Peptide Coupling Reactions
Received: 07-Feb-2015 / Accepted Date: 09-Feb-2015 / Published Date: 15-Feb-2015 DOI: 10.4172/2329-9053.1000e119
1662Peptide bond formation is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of an amino group (nucleophile) at a carboxyl group involving a tetrahedral intermediate. Furthermore, the peptide coupling reaction must be performed under mild conditions, and preferably at room temperature. Activation of the carboxyl component is achieved by the introduction of electron accepting moieties [1]. Carboxyl components can be activated as acyl halides, acyl azides, acylimidazoles, anhydrides, esters etc. There are different ways of coupling reactive carboxyl derivatives with an amine [2].
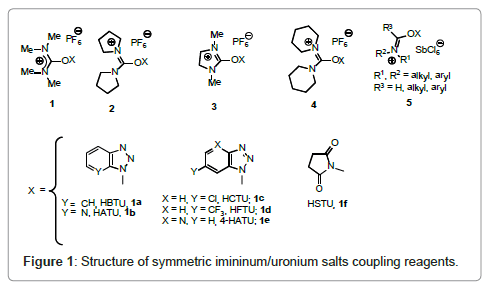
In recent years, peptide-coupling reactions have significantly advanced in accord with the development of new peptide-coupling reagents and their application to both solution and solid- phase synthesis [3,4]. The formerly techniques of carbodiimide is being replaced with iminium/uronium derivatives 1-5 [5-21] (Figure 1).
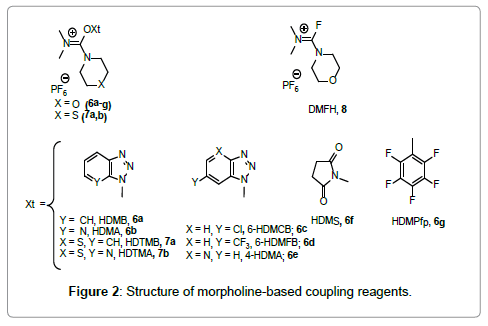
Later, El-Faham and Albericio [22] reported a new family of coupling reagents based on the modification of the structures of the carbocation skeleton moiety, which feature relatively high reactivity and low racemization during peptide bond formation [22]. Very recently, El-Faham and Albericio [23] extended their work taking an N-containing 6-membered ring structure containing O, S, and N-CH3 for synthesis of novel coupling reagents [24] (Figure 2).
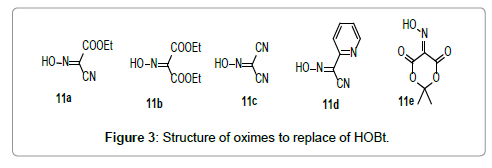
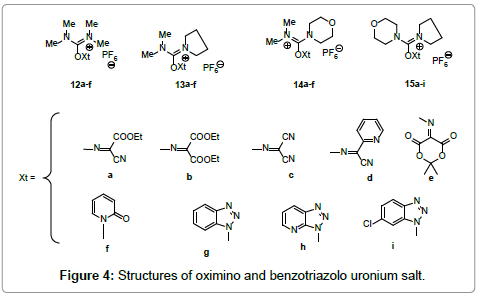
Recent reports confirmed the explosive properties of HOBt derivatives [25]. Accordingly, El-Faham and Albericio [25,26] reported the new additives as well as their uronium salts derivatives as replacement for HOBt and HOAt derivatives (Figures 3 and 4). Among these entire additives Oxyma [26] (Figure 3) and its uronium salt COMU (Figure 4) showed an excellent replacement for HOBt and its analogues [26,27].
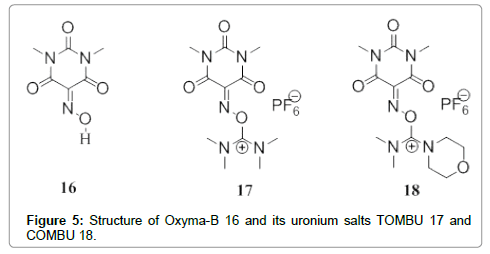
More recently, we have reported 5-(hydroxyimino)-1,3- dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6 (1H,3H,5H)-trione (Oxyma-B) as an excellent additive for the suppression of racemization during peptide synthesis [27]. Oxyma-B, has the same structure future for the carbonyl moiety in which the oxime group is flanked between the two carbonyl group as in HONM. In addition, Oxyma-B performs better as a racemization suppressor than Oxyma Pure and even better than HOAt in both stepwise and segment coupling in solid- and solution-phase peptide synthesis [28]. Lately,a new class of O-form uronium-type coupling reagents derived from Oxyma-B were introduced TOMBU and COMBU (Figure 5) [29].
References
- Montalbetti CAGN, Falque V (2005) Amide bond formation and peptidecoupling.Tetrahedron 61: 10827-10852.
- El-Faham A, Albericio F (2011) Peptide Coupling Reagents, More than a Letter Soup.Chem Rev 111: 6557-6602.
- Albericio F, Carpino LA (1997)Methods Enzymol: Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fields,Academic Press, Orlando 289: 104-126.
- Albericio F, Kates SA (2000) In Solid-Phase Synthesis,A Practical Guide, Marcel Dekker, New York 275-330
- Albericio F, Chinchilla R, Dodsworth D J, Najera C (2001)Â New Trends inPeptideCouplingReagents. Org Prep Proced Int 33: 203-303.
- Humphrey JM, Chamberlin AR (1997) Chemical Synthesis of Natural Product Peptides: Coupling Methods for the Incorporation of Noncoded Amino Acids into Peptides. Chem Rev 97: 2243-2266.
- Valeur E, Bradley M (2009) Amide bond formation: beyond the myth of couplingreagents. Chem Soc Rev 38: 606-631.
- König W, Geiger RA (1970) Newmethodfor the synthesis of peptides: activation of the carboxyl group with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 1-hydroxybenzotriazoles. Chem Ber 103: 788-798.
- Carpino LA (1993) 1-Hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole. An efficientpeptidecouplingadditive. J Am Chem Soc 115: 4397-4398.
- Knorr R, Trzeciak A, Bannwarth W, Gillessen D (1989) New coupling reagents in peptide chemistry.Tetrahedron Lett 30: 1927-1930.
- Abdelmoty I, Albericio F, Carpino LA, Forman BM, Kates SA (1994)Structuralstudies of reagentsforpeptide bond formation: Crystal and molecular structures of HBTU and HATU. Lett Pept Sci 1: 57-67.
- Dourtoglou V, Ziegler J C, Gross B (1978) O-Benzotriazolyl-N,N-tetramethyluroniumhexafluorophosphate: a new and effectivereagentforpeptidecoupling.Tetrahedron Lett: 1269-1272.
- Wijkmans JCHM, Blok FAA, Van der Marel GA, Van Boom JH, Bloemhoff W (1995)CF3-NO2-PyBOP: a new and highlyefficientcouplingreagentfor N-methyl amino acids. Tetrahedron Lett 36: 4643-4646.
- Carpino LA, El-Faham A, Albericio F (1995)Efficiency in PeptideCoupling: 1-Hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole vs 3, 4-Dihydro-3-hydroxy-4-oxo-1,2,3-benzotriazine.J Org Chem 60: 3561-3564.
- Klose J, El-Faham A,Henklein P, Carpino LA, Bienert, M (1999) Addtion of HOAtDramaticallyImprove the Effectiveness of Pentafluorophenyl-BasedCouplingReagents. Tetrahedron Lett 40: 2045-2048.
- Chen SQ, Xu JC (1992) A new coupling reagent for peptide synthesis. Benzotriazolvyloxy-bis (pyrroltdino)-carboniumhexaflouorophosphate (BBC). Tetrahedron Lett 33: 647-650.
- Carpino LA, El-FahamA (1994) Effect of Tertiary Bases on O-Benzotri- azolyluronium Salt-Induced Peptide Segment Coupling. J Org Chem 59: 695-698.
- Carpino LA, Xia J, El-Faham A (2004) 3-Hydroxy-4-oxo-3, 4-dihydro-5-azabenzo-1,2,3-triazene. J Org Chem 69: 54-61.
- Carpino LA, Henklein P, Foxman BM, Abdelmoty I, Costisella B, et al. (2001) The Solid and SolutionStructure of HAPyU. J Org Chem 66: 5245-5247.
- Li P, Xu JC (2000) New and Highly Efficient Immonium Type Peptide Coupling Reagents: Synthesis, Mechanism and Application. Tetrahedron 56: 4437-4445
- Li P, Xu JC (2000)HOBt and HOAt-derived immonium salts: new and highly efficient coupling reagents for peptide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 41: 721-724.
- El-Faham A, KhattabSh N, Abdul-Ghani M, Albericio F (2006) Design and Synthesis of New Immonium-Type Coupling Reagents. Eur J Org Chem 1563-1573.
- El-Faham A, Albericio F (2007) Novel Proton Acceptor Immonium-Type Coupling Reagents: Application in Solution and Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. Org Lett 9: 4475-4477.
- Faham A, Albericio F (2008) Morpholine-BasedImmonium and HalogenoamidiniumSalts as CouplingReagents in PeptideSynthesis. J Org Chem 73: 2731-1737.
- Wehrstedt KD, Wandrey PA, Heitkamp D (2005) Explosiveproperties of 1-hydroxybenzotriazoles. J Hazard Mater 126: 1-3.
- Subiros-Funosas R, Prohens R, Barbas R, El-Faham A, Albericio F (2009) Oxyma: an efficient additive for peptide synthesis to replace benzotriazole-based HOBt and HOAt with a lower risk of explosión. Chem Eur J 15: 9394-9403.
- El-Faham A, Subirós-Funosas R, Prohens R, Albericio F (2009)COMU, a Safer and More Effective Replacement for Benzotriazole-based Uronium Coupling Reagents.Chem Eur J 15: 9404-9416.
- Jad YE, KhattabSh N, Govender Th, Kruger HG, El-Faham A, et al. (2014) Oxyma-B, an Excellent Racemization Suppressor. Org and Bio Chem 12: 8379-8385.
- Jad YE, KhattabSh N, de la Torre BG, Govender Th, Kruger HG, et al. (2014) TOMBU and COMBU as novel uronium-type peptide coupling reagents derived from Oxyma-B. Molecules 19: 18953-18965.
Citation: Khattab NS, El-Faham A, Albericio F (2015) Peptide Coupling Reactions. J Mol Pharm Org Process Res 3: e119. DOI: 10.4172/2329-9053.1000e119
Copyright: ©2015 Khattab NS, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 21207
- [From(publication date): 3-2015 - Mar 28, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 16273
- PDF downloads: 4934