Note on Digital Breast Tomography Synthesis and Mammography
Received: 03-Dec-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-83872 / Editor assigned: 05-Dec-2022 / PreQC No. roa-22-83872 (PQ) / Reviewed: 19-Dec-2022 / QC No. roa-22-83872 / Revised: 23-Dec-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-83872 (R) / Published Date: 30-Dec-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000418
Image Article
Imaging the breasts for screening or diagnostic purposes is the practice of breast imaging, which is a subspecialty of diagnostic radiology. Breast imaging can be done in a number of different ways with a variety of technologies, as will be shown in detail below. X-ray technology is used in traditional mammography screening and diagnosis. Breast tom synthesis is a new digital mammography technique that uses X-rays to make three-dimensional images of the breast. Xeromammography and galactography also use X-ray technology to make images of the breast, but they are only used occasionally to find breast cancer. Breast MRI is another technology reserved for highrisk patients and can help determine the extent of cancer if diagnosed. Finally, scintimammography is used in a subset of patients who have abnormal mammograms or whose screening is not reliable on the basis of using traditional mammography or ultrasound. Breast ultrasound is another technology used in diagnosis and screening. It specifically can help differentiate between fluid-filled and solid lumps, which can help determine if cancerous.
It has a bogus negative (missed cancer) pace of somewhere in the range of 7 and 12 percent. This is in part because the cancer is obscured by dense tissues and because the appearance of cancer on mammograms is very similar to that of normal tissues. In addition, women undergoing breast surgery, such as enlargement, reduction (or) mastopexy should not have their mammograms performed more frequently [1,2].
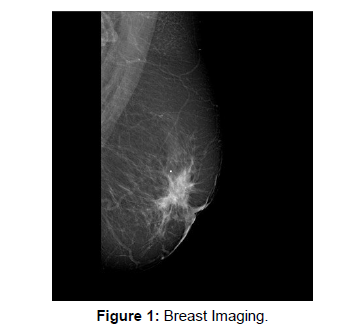
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
When compared to standard mammography, digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) may offer a higher degree of diagnostic accuracy. Understanding the difference between an X-ray and a CT is similar to understanding DBT. Specifically the first is three-dimensional, while the second is flat. Digital tomosynthesis uses X-rays to create a threedimensional image of the breast, whereas a mammogram typically takes two X-rays of each breast from different angles (Figure 1).
Acknowledgement
None
Conflict of Interest
None
References
- Thomassin-Naggara I, Cornelis F, Kermarrec E (2019) Breast interventional imaging. Presse Med 48: 1169-1174.
- Whitman GJ (2021) Breast Ultrasound: An Essential Tool. Ultrasound Q 37: 1-2.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Akirha T (2022) Note on Digital Breast Tomography Synthesis and Mammography. OMICS J Radiol 11: 418. DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000418
Copyright: © 2022 Akirha T. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 1156
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Mar 29, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 848
- PDF downloads: 308