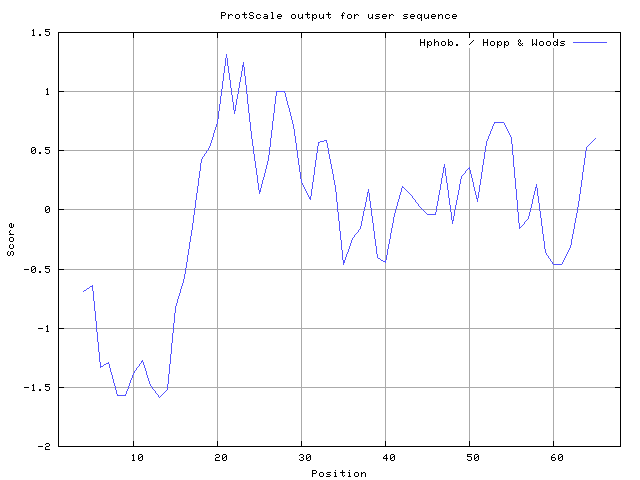
In this study, we found the antigenic determinants by finding the area of greatest local hydrophilicity. Hopp and Woods hydrophobicity scale is used to identify of potentially antigenic sites in proteins. Hydrophilicity Prediction result data found high in sequence position at 21-23, 27-28 in a protein this scale is basically a hydrophilic index where a polar residues have been assigned negative values. The Window size of 5-7 is good for finding hydrophilic regions, greater than 0 values are consider as hydrophilic which is consider as antigenic.
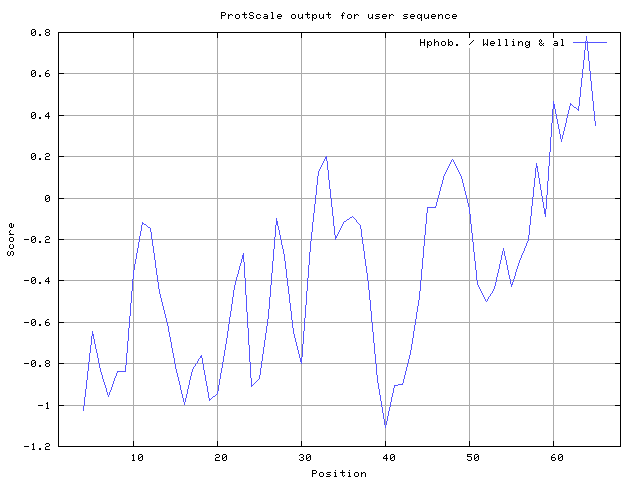
Welling used information on the relative occurrence of amino acids in antigenic regions to make a scale which is useful for prediction of antigenic regions and the predicted result data found high in sequence position 62-64. Welling antigenicity plot gives value as the log of the quotient between percentage in a sample of known antigenic regions and percentage in average proteins.
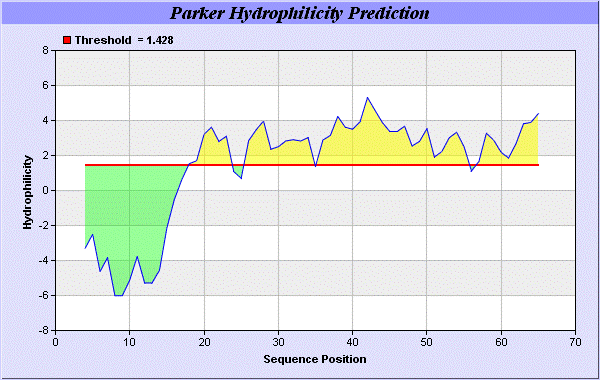
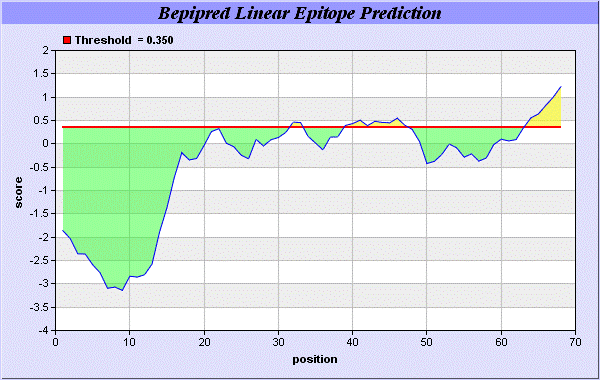
We also study Hydrophobicity plot of HPLC / Parker Hydrophilicity Prediction Result Data found 39-CNGCGDQ-45 (5.314), 61-TDDCNPH-67 (5.400), 60-STDDCNP-66 6.029 (maximum). BepiPred predicts the location of linear B-cell epitopes Result found that 32-FT-33, 39-CNGCGDQVA-47, and 64-EAQKG-68. There are 3 antigenic determinant sequences is found by Kolaskar and Tongaonkar [
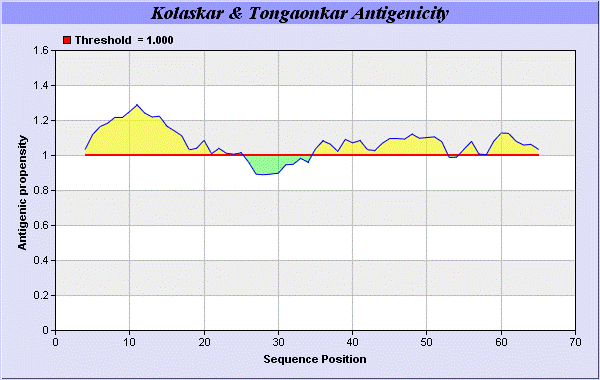
19] antigenicity scales the results show highest pick at position 4-QLMICLVLLPCFFCEPDEICRA-25, 35-KSNVCNGCGDQVAACEAE-52 (Figure 1-5).
Result of determined antigenic sites on proteins has revealed that the hydrophobic residues if they occur on the surface of a protein are more likely to be a part of antigenic sites. This method can predict antigenic determinants with about 75% accuracy and also gives the information of surface accessibility and flexibility. Further this region form beta sheet which show high antigenic response than helical region of this peptide and shows highly antigenicity.
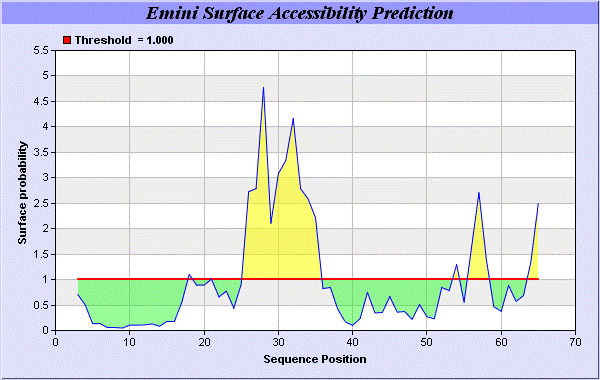
We predict Solvent accessibility by using Emani et al., the result found the highest probability i.e. found 26-RMTNKEFTYK-35, that a given protein region lies on the surface of a protein and are used to identify antigenic determinants on the surface of proteins [
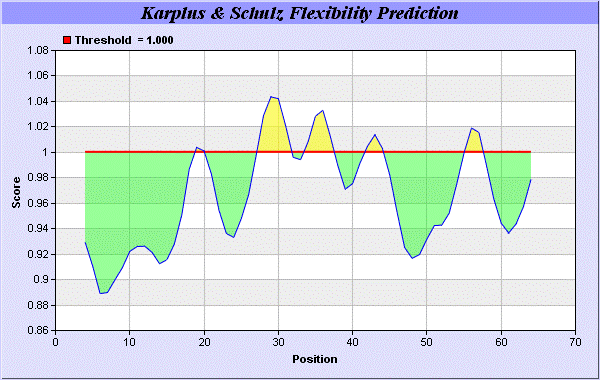
26]. This algorithm also used to identify the antigenic determinants on the surface of proteins and Karplus and Schulz [
27] predict backbone or chain flexibility on the basis of the known temperature B factors of the a-carbons here we found the result with High score is i.e. found 1.042 maximum in 26-RMTNKEF-32 (Figures 6 and 7). We predict Solvent accessibility of alpha-neurotoxins of ITX-3
Tegenaria agrestis for delineating hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics of amino acids. Solvent accessibility used to identify active site of functionally important residues in membrane proteins.
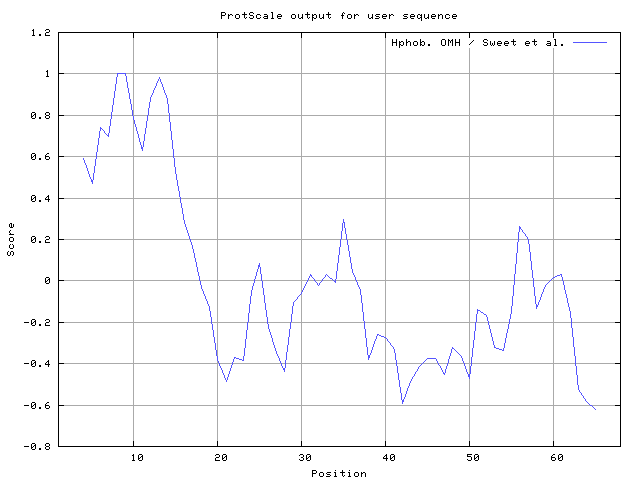
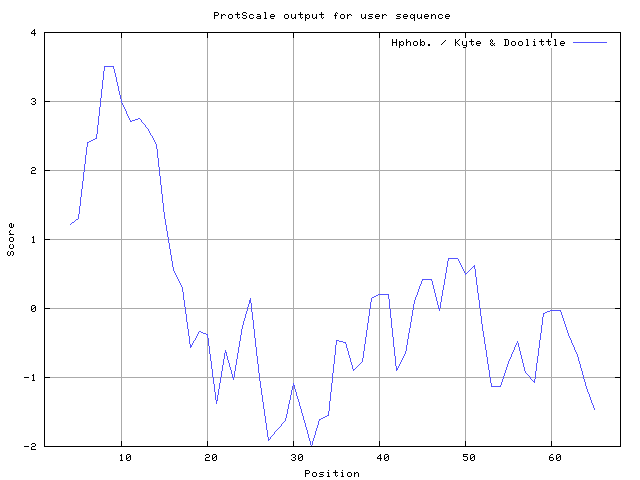
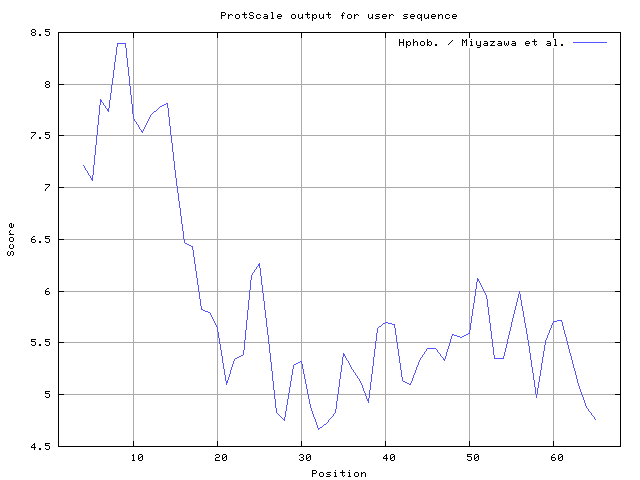
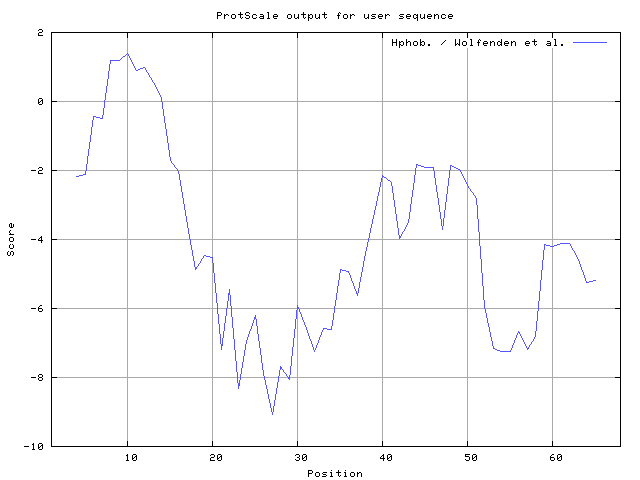
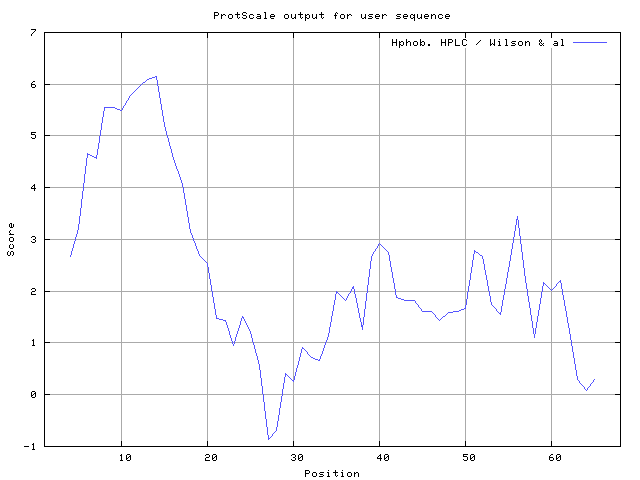
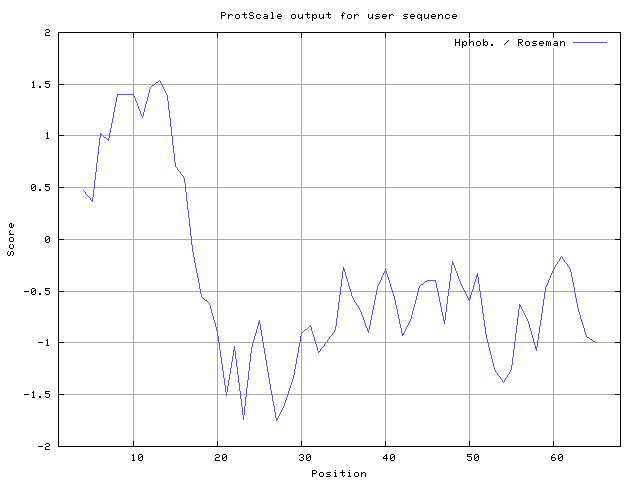
We also found the i.e. Sweet and Eisenberg [1983] hydrophobicity prediction result data found high in position 8-9, 12-14, Kyte and Doolittle [
29] result high in position 8-9, Abraham and Leo [
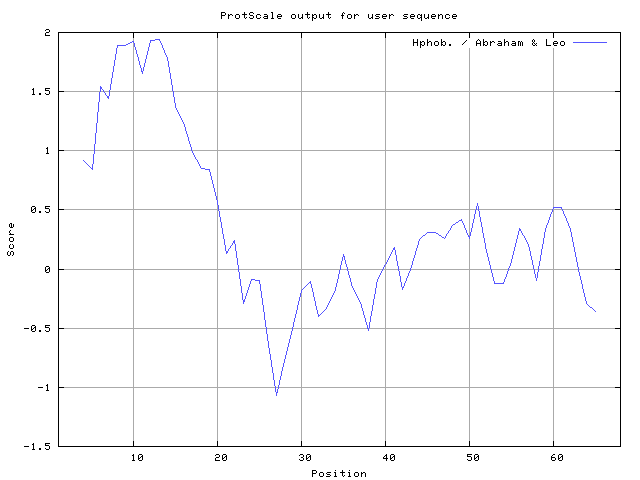
30] result high in position 8-10, 12-13, Bull and Breese [
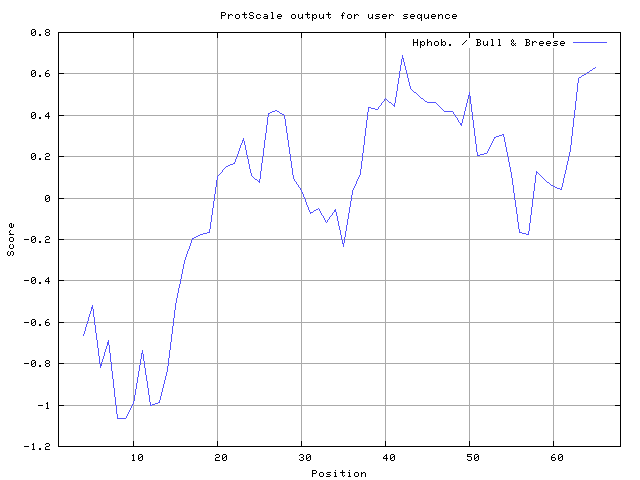
31] result high in position 41-43,63-65, Miyazawa and Jernigen [
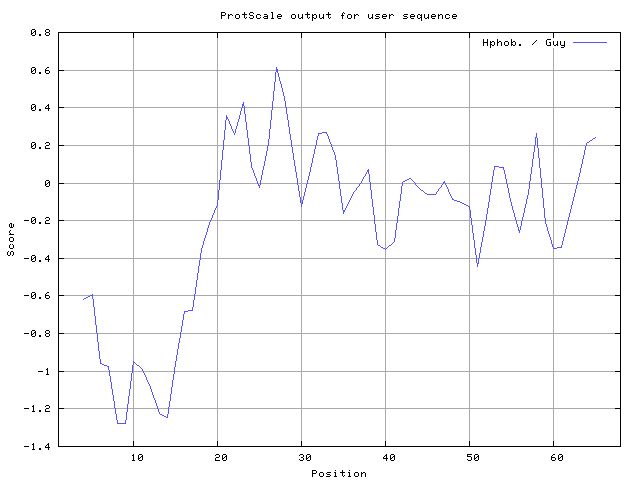
32] result high in position 8-9, Roseman [
33] result high in position 8-10,12-14, Wolfenden et al. [
34] result high in position 8-10,11-12, Wilson et al. [
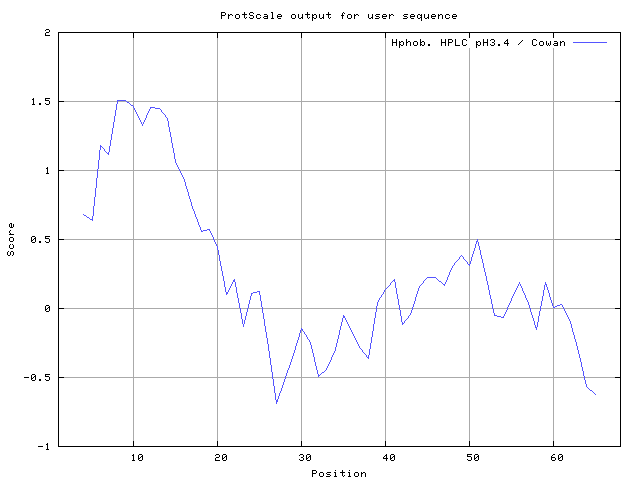
35] 8-12,13-15, Cowan and Whittaker [
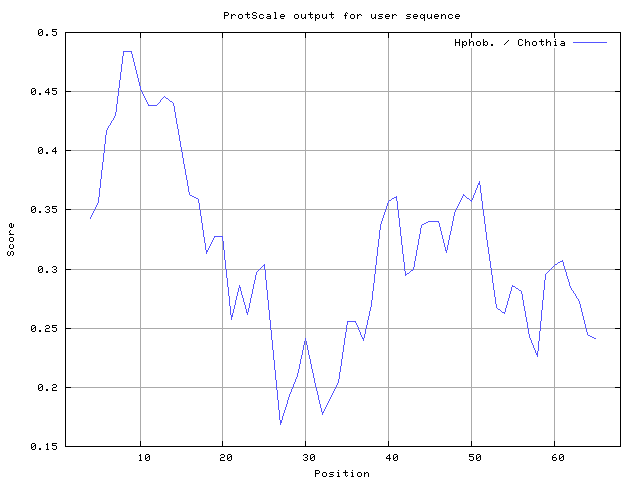
36] 6-7,8-10, Chothia [
37] 6-9,10-14 (Figures 8-18). These scales are a hydrophilic with a polar residues assigned negative value. Because the N- and C- terminal regions of proteins are usually solvent accessible and unstructured, antibodies against those regions recognize the antigenic protein.
Solvent-accessible surface areas and backbone angles are continuously varying because proteins can move freely in a three-dimensional space. The mobility of protein segments which are located on the surface of a protein due to an entropic energy potential and which seem to correlate well with known antigenic determinants.
In this study, we found predicted MHC-I peptide binders of toxin protein for 4 different alleles i.e. H2-Db (mouse) 8mer, H2-Db (mouse) 9mer, H2-Db (mouse) 10mer, H2-Db (mouse) 11mer (Table 1) and MHC-II peptide binders for I_Ab, I_Ad, I_Ag7 alleles highlighted in red represent predicted binders (Table 2). We also use a cascade SVM based TAPPred method which found 17 High affinity TAP Transporter peptide regions which represents predicted TAP binders residues which occur at N and C termini from ITX-3
Tegenaria agrestis. TAP is an important transporter that transports
antigenic peptides from cytosol to ER. TAP binds and translocate selective antigenic peptides for binding to specific MHC molecules. The efficiency of TAP-mediated translocation of antigenic peptides is directly proportional to its TAP binding affinity. Thus, by understanding the nature of peptides, that bind to TAP with high affinity, is important steps in endogenous antigen processing. The correlation coefficient of 0.88 was obtained by using jackknife validation test.
In this test, we found the MHCI and MHCII binding regions. T cell immune responses are derived by antigenic epitopes hence their identification is important for design synthetic peptide vaccine. T cell epitopes are recognized by MHCI molecules producing a strong defensive immune response against alpha-neurotoxins of ITX-3
Tegenaria agrestis. Therefore, the prediction of peptide binding to MHCI molecules by appropriate processing of antigen peptides occurs by their binding to the relevant MHC molecules. Because, the C-terminus of MHCI-restricted epitopes results from cleavage by the proteasome and thus, proteasome specificity is important for determining T-cell epitopes. Consequently, RANKPEP also focus on the prediction of conserved epitopes. C-terminus of MHCI-restricted peptides is generated by the proteasome, and thus RANKPEP also determines whether the C-terminus of the predicted MHCI-peptide binders is the result of proteasomal cleavage. Moreover, these sequences are highlighted in purple in the output results. Proteasomal cleavage predictions are carried out using three optional models obtained applying statistical language models to a set of known epitopes restricted by human MHCI molecules as indicated here.