Make the best use of Scientific Research and information from our 700+ peer reviewed, Open Access Journals that operates with the help of 50,000+ Editorial Board Members and esteemed reviewers and 1000+ Scientific associations in Medical, Clinical, Pharmaceutical, Engineering, Technology and Management Fields.
Meet Inspiring Speakers and Experts at our 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events with over 600+ Conferences, 1200+ Symposiums and 1200+ Workshops on Medical, Pharma, Engineering, Science, Technology and Business
Research Article Open Access
Multi-Element Detection in Green, Black, Oolong, and Pu-Erh Teas by ICP-MS
| Qiang Han*, Shozo Mihara, and Tatsuya Fujino | |
| Department of Chemistry, Tokyo Metropolitan University, Hachioji-Shi, Tokyo | |
| *Corresponding Author : | Qiang Han Department of Chemistry Tokyo Metropolitan University 1-1 Minami-Osawa, Hachioji-Shi Tokyo 192-0397 Tel: +81 042 6773135 Fax: +81 042 677 3135; Email: han-qiang@ed.tmu.ac.jp |
| Received May 08, 2014; Accepted May 21, 2014; Published May 28, 2014 | |
| Citation: Han Q, Mihara S and Fujino T (2014) Multi-Element Detection in Green, Black, Oolong, and Pu-Erh Teas by ICP-MS. Biochem Physiol 3:132. doi:10.4172/2168-9652.1000132 | |
| Copyright: © 2014 Han Q, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |
Visit for more related articles at Biochemistry & Physiology: Open Access
Abstract
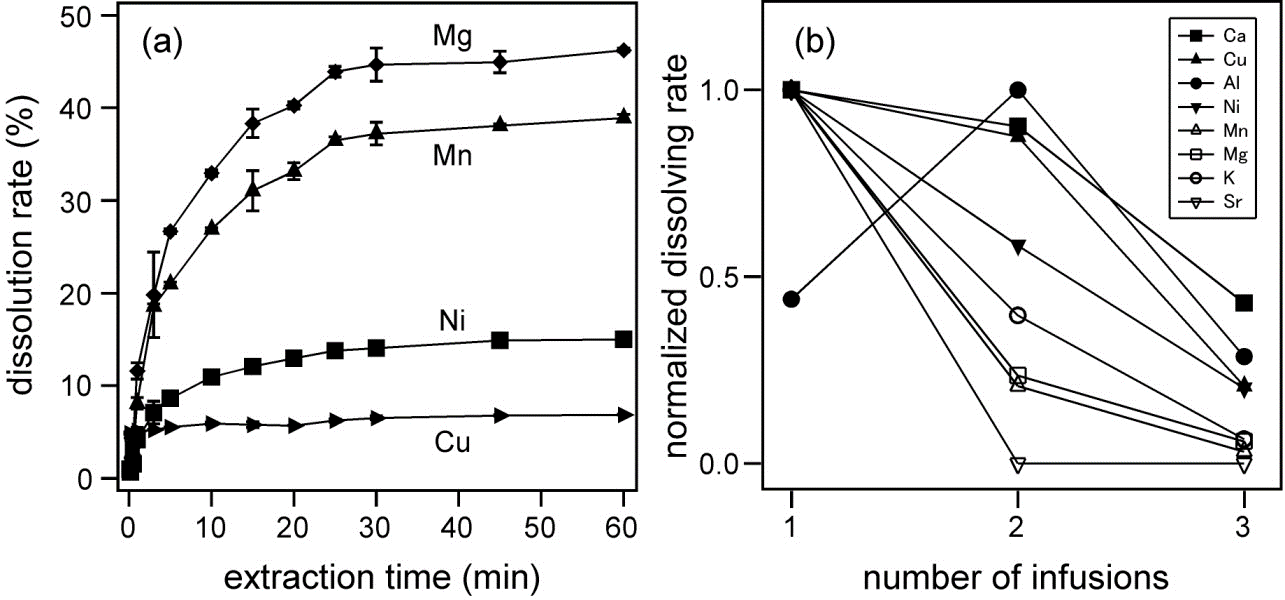
The contents of various elements in green, black, oolong, and pu-erh teas were measured by ICP-MS. The dependence of the dissolution rate of each element on the extraction time and the number of infusion was determined. By calculating the estimated daily dietary intake as a result of consuming 15 g of tea leaves a day, it was revealed that Cr and Mn exceeded the adequate intake for one day.
Tables and Figures at a glance
| Table 1 | Table 2 | Table 3 |
Figures at a glance
 |
| Figure 1 |
Post your comment
Relevant Topics
- Analytical Biochemistry
- Applied Biochemistry
- Carbohydrate Biochemistry
- Cellular Biochemistry
- Clinical_Biochemistry
- Comparative Biochemistry
- Environmental Biochemistry
- Forensic Biochemistry
- Lipid Biochemistry
- Medical_Biochemistry
- Metabolomics
- Nutritional Biochemistry
- Pesticide Biochemistry
- Process Biochemistry
- Protein_Biochemistry
- Single-Cell Biochemistry
- Soil_Biochemistry
Recommended Journals
- Biosensor Journals
- Cellular Biology Journal
- Journal of Biochemistry and Microbial Toxicology
- Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
- Journal of Biological and Medical Sciences
- Journal of Cell Biology & Immunology
- Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology
- Journal of Chemical Biology & Therapeutics
- Journal of Phytochemicistry And Biochemistry
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 13516
- [From(publication date):
June-2014 - Nov 23, 2024] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 9045
- PDF downloads : 4471
