Mitigation of Diseases palliative Oncology in Pediatric Patients
Received: 18-Jan-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-51819 / Editor assigned: 20-Jan-2022 / PreQC No. roa-22-51819(PQ) / Reviewed: 03-Feb-2022 / QC No. roa-22- 51819 / Revised: 08-Feb-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-51819(R) / Published Date: 15-Feb-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000362
Image article
Mitigation of disease related manifestations is a crucial part of clinical oncology. Kids and youths with disease are an especially weak populace and their enduring might go unnoticed via care suppliers new to the remarkable idea of Pediatric malignancies. Most of Pediatric patients who capitulate to their malignancies will encounter side effects requiring mitigation sooner or later during their treatment and in certain cases a long time before the finish of life. A comprehension of the signs, timing, possible poisonousness, and expected advantages for palliative mediations is consequently fundamental information for suppliers really focusing on Pediatric malignant growth patients [1].
Pediatric palliative consideration is a wide discipline including all physical and psychosocial intercessions expected to ease enduring and work on personal satisfaction of youngsters and their families. In the oncology setting, radiation treatment (RT) can be an important part of a multispecialty way to deal with vindication of torment or different indications emerging in essential or metastatic tumor across an assortment of organ frameworks. Palliative RT conveys radiation to indicative locales of infection or regions at high danger for becoming suggestive, fully intent on controlling or lessening cancer trouble [2]. As opposed to RT given as a feature of authoritative oncologic administration, which might include medicines conveyed to a huge region throughout the span of weeks to months, palliative RT courses are normally more restricted in field degree, aggregate portion, and length.
Basics of palliative radiotherapy
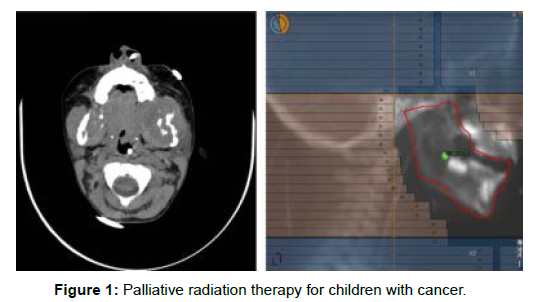
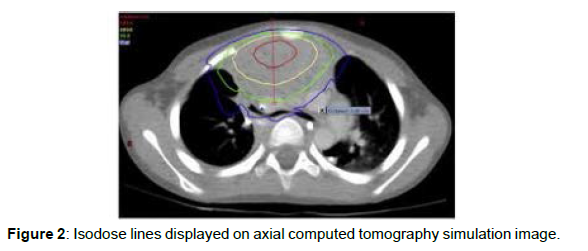
Palliative RT conveys high-energy X-beams, electrons, or nuclear particles to indicative essential cancer or metastases, initiating demise of imitating growth cells by collection of DNA harm. Palliative RT is furnished with one radiation therapy (or portion) given every day over a set number of days. Each negligible portion of RT typically requires the patient to lie still on a therapy table for roughly 10-15 minutes while radiation is conveyed from a straight gas pedal. Extremely little youngsters or those incapable to remain enough actually may require treatment under sedation [3]. Palliative RT dosages are regularly lower than those utilized for authoritative administration of malignancies, diminishing the danger of intense incidental effects from harm to neighbouring solid tissue. While late radiation-instigated poison levels are a legitimate worry with authoritative RT in kids and teenagers, they ought not to be a boundary in the palliative setting attributable to the by and large restricted future of youngsters getting palliative RT. For instance, optional malignancies are extremely improbable in the initial 5 to 7 years following RT. Most of palliative regimens are finished in 10 or less parts, or fourteen days of every day medicine (Figure 1 and 2).
Contrast for CT or MRI
In most cases, patients will get a differentiation specialist for one or the other CT or MRI reproduction. The patient’s timetable will contain headings about not eating or drinking prior to getting the differentiation. It is vital to observe the rules precisely. Advise the treatment group of any set of experiences of aversions to differentiate [4].
In the event that differentiation is utilized the patient will require an IV. On the off chance that the patient doesn’t have a port, focal line, or other IV gadget, a medical caretaker should begin an IV.
References
- Vassilios Vassiliou, Haris Charalambous (2013) Curative Intent versus Palliative Intent Radiation Oncology 31-42.
- Deborah Watkins Bruner, Lawrence B Berk (2013) Design Challenges in Palliative Radiation Oncology Clinical Trials 317-328.
- Stephen Jones J (2016) Genitourinary Complications in Palliative Oncology 1276-1281.
- Alysa Fairchild (2013) Side Effects of Palliative Radiotherapy. Radiation Oncology in Palliative Cancer Care.
Citation: Ooltewah A (2022) Mitigation of Diseases palliative Oncology in Pediatric Patients. OMICS J Radiol 11: 362. DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000362
Copyright: © 2022 Ooltewah A. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2464
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Mar 29, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1951
- PDF downloads: 513