy but failed to achieve eradication later underwent secondary eradication after PPI/AM therapy and showed successful eradication (100%). Ultimately, 99.2% (119/120) of patients infected with H. pylori were successfully eradicated by primary and secondary eradication therapy. The successful eradication rate of total primary and secondary PPI/AM therapy was also significantly higher than primary PPI/AC therapy (46/47 vs. 73/92: P=0.007) (Figure 2).
Discussion
PPI/AM therapy, which showed a favorable H. pylori eradication rate, was much more effective than PPI/AC therapy in Katori City, Chiba Prefecture, Japan. In total, H. pylori was eradicated with PPI/AM therapy in 99% of infected patients. By contrast, PPI/AC therapy failed to eradicate H. pylori infection in 21% of patients in the study. Recently, an increase in PPI/AC therapy resistant patients with H. pylori infection has been reported in large cities in Japan [2,6,7]. The reports show failure to eradicate H. pylori infection in about 30% of patients by primary PPI/AC therapy, due to the recent increase in CAM-resistant H. pylori. Because H. pylori eradication therapy has commonly been performed in recent years in Katori City, the eradication success rate of PPI/AC therapy in Katori City has been higher than such large cities. Nevertheless, PPI/AC therapy for H. pylori eradication has been shown to be inferior to PPI/AM therapy.
The use of H. pylori eradication therapy has been indicated under Japanese national health insurance since 2000, and the resistance rate to CAM has been rising every year. This resistance has resulted in a decline in the success rate of primary eradication. The five-year trend in CAM resistance rates since 2002 has been shown by the Japanese Society for Helicobacter Research [2]. The CAM resistance rate, which was less than 10% in the 2000 national aggregate as reported by the Japanese Society of Chemotherapy, rose to 29% in 2005, with CAM resistance continuously increasing [6]. Possible factors influencing this decline include the recent increase in the administration of macrolides for the treatment of community-acquired infections such as mycoplasma pneumonia. The likelihood of a future decrease in the use of macrolides is low, and there may even be an increase in the eradication resistance rate of H. pylori to CAM. In CAM-resistant bacterial infection cases, eradication therapy that includes CAM has also seen a marked drop in eradication rates [8], and it has been reported that CAM resistance develops easily in cases of failed eradication [9,10]. Studies have also shown that CAM resistance rates increase with age [11], and thus, early, reliable eradication is essential. However, to date, most primary eradication therapies for patients with H. pylori used PPI/AC in Japan, because other primary eradication therapies were not available under Japanese national health insurance. Therefore, there are remarkably few studies comparing primary eradication PPI/AC therapy with other primary eradication therapies in Japan.
With the acquired resistance to CAM, a national health insurance indication for a three-drug combination PPI/AM therapy was established in August 2007 by using MNZ instead of CAM as a secondary eradication regimen for H. pylori. The results showed a highly favorable eradication rate when using PPI/AM therapy, although MNZ remains indicated for secondary eradication under national health insurance, and three-drug combination therapy using MNZ as primary treatment is at the patient’s own expense. PPI/AM therapy cannot be used as the primary eradication regimen under national health insurance because of the need for 5 years of market research after approval for public application; the fear of increase in resistant bacteria is due to the increased use of MNZ and the lack of data on primary eradication using PPI/AM therapy.
The frequency of MNZ prescription in daily clinical practice in Japan is low compared to macrolides or new quinolone preparations. Furthermore, MNZ has been shown to be 96.8% effective on susceptible strains (61/63) and 81.8% on resistant strains (18/22), and although a significant difference was noted between the 2 types of strains, even MNZ-resistant bacteria exhibited an eradication rate of 80% or higher. The primary eradication rate of resistant bacteria by using MNZ in Japan was between 2 and 5%, and the minimum inhibitory concentration of MNZ showed no major change over the past few years, and thus, it has the potential for high eradication rates in the future as well. Moreover, although PPI/AC therapy shows a significant difference in resistance rates depending on age, studies have shown that PPI/AM therapy does not show this discrepancy. Recent studies have also described the use of a four-drug combination therapy using levofloxacin [12,13], as well as a three-drug combination therapy using ecabet sodium [14]. Although these drug combinations show markedly high eradication rates compared to PPI/AC therapy, the results have not been compared to PPI/AM therapy, and are currently regarded as a potential option for tertiary eradication. PPI + AMPC + CAM + MNZ therapy has also been reported [15], but is not expected to have a high eradication rate based on the development of resistance to CAM in Japan.
This study clearly showed the superiority of PPI/AM therapy for H. pylori eradication compared with PPI/AC therapy. Study patients were given different eradication therapy depending on whether they suffered from gastroduodenal ulcer or not. However, secondary PPI/AM therapy had a very high H. pylori eradication success rate for patients who failed H. pylori eradication by primary PPI/AC therapy. Thus, the facts suggest the use of PPI/AM therapy as a primary eradication regimen that has the potential of achieving high eradication rates. However, the study has several shortcomings: 1) it was retrospective; 2) the number of subjects was different in the two groups; 3) primary eradication therapies differed whether patients suffered from gastroduodenal ulcer or not; 4) patients with only H. pylori associated gastritis, who did not wish to receive eradication therapy at their own expense, were not treated; 5) re-infection with H. Pylori was not considered in patients who had negative 13C-urea breath test 8 weeks after therapy; 6) the study did not investigate drug susceptibility to CAM and MNZ; 7) the study was performed at locally in Japan. Further studies are required to address these points.
In conclusion, although PPI/AM therapy for H. pylori eradication is currently used in Japan as a primary off-label regimen, it has achieved a much higher eradication rate than PPI/AC therapy, and should be recommended as the primary treatment for patients with H. pylori infection.
References
- Asaka M, Satoh K, Sugano K, Sugiyama T, Takahashi S, et al. (2001) Guidelines in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan. Helicobacter 6: 177-186.
- Sasaki M, Ogasawara N, Utsumi K, Kawamura N, Kamiya T, et al. (2010) Changes in 12-Year First-Line Eradication Rate of Helicobacter pylori Based on Triple Therapy with Proton Pump Inhibitor, Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin. J ClinBiochemNutr 47: 53-58.
- Asaka M, Kato M, Takahashi S, Fukuda Y, Sugiyama T, et al. (2010) Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: 2009 revised edition. Helicobacter 15: 1-20.
- Murakami K, Sato R, Okimoto T, Nasu M, Fujioka T, et al. (2003) Efficacy of triple therapy comprising rabeprazole, amoxicillin and metronidazole for second-line Helicobacter pylori eradication in Japan, and the influence of metronidazole resistance. Aliment PharmacolTher 17: 119-123.
- Isomoto H, Inoue K, Furusu H, Enjyoji A, Fujimoto C, et al. (2003) High-dose rabeprazole-amoxicillin versus rabeprazole-amoxicillin-metronidazole as second-line treatment after failure of the Japanese standard regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment PharmacolTher 18: 101-107.
- Suzuki H, Nishizawa T, Hibi T (2010) Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Future Microbiol 5: 639-648.
- Japanese Society of Chemotherapy (2000) Antimicrobial Susceptibility Subcommittee on Helicobacter pylori MIC breakpoints for clarithromycin and Amoxicillin. J JpnSoc Chemo Ther 48: 561-567.
- Murakami K, Fujioka T, Okimoto T, Sato R, Kodama M, et al. (2002) Drug combinations with amoxycillin reduce selection of clarithromycin resistance during Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Int J Antimicrob Agents 19: 67-70.
- Murakami T, Fujioka T. (1998) Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy and drug resistance in Japan. Helicobacter Res 2:423-428.
- Wurzer H, Rodrigo L, Stamler D, Archambault A, Rokkas T, et al. (1997) Short-course therapy with amoxicillin-clarithromycin triple therapy for 10 days (ACT-10) eradicates Helicobacter pylori and heals duodenal ulcer. Aliment PharmacolTher 11:934-952.
- Sugano H, Tokunaga K, Tanaka A, Takahashi Si (2010) [Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy for gastric ulcer in elderly]. Nihon Rinsho 68: 2052-2056.
- Basu PP, Rayapudi K, Pacana T, Shah NJ, Krishnaswamy N, et al. (2011) A randomized study comparing levofloxacin, omeprazole, nitazoxanide, and doxycycline versus triple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol 106:1970-1975.
- Gisbert JP, Morena F (2006) Systematic review and meta-analysis: levofloxacin-based rescue regimens after Helicobacter pylori treatment failure. Aliment PharmacolTher 23: 35-44.
- Furuta T, Kato M, Sugimoto M, Sasaki M, Kamoshida T, et al. (2011) Triple therapy with ecabet sodium, amoxicillin and lansoprazole for 2 weeks as the rescue regimen for H. pylori infection. Intern Med 50: 369-374.
- Greenberg ER, Anderson GL, Morgan DR, Torres J, Chey WD, et al. (2011) 14-day triple, 5-day concomitant, and 10-day sequential therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection in seven Latin American sites: a randomised trial. Lancet 378: 507-514
Relevant Topics
- Constipation
- Digestive Enzymes
- Endoscopy
- Epigastric Pain
- Gall Bladder
- Gastric Cancer
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Gastrointestinal Hormones
- Gastrointestinal Infections
- Gastrointestinal Inflammation
- Gastrointestinal Pathology
- Gastrointestinal Pharmacology
- Gastrointestinal Radiology
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis
- GIST Sarcoma
- Intestinal Blockage
- Pancreas
- Salivary Glands
- Stomach Bloating
- Stomach Cramps
- Stomach Disorders
- Stomach Ulcer
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 14831
- [From(publication date):
November-2014 - Jul 16, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 10211
- PDF downloads : 4620