The Effect of Oral Supplementation of Vitamin D3 on Serum Levels of Vitamin D: A Review
Received: 29-Dec-2013 / Accepted Date: 10-Feb-2014 / Published Date: 12-Feb-2014 DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000148
Abstract
Due to the strong interest in the role of vitamin D in health, we tried to find data to illustrate the relationship between oral supplementation and change in serum levels of vitamin D. We reviewed the literature of randomized, placebo-controlled trials of oral supplementation and serum levels of vitamin D through 2014. We found 25 informative studies which showed a significant dose-response between oral supplementation and serum levels of vitamin D with an r2 of 0.61.These data are consistent with single studies and meta-analyses.In conclusion, the data show a consistent relationship that appears to be independent of multiple confounders.
Keywords: Ultraviolet radiation; Cholecalciferol; Serum levels
161259Introduction
Recently there has been a resurgence of interest in the role of vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol, supplementation in disease prevention and health maintenance. Systematic reviews have recently been published with a focus on specific groups, such as those over 50 [1] or by body mass index [2]. Studies have been carried out on serum vitamin D levels to evaluate the role of supplementation on risk for multiple health conditions, ranging from bone health to cancer.
However, the benefits and risks of cholecalciferol supplementation are under debate after the publication of a 2010 Institute of Medicine Report that recommended supplementary and dietary reference levels for Vitamin D [3]. From an epidemiological perspective, cholecalciferol is unique, as it can be obtained not only through food and supplementation, but also from ultraviolet radiation, specifically UVB (280-320 nm) [4]. Thus, some groups have suggested that people increase time in the sun and forgo sunscreen in an effort to increase their serum 25-(OH)D levels [5]. However, because over exposure to UVB rays can also lead to an increase in skin cancer incidence, the health effects associated with UV exposure may be problematic.
Oral supplementation of Vitamin D3 may be a safe alternative to UVB and should be easy to regulate to achieve optimum dosage [6]. Unfortunately, outside of single studies, there is little research that evaluates the dose-response relationship between oral intake of cholecalciferol and subsequent serum levels of vitamin D.Because of this knowledge gap, we conducted a literature review to gain perspective on current knowledge about the dose-response of serum vitamin D with supplementation.
Methods
We reviewed studies identified through a combination of personal archives and the National Library of Medicine database PubMed using the search terms “vitamin D supplementation,” “vitamin D serum” “randomized trials of vitamin D” and “25-(OH)D.” The earliest eligible study available was from 1991 and the most recent was from 2013. Studies were excluded for incomplete, or inaccessible data, leaving 36 studies that were included in this review. Of these 36 studies, 25 were analyzed (Table 1) and evaluated through graphical analysis (Figure 1), and 11 were listed separately (Table 2) because of irregular dose patterns, such as a one-time bolus intervention.
| Study Number and Author | Location | Subjects [number, age, and sex] | Length of Study | Amount of Supplemental Vitamin D Given | Serum levels – Baseline and After [nmol/L] | Change in serum level [nmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biancuzzo RM et al. [7] | Boston, Massachusetts | 34 healthy adults, 18-79 | 11 weeks | 1000 IU/D | Baseline: 53.2 After: 83.9 |
30.7 |
| Al-Shaar L et al. [8] | Lebanon | 336 healthy adolescents | 1 year | 200 IU/D 2000 IU/D |
200 Baseline: 37.4 200 After: 46.4 2000 Baseline: 37.4 2000 After: 90.6 |
200: 8.9 2000: 53.2 |
| Ng K et al. [9] | Boston, Massachusetts | 328 African American, 30-80 years old | 3 months | 1000 IU/D 2000 IU/D 4000 IU/D |
1000 Baseline: 40.4 1000 After: 74.1 2000 Baseline: 34.7 2000 After: 86.9 4000 Baseline: 39.2 4000 After: 114.6 |
1000: 26.9 2000: 48.2 4000: 75.6 |
| Ala-Houhala MJet al. [10] | Tampere, Finland | 33 healthy hospital employees | 4 weeks | 800 IU/D | Baseline: 53.5 After: 73.7 |
20.2 |
| Holmlund-Suila Eet al. [11] |
Helsinki, Finland | 113 healthy newborn infants from a single hospital | 10 Weeks | 400, 1200. Or 1600 IU/D | 400 Baseline: 53 400 After: 88 1200 Baseline: 53 1200 After: 124 1600 Baseline: 53 1600 After: 153 |
400: 35 1200: 71 1600: 100 |
| Gepner A Det al. [12] | Madison, Wisconsin | 114 healthy post-menopausal women mean age 63.9, | 4 Months | 2500 IU/D | Baseline: 78.1 After: 117.3 |
39.2 |
| Holvik Ket al. [13] | Oslo, Norway | 55 subjects. Healthy adults], average age 28 years, 63.6% women] | 4 weeks | 400 IU/D | Baseline: 44.3 After: 78.4 |
34.1 |
| Toss Get al. [14] | Linköping, Sweden | 45 subjects of which 32 were female, aged 55-84 | 1 Year | 1600 IU/D | Baseline: 50.4 After: 84.2 |
33.8 |
| Dong Yet al. [15] | Augusta, Georgia | 49 Normotensive African American boys and girls, mean age 16.3 | 16 Weeks | 400 IU/D or 2000 IU/D | 400 Baseline: 34 400 After: 59.8 2000 Baseline: 33.1 2000 After: 85.7 |
400: 25.8 2000: 52.6 |
| Pfeifer Met al. [16] | Bad Prymont, Germany Graz, Austria |
114 healthy men and women, 70+ years | 1 year | 400 IU/D | Baseline: 55 After: 84 |
29 |
| Holick M Fet al. [17] | Boston, Massachusetts | 68 healthy, different racial/ethnic groups, 18-84 years old | 11 weeks | 1000 IU/D | Baseline: 48.9 After: 72.1 |
23.2 |
| Heany R Pet al. [18] | Omaha, Nebraska | 67 healthy men, average age 38.7 | 20 weeks | 1,000, 5,000 or 10,000 IU/D | 1000 baseline: 72.1 1000 after: 84.1 5,000 Baseline: 69.3 5,00 After: 161.2 10,000 Baseline: 65.6 10,000 After: 225.0 |
1000: 12 5,000: 91.9 10,000: 159.4 |
| Trang H Met al. [19] | Toronto, Canada | 72 subjects, mean age 38 | 14 days | 4000 IU/D | Baseline: 41.3 After: 64.6 |
23.3 |
| Lips Pet al. [20] | Amsterdam, Netherlands | 2578 people, including 1916 women and 662 men, mean age 80, with no major health problems | 3.5 years | 4000 IU/D | Baseline: 23 After: 60 |
37 |
| Chapuy MCet al. [21] | Lyon, France | 142 Healthy, ambulatory women aged 84 ± 6 years | 18 months | 800 IU/D | Baseline: 39.9 After: 104.8 |
64.9 |
| Dawson-Hughes Bet al. [22] | Massachusetts | 333 healthy, postmenopausal women, mean age 61.4 | 1 year | 400 IU/D | Summer baseline: 81.6 Post summer: 97 Winter baseline: 60.6 Post winter: 92.1 |
Summer: 15.4 Winter: 31.5 |
| Gallagher JCet al. [23] | Omaha, Nebraska | 163 postmenopausal white females with vitamin D insufficiency, mean age 67, divided into 8 study groups of 20 or 21 participants | 1 year | 400, 800, 1600, 2400, 3200, 4000, or 4800 IU/D | 400 Baseline: 37.8 400 After: 60.9 800 Baseline: 39.0 800 After: 74.4 1600 Baseline: 37.4 1600 After: 87.9 2400 Baseline: 38.2 2400 After: 95.8 3200 Baseline: 39.8 3200 After: 101.3 4000 Baseline: 37.2 4000 After: 105.8 4800 Baseline: 38.6 4800 After: 109.3 |
400: 23.1 800: 35.4 1600: 50.5 2400: 57.6 3200: 61.5 4000: 68.6 4800: 70.7 |
| Bogh MKet al. [24] | Malmö, Sweden | 32 vitamin D deficient patients from a primary care center in Malmö, Sweden, mean age of 32 | 6 weeks | 1600 IU/D | Baseline: 23.3 After: 60.6 |
37.7 |
| Al-Daghri NMet al. [25] | Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia | 92 total, 58 women, median age 56.6 and 34 men, medial age 51.2. All had Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 |
18 Months | 2000 IU/D | Baseline: 32.2 After: 54.7 |
22.5 |
| Harris SSet al. [26] | Boston, Massachusetts | 89, Overweight or obese African Americans with prediabetes or diabetes | 12 Weeks | 4000 IU/D | Baseline: 40 After: 81 |
41 |
| Yiu Yet al. [27] | Hong Kong, China | 100 type 2 DM patients with 25[OH]D concentration <30 ng.mL | 12 weeks | 5000 IU/D | Baseline: 54.9 After: 152.4 |
97.5 |
| Pierrot- Deseilligny Cet al. [28] |
Paris, France | 156 Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients under first line immunomodulatory therapy and initial serum levels less than 100 nmol/L | 29.1 Months | 3010 IU/D | Baseline: 49 After: 110 |
61 |
| Garrett-Mayer Eet al. [29] | Columbia, South Carolina | 47 patients, 12 African American [mean age 63.2] and 35 White men [mean age 65.3] with early-stage low-risk prostate cancer | 1 year | 4000 IU/D | Caucasian Baseline: 91.6 Caucasian After: 167.9 African American Baseline: 53.4 African American After: 168.9 |
Caucasian: 76.3 African American: 115.5 |
| Bischoff-Ferrari HAet al. [30] | Zurich, Switzerland | 173 patients with previous hip fracture age > 65 [average age 84 years] 79% Women | 1 year | 800 IU/D or 2000 IU/D | 800 Baseline: 31.5 800 After: 92.0 2000 Baseline: 34.1 2000 After: 116.21 |
800: 60.6 2000: 82.2 |
| Suzuki Met al. [31] | Tokyo, Japan | 114 patients with Parkinson’s Disease, aged 45-85 | 1 year | 1200 IU/D | Baseline: 56.2 After: 104.1 |
47.9 |
Table 1: Randomized studies of daily vitamin D [IU/D] with change in serum level [nmol/L] over baseline.
| Study Number and Author | Location of Study | Subjects [number, age, and sex] | Length of Study | Amount of Supplemental Vitamin D Given | Serum levels- Baseline and After [nmol/L] | Change in serum level [nmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matias PJet al. [32] | Portugal | 158 Hemodialysis Patients | 6 months | 50,000 IU/week [25[OH]D<15 ng/mL] 10,000 IU/week [25[OH] 16-30 ng/mL] 2,700 IU/week [25[OH]D > 30ng/mL |
Baseline: 55.7 After: 104.8 |
49.1 |
| Goswami Ret al. [33] | New Delhi, India | 173 Healthy Asian Indian females with a mean age of 21.7 | 6 Months | 60,000 IU/ week | Baseline: 57.9 After: 186.2 |
128.3 |
| Alvarez JAet al. [34] | Atlanta, GA | 46 patients with stage 2 & 3 CKD 18-90 years | 12 months | 50,000 IU/week for 12 weeks 50,000 IU/ every other week for 40 weeks |
Baseline: 67.4 After: 116.6 |
49.2 |
| Markmann Pet al. [35] | Odense, Denmark | 52 Chronic Kidney Disease patients, male and female, mean age 71 | 8 Weeks | 40,000 IU/ week | Baseline: 23.8 After: 141.6 |
117.8 |
| Armas LAet al. [36] | Omaha, Nebraska | Patients with Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease | 15 Weeks | 10,333 IU/ week | Baseline: 33.2 After: 92.1 |
58.9 |
| Lips Pet al. [37] | Subjects came from Mexico Washington, Indiana, Nebraska, Netherlands, Germany, and, Canada | 226 men and women, mean age 78.5, who were vitamin D deficient | 16 Weeks | 8400 IU/ week | Baseline: 34.7 After: 65.4 |
30.7 |
| Tokmak Fet al. [38] | North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany | 64 haemodialysis patients | 9 months | 20,000 IU/ week | Baseline: 16.7 After: 79.5 |
62.8 |
| Jakopin Eet al. [39] | Slovenia | 101 Hemodialysis patients [52 men, 49 women] Average age 63.3 years | 24 months | 40,000 IU/month | Baseline: 28.6 After: 54.9 |
26.3 |
| Witham MCet al. [40] | Dundee, United Kingdom | 74 subjects with a history of myocardial infarction, average age 66 years | 6 months | 100,000 IU Bolus every two months | Baseline: 49 After: 62 |
13 |
| Grossman REet al. [41] | Atlanta, Georgia | 30 Adults in the hospital for Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbation, mean age 24.9, both male and female, all Caucasian | 12 Weeks | One time 250,000 IU Bolus | Baseline: 76.4 After: 91.6 |
15.2 |
| Tran Bet al. [42] | Australia | 615 population-based, 60-84 years old | 1 year | 30,000 IU/month 60,000 IU/month |
30,000 Baseline: 41.6 30,000 After: 63.9 60,000 Baseline: 41.7 60,000 After: 77.9 |
30,000: 22.3 60,000: 36.1 |
Table 2: Randomized studies of vitamin D [IU] that gave weekly, monthly or bolus supplementation [nmol/L].
The studies we reviewed were chosen from available literature addressing vitamin D and met pre-determined criteria for involvement.These criteria included information as to the dose of oral supplementation of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) and serum levels of 25-(OH)D at baseline and post-intervention and included placebo groups for comparison (Tables 1 and 2). We found that many studies looked at the effect of vitamin D supplementation and dietary intake on disease outcome. Sixteen studies meeting our criteria evaluated healthy individuals [7-22]. Nine studies meeting our criteria evaluated individuals with disease included individuals with vitamin D deficiency [23,24], individuals with diabetes [25-27], relapsing multiple sclerosis patients [28], individuals with early stage prostate cancer [29], patients with previous hip fractures [30], and Parkinson Disease [31]. The number of studies that included the necessary information on serum levels pre- and post-supplementation were limited, and only a few addressed serum vitamin D levels exclusively in response to oral supplementation.
Although we wished to perform a meta-analysis, we found that the data were too heterogeneous for valid statistical evaluation. Some of the factors that contributed to the heterogeneity included varying geographical latitude, age, pre-existing medical conditions, dose size, and calcium supplementation, frequency of dose, follow-up time, and overall quality of the study. In addition, we found that several studies did not include crucial information, such as standard deviation or baseline levels, because vitamin D was not the primary focus of their research. Studies that were not placebo-controlled, randomized, or had an inadequate sample size (i.e., fewer than 20) were eliminated from our main analysis. It should be noted that seven of the studies gave weekly doses of cholecalciferol (Table 2) while three others administered onetime only bolus doses. These two groups were evaluated separately and not included in the daily dose results.
In order to determine the change in serum vitamin D per amount of oral supplementation, we subtracted the baseline serum level from the post-intervention serum level and correlated that with the amount of oral vitamin D given. This information was calculated by linear regression using change from baseline serum vitamin D and with duration included as both a quadratic and linear term using SAS 9.3 (Carr, NC).
Results
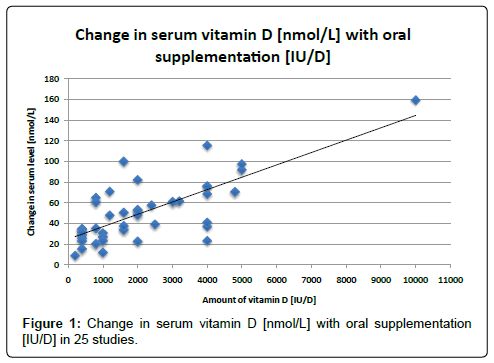
Analyses of the best available data show a clear trend. Figure 1, which shows the data from the twenty most reliable and homogeneous studies [7-26], exhibits a positive correlation between amounts of oral vitamin D administered and change in serum vitamin D levels. Figure 1 shows the change in vitamin D serum levels from the most rigorous studies that gave daily doses of cholecalciferol. These values are highly significantly correlated with a P-value<0.001 and an r2 of 0.61. We did not analyze the data from Table 2 statistically because the data were too few for meaningful analysis.
Discussion
These results demonstrate the overall coherence of the more generalizable studies, all of which were double blind and had an adequate sample size. Interestingly, our simple model is quite robust. There is a relatively strong dose-response between the amount of supplement and the change in serum vitamin D status.Surprisingly, results did not change significantly when we restricted them to studies of healthy individuals or to studies with intervention of 6 months or more. From the large scatter noted in Figure 1, it is clear that a great deal more information needs to be evaluated regarding the appropriate dose if vitamin D3 to raise serum vitamin D to a specific level. In addition, there is a clear need for additional placebo-controlled, double-blind studies to be conducted on the effects of serum 25-(OH)D levels in response to oral supplementation. One of the main limitations to our research was the fact that there are actually few randomized studies of cholecalciferol supplementation. To be useful for study of the effect of cholecalciferol on health and disease outcomes as well as clinical utility, it is important to know how different doses of vitamin D change serum vitamin D. Thus more studies need to be conducted on the oral supplementation of cholecalciferol before the scientific community can understand the importance of vitamin D supplementation to health.
Limitations include the heterogeneous nature of the studies and the fact that our analysis did not take into account the climate zone in which a person lives, or the role of age, body mass index, activity and diet in determining serum levels of vitamin D. In addition, the linear regression and slope determined using Figure 1, do not account for the “plateau” of serum vitamin D levels at high concentrations (e.g., 23). However, as a beginning, our study provides a baseline from which develop a more precise evaluation. This is especially important in light of the aging US population, the recent increase in interest in the role of vitamin D in disease prevention and the urgent need to carefully understand the role of vitamin D in health-whether it is a symptom of poor health or a means to better health.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health (K05 CA131675 to M.B).
References
- Autier P, Gandini S, Mullie P (2012) A systematic review: influence of vitamin D supplementation on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97: 2606-2613.
- Zittermann A, Ernst JB, Gummert JF, Börgermann J (2013) Vitamin D supplementation, body weight and human serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D response: a systematic review. Eur J Nutr .
- IOM (Institute of Medicine) (2011) Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC.
- McDonnell SL, French CB, Heaney RP (2013) Quantifying the non-food sources of basal vitamin D input. J Steoid Biochem Mol Biol.
- Lagunova Z, Porojnicu AC, Aksnes L, Holick MF, Iani V, et al. (2013) Effect of vitamin D supplementation and ultraviolet B exposure on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in healthy volunteers: a randomized, crossover clinical trial. Br J Dermatol 169: 434-440.
- Ashwell M, Stone EM, Stolte H, Cashman KD, Macdonald H, et al. (2010) UK Food Standards Agency Workshop Report: an investigation of the relative contributions of diet and sunlight to vitamin D status. Br J Nutr 104: 603-611.
- Biancuzzo RM, Clarke N, Reitz RE, Travison TG, Holick MF (2013) Serum concentrations of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in response to vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 supplementation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98: 973-979.
- Al-Shaar L, Mneimneh R, Nabulsi M, Maalouf J, Fuleihan GE (2013) Vitamin D3 dose requirement to raise 25-hydroxyvitamin D to desirable levels in adolescents: Results from a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res.
- Ng K, Scott JB, Drake BF, Chan AT, Hollis BW, et al. (2013) Dose response to vitamin D supplementation in African Americans: results of a 4-arm, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am J ClinNutr .
- Ala-Houhala MJ, Vähävihu K, Hasan T, Kautiainen H, Ylianttila L, et al. (2012) Comparison of narrowband ultraviolet B exposure and oral vitamin D substitution on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration. Br J Dermatol 167: 160-164.
- Holmlund-Suila E, Viljakainen H, Hytinantti T, Lamberg-Allardt C, Andersson S, et al. (2012) High-dose vitamin d intervention in infants--effects on vitamin d status, calcium homeostasis, and bone strength. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97: 4139-4147.
- Gepner AD, Ramamurthy R, Krueger DC, Korcarz CE, Binkley N, et al. (2012) A prospective randomized controlled trial of the effects of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular disease risk. PLoS One 7: e36617.
- Holvik K, Madar AA, Meyer HE, Lofthus CM, Stene LC (2012) Changes in the vitamin D endocrine system and bone turnover after oral vitamin D3 supplementation in healthy adults: results of a randomised trial. BMC Endocr Disord 12: 7.
- Toss G, Magnusson P (2012) Is a daily supplementation with 40 microgram vitamin D3 sufficient? A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Nutr 51: 939-945.
- Dong Y, Stallmann-Jorgensen IS, Pollock NK, Harris RA, Keeton D, et al. (2010) A 16-week randomized clinical trial of 2000 international units daily vitamin D3 supplementation in black youth: 25-hydroxyvitamin D, adiposity, and arterial stiffness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95: 4584-4591.
- Pfeifer M, Begerow B, Minne HW, Suppan K, Fahrleitner-Pammer A, et al. (2009) Effects of a long-term vitamin D and calcium supplementation on falls and parameters of muscle function in community-dwelling older individuals. Osteoporos Int 20: 315-322.
- Holick MF, Biancuzzo RM, Chen TC, Klein EK, Young A, et al. (2008) Vitamin D2 is as effective as vitamin D3 in maintaining circulating concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 677-681.
- Heaney RP, Davies KM, Chen TC, Holick MF, Barger-Lux MJ (2003) Human serum 25-hydroxycholecalciferol response to extended oral dosing with cholecalciferol. Am J Clin Nutr 77: 204-210.
- Trang HM, Cole DE, Rubin LA, Pierratos A, Siu S, et al. (1998) Evidence that vitamin D3 increases serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D more efficiently than does vitamin D2. Am J ClinNutr 68: 854-858.
- Lips P, Graafmans WC, Ooms ME, Bezemer PD, Bouter LM (1996) Vitamin D supplementation and fracture incidence in elderly persons. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 124: 400-406.
- Chapuy MC, Arlot ME, Duboeuf F, Brun J, Crouzet B, et al. (1992) Vitamin D3 and calcium to prevent hip fractures in the elderly women. N Engl J Med 327: 1637-1642.
- Dawson-Hughes B, Dallal GE, Krall EA, Harris S, Sokoll LJ, et al. (1991) Effect of vitamin D supplementation on wintertime and overall bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women. Ann Intern Med 115: 505-512.
- Gallagher JC, Sai A, Templin T 2nd, Smith L (2012) Dose response to vitamin D supplementation in postmenopausal women: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 156: 425-437.
- Bogh MK, Gullstrand J, Svensson A, Ljunggren B, Dorkhan M (2012) Narrowband ultraviolet B three times per week is more effective in treating vitamin D deficiency than 1600 IU oral vitamin D₃ per day: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol 167: 625-630.
- Al-Daghri NM, Alkharfy KM, Al-Othman A, El-Kholie E, Moharram O, et al. (2012) Vitamin D supplementation as an adjuvant therapy for patients with T2DM: an 18-month prospective interventional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11: 85.
- Harris SS, Pittas AG, Palermo NJ (2012) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation to improve glycaemia in overweight and obese African Americans. Diabetes ObesMetab 14: 789-794.
- Yiu YF, Yiu KH, Siu CW, Chan YH, Li SW, et al. (2013) Randomized controlled trial of vitamin D supplement on endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 227: 140-146.
- Pierrot-Deseilligny C, Rivaud-Péchoux S, Clerson P, de Paz R, Souberbielle JC (2012) Relationship between 25-OH-D serum level and relapse rate in multiple sclerosis patients before and after vitamin D supplementation. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 5: 187-198.
- Garrett-Mayer E, Wagner CL, Hollis BW, Kindy MS, Gattoni-Celli S (2012) Vitamin D3 supplementation (4000 IU/d for 1 y) eliminates differences in circulating 25-Hydorxyvitamin D between African American and white men. Am J Clin Nutr 96:332-336.
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dawson-Hughes B, Platz A, Orav EJ, Stähelin HB, et al. (2010) Effect of high-dosage cholecalciferol and extended physiotherapy on complications after hip fracture: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med 170: 813-820.
- Suzuki M, Yoshioka M, Hashimoto M, Murakami M, Noya M, et al. (2013) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation in Parkinson disease. Am J Clin Nutr 97: 1004-1013.
- Matias PJ, Jorge C, Ferreira C, Borges M, Aires I, et al. (2010) Cholecalciferol supplementation in hemodialysis patients: effects on mineral metabolism, inflammation, and cardiac dimension parameters. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:905-911.
- Goswami R, Vatsa M, Sreenivas V, Singh U, Gupta N, et al. (2012) Skeletal muscle strength in young Asian females after vitamin D and calcium supplementation: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:4709-4716.
- Alvarez JA, Zughaier SM, Law J, Hao L, Wasse H, et al. (2013) Effects of high-dose cholecalciferol on serum markers of inflammation and immunity in patients with early chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Nutr 67: 264-269.
- Marckmann P, Agerskov H, Thineshkumar S, Bladbjerg EM, Sidelmann JJ, et al. (2012) Randomized controlled trial of cholecalciferol supplementation in chronic kidney disease patients with hypovitaminosis D. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27: 3523-3531.
- Armas LA, Andukuri R, Barger-Lux J, Heaney RP, Lund R (2012) 25-Hydroxyvitamin D response to cholecalciferol supplementation in hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 1428-1434.
- Lips P, Binkley N, Pfeifer M, Recker R, Samanta S, et al. (2010) Once-weekly dose of 8400 IU vitamin D(3) compared with placebo: effects on neuromuscular function and tolerability in older adults with vitamin D insufficiency. Am J Clin Nutr 91: 985-991.
- Tokmak F, Quack I, Schieren G, Sellin L, Rattensperger D, et al. (2008) High-dose cholecalciferol to correct vitamin D deficiency in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 4016-4020.
- Jakopin E, PecovnikBalon B, Ekart R, Gorenjak M (2011) High-dose cholecalciferol supplementation for vitamin D deficiency in haemodialysis patients. J Int Med Res 39: 1099-1106.
- Witham MD, Dove FJ, Khan F, Lang CC, Belch JJ, et al. (2013) Effects of Vitamin D supplementation on markers of vascular function after myocardial infarction--a randomised controlled trial. Int J Cardiol 167: 745-749.
- Grossmann RE, Zughaier SM, Kumari M, Seydafkan S, Lyles RH, et al. (2012) Pilot study of vitamin D supplementation in adults with cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbation: A randomized, controlled trial. Dermatoendocrinol 4: 191-197.
- Tran B, Armstrong BK, Carlin JB, Ebeling PR, English DR, et al. (2012) Recruitment and results of a pilot trial of vitamin D supplementation in the general population of Australia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97: 4473-4480.
Citation: Jarrett F, Ducasa GM, Buller DB, Berwick M (2014) The Effect of Oral Supplementation of Vitamin D3 on Serum Levels of Vitamin D: A Review. Epidemiol 4:148. DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000148
Copyright: © 2014 Jarrett F, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 17011
- [From(publication date): 4-2014 - Apr 03, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 12341
- PDF downloads: 4670