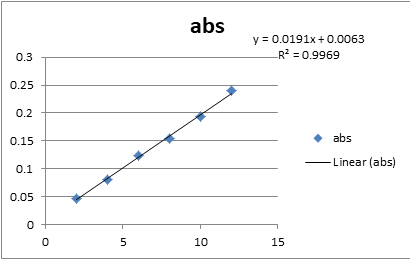METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF ROSUVASTATIN IN BULK DRUG FORMULATION AND STRESS DEGRADATION STUDIESBY UV
Received: 25-Mar-2022 / Manuscript No. ico-22-58565 / Editor assigned: 06-May-2022 / PreQC No. ico-22-58565 (PQ) / Reviewed: 20-Jul-2022 / QC No. ico-22-58565 / Revised: 23-Jul-2022 / Manuscript No. ico-22-58565 (R) / Published Date: 29-Jul-2022
Abstract
A simple, accurate, precise, and sensitive UV spectrophotometric method was developed for the determination of Rosuvastatin Calcium in bulk form. The optimum conditions for the analysis of the drug were established. Rosuvastatin Calcium was subjected to stress degradation under different conditions recommended by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). The samples so generated were used forced degradation studies using the developed method. The solvent used is ammonium acetate buffer and acetonitrile (30:70) the wavelength corresponding to maximum absorbance of the drug was found at 242 nm. Beers law was observed in the concentration range of 2-12 μg/ml with correlation coefficient 0.996. The linear regression equation obtained by least square regression method were y=0.0191X-0.0063, where y is the absorbance and x is the concentration of the pure drug solution. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) for estimation of Rosuvastatin Calcium were 0.769306 μg/ml and 2.331231 μg/ml respectively. The method was validated for several parameters like accuracy, precision as per ICH guidelines. The values of relative standard deviation and % recovery were found to be satisfactory, indicating that the proposed method is precise and accurate and hence can be used for the routine analysis of Rosuvastatin Calcium in bulk form.
Keywords: Rosuvastatin calcium; UV spectroscopy; Validation; Assay
Introduction
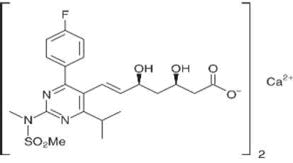
Rosuvastatin calcium is used as an antihyperlipidemic, which is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, a rate limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. It is used in the treatment of dyslipidemia, which is effective at low doses and its half-life is more compared to other statins. Chemically it is, calcium salt of (3R,5S,6e)-7-(4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-(ethyl(methylsulfonyl)amino)-5-pyrimidinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid and molecular formula is (C22H27FN3O6S)2Ca (Figure 1) [1]. Extensive literature survey reveals that a few spectrometric were available for the estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium in bulk and formulations [2-9]. The objective of the present study is to develop a new simple, sensitive, accurate, rapid and economic method for the estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium in bulk and tablet formulation.
Literature survey reveals that only an LC-MS study has been reported for the quantification of Rosuvastatin calcium in human plasma. Some UV spectrophotometric method has been reported for the estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium. The objective of the present work was to develop a simple, sensitive, precise and accurate UV spectrophotometric method for the determination of Rosuvastatin calcium in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations as per ICH Guidelines [10].
Materials and Methods
Instruments
A Shimadzu UV-visible spectrophotometer (UV 1800, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) was used for all absorbance measurements with matched quartz cells.
Chemicals and reagents
All chemicals acetonitrile ammonium acetate and reagents were of analytical grade. Rosuvastatin calcium in the form of powder with certificate of analysis was provided by Cipla Research Centre, Mumbai. Pharmaceuticalgrade excipients were obtained from Pharmaceutical Technology Lab of Maharashtra.
Results
Determination of maximum wavelength (λmax)
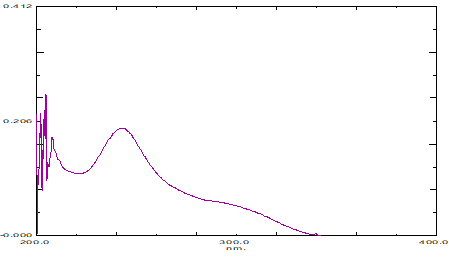
Standard stock solution of 100 μg/ml of Rosuvastatin calcium was prepared in mobile phase. From the above stock solution, pipette out 1 ml into 10 ml volumetric flask and finally made up the volume with mobile phase to produce a concentration of 10 μg/ml. The samples was then scanned in UV spectrophotometer from a range of 200-400 nm against mobile phase as blank and the wavelength corresponding to maximum absorbance in methanol was found at 242 nm (Figure 2).
Preparation of standard calibration curve
For the preparation of standard calibration curve, use stock of 100 μg/ml concentrations and 2-12 μg/ml concentration were prepared for analyzing calibration curve by pipetting out 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2 ml from the stock solution into a 10 ml volumetric flask and made up the volume with mobile phase [11-13]. The absorbance of each solution was measured at 242 nm as blank. Calibration curve of the drug was then plotted by taking the absorbance obtained on y-axis and the concentration of the solution on x-axis (Figure 3).
Validation
Validation can be defined as (ICH) establishing documented evidence, which provides a high degree of assurance that a specific activity will consistently produce a desired result or product meeting its predetermined specifications and quality characteristics.
The method was validated for several parameters like linearity, accuracy, precision, ruggedness, robustness, Limit of Detection (LOD), and Limit of Quantification (LOQ) according to ICH guidelines.
Linearity
The linearity of the analytical method was its ability to elicit test results which are directly proportional to analyte concentration in samples within a given range. To establish the linearity of the proposed method, various aliquots ofthe standard solution of the drug were prepared from stock solution and analyzed [14]. The drug showed linearity in therange of 2-12 μg/with correlation coefficient 1. Linearity data are shown (Table 1 and Table 2).
| Concentration μg/ml | Absorbance |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0.047 |
| 4 | 0.08 |
| 6 | 0.124 |
| 8 | 0.155 |
| 10 | 0.193 |
| 12 | 0.24 |
Table 1: Linearity table of Rosuvastatin calcium.
| Parameters | Data |
|---|---|
| Range | 2-12 μg/ml |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.996 |
| Slop | 0.0191 |
| Intercept | 0.004429 |
Table 2: Linear regression data for calibration curve.
Accuracy
This study was carried out using the stock solution (100 μg/ml). Take three concentrations 2 μg/ml, 6 μg/ml, and 12 μg/ml. And take six reading of these concentrations [15]. The result was reported as % RSD. The accuracy result showed a good with percent relative standard deviation less than 2. A result shows that the method is accurate up to 12 μg/ml.
Precision
Precision studies were carried out to ascertain the reproducibility of the proposed method. Repeatability was determined by preparing six replicates of same concentration of the sample and the absorbance was measured.
Intraday precision study was carried out by preparing drug solution of same concentration and analyzing it at three different times in a day. The same procedure was followed for one day to determine interday precision.
The result was reported as % RSD. The precision result showed a good reproducibility with percent relative standard deviation less than 2. The result shows that the method was found to be precise.
Robustness
Analysis was carried out at two different wavelengths to determine the robustness of the method and the respective absorbance was measured. The result was indicated as % RSD which is less than 2%. The results show that the method is robust for change in wavelength.
LOQ and LOD
Limit of Detection (LOD) is the lowest amount of analyte in the sample that can be detected. Limit of Quantification (LOQ) is the lowest amount of analyte in the sample that can be quantitatively determined by suitable precision and accuracy. The values of LOQ and LOD were found to be 0.769306 and 2.331231 μg/ml respectively.
Degradation Studies
The ICH guidelines Q1A (R2) entitled stability testing of new drug substances and products that required stress testing to be carried out to elucidate the inherent stability characteristics of the active substance. The aim of this study was to perform the stress degradation studies on Rosuvastatin calcium using the developed method.
Stress degradation by hydrolysis under acidic condition
The preparation of 0.01 N Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) was done by diluting 0.085 ml of conc. HCL to 100 ml of distilled water. Amount of drug was weighed and was transferred to a labeled round bottomed flask. Refluxed the sample for 2 hrs and pipette out 1 ml to 10 ml volumetric flask, made up the volume with mobile phase to get the final dilution so as to get final test concentration. Taken the reading on UV. Check the degradation behavior of drug.
Stress degradation by hydrolysis under alkaline condition
The 0.01 N Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) was prepared by dissolving 0.04 gm of sodium hydroxide pellets in 100 ml of distilled water. Amount of drug was weighted and was transferred to a labeled round bottom flask. Reflux the sample for 2 hrs. and pipette out 1 ml to 10 ml volumetric flask, made up the volume with diluent to get the final dilution so as to get final test concentration to get the final test concentration 10 ppm. Take the reading on UV. Check the degradation behavior of drug.
Stress degradation by neutral condition
Amount of drug was weighed and transferred in to 100 ml water in round bottom flask. Reflux it for 2 hours. Pipette out 1 ml in to 10 ml volumetric flask, made up the volume with diluent to get the final dilution so as to get final test concentration 10 ppm. Take the reading on UV. Check the degradation behavior of drug.
Photolytic degradation
Photo stability was performed by placing amount of drug in daylight for 24 hours. The samples were diluted with mobile phase up to 10 ml in a volumetric flask. Pipette out 1 ml sample diluted up to 10 ml by diluent to get the final dilution so as to get final test concentration 10 ppm. Take the reading on UV. Check the degradation behavior of drug.
Dry heat induced degradation
Standard drug was placed in an oven at 60°C for 2 hours to study dry heat degradation. Amount of drug samples were diluted with mobile phase up to 100 ml in a volumetric flask. Pipette out 1 ml and were diluted up to 10 ml by diluent to get the final dilution so as to get final test concentration 10 ppm. Take the reading on UV. Check the degradation behavior of drug.
Oxidative degradation
Weight accurately amount of drug and transfer into 10 ml of volumetric flask which containing 3% hydrogen peroxide. Keep it in dark place for 2 hours. Pipette out 1 ml sample diluted up to 10 ml by diluent to get the final dilution so as to get final test concentration 10 ppm. Take the reading on UV. Check the degradation behavior of drug(Table 3).
| Stress condition | % Degradation | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01 N HCl | 58.21% | Unstable |
| 0.01 N NaOH | 12.30% | Stable |
| Water | 30.03% | Unstable |
| Dry Heat | 29.20% | Unstable |
| Photolytic | 23.23% | Unstable |
| H2O2 | 28.28% | Unstable |
Table 3: % Degradation under stress conditions.
Conclusion
The proposed UV method is simple, accurate, precise, specific and highly sensitive. The method is economical rapid and do not require any sophisticated apparatus in contrast to spectroscopic methods. The proposed method is also useful for the determination of Rosuvastatin calcium stability in samples of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Hence, the proposed method can be successfully used for routine quality control analysis of drug in marketed preparations.
Acknowledgment
The authors take this opportunity to thanks Cipla Research Centre, Mumbai for providing gift sample. The authors would like to acknowledge Principal Dr. Sanjay Thonte, Channabasweshwar Pharmacy College, Latur for providing facilities for conducting research.
References
- Pandya B, Channabasavaraj KP, Jaydeep D, Chudasamamani TT (2010) Development and Validation of RP-HPLC method for determination of Rosuvastatin calcium in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Int J Pharma Sci Rev Res 5:82-86.
- Sevda R, Ravetkar AS, Shirote PJ (2011) UV spectrophotometric estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium and Fenofibrate in bulk drug and dosage form using simultaneous equation method. Int J Chem Tech 3:630-635.
- Narayankar M, Sakpal PH, Bhingare CL, Ingale PL (2015) Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for the estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium and Niacin in combined tablet dosage form. Int J Pharm Res Rev 4:44-50.
- Donthula S, Kumar MK, Teja GS, Y Kumar M, J Yasodha K, et al. (2011) A New validated RP-HPLC method for determination of Rosuvastatin calcium in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Der Pharm Lett 3:350-356.
- Lahare Y, Phuge AN, Gite AL, Jadhav AK (2014) A review on ultraviolet spectrophotometric determination of Rosuvastatin calcium in marketed formulation. Int J Pure App Bio sci 2:169-174.
- Ramu K, Aleti P, Venisetty RK (2013) Analytical method development and validation of simultanious estimation of Ezetamibe and Rosuvastatin in tablet dosage form by RP HPLC. Int J Pharm Biol Sci 3:343-353.
- Sumalatha M, Haritha PK (2013) Analytical method development and validation for the simultaneous estimation of Rosuvastatin and Finofibate in tablet dosage form by reverse phase high. Indian J Res Pharm Biotechnol 1:850 856
- Badawy M, Mostafa NM, Abd El Aziz B, Aleem A El, Lamie NT (2011) Stability indicating spectrophotometric methods for determination of Rosuvastatin in thepresence of its acid degradation products by derivative spectrophotometric tecniques. J Adv Pharm Res 2:44-55.
- Tajane D, Raurale AM, Bharande PD, Mali AN, Gadkari AV, et al. (2012) Development and validation of a RP HPC Pda method for simultaneous determination of Rosuvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate in pharmaceutical dosage form. J Chem Pharm Res 4:2789-2794.
- Joshi H, Kumar S, Yadav YC, K Seth (2012) A new analytical method development and validation of Rosuvastatin and Ezetimibe in tablet dosage form. Int J Drug Discovery Med Rese 1:22-29.
- Patel B, Shah Binal B, Gohil Kirtan N, Patel Piyush M (2012) Development and validation of spectrophotometric method for simultaneous estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium and Aspirin in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. IJPRS 2:115-122.
- Rekha R, Anbazhagan S, Kumar PR (2012) Analytical method development and validation of Rosavastatin calcium in pure form and pharmaceutical formulations by UV spectroscopy. Int J Pharmtech Res 4:1601 1605.
- Sailaja B, Sravana K (2016) Analytical method development and validation for the estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium in raw material and tablet formulation by UV. Saudi J Med Pharm Sci 2:7-11.
- Patel B, Jadav A, Solanki H, Parmar S, Parmar V, et al. (2013) Development and validation of derivative spectroscopic method for the simultaneous estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium and fenofibrate in tablet. Int J Pharma Res Rev 2:1 6.
- Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology, ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guidelines (1995); 1-15.
Citation: Gholve S, Radha VJ (2022) Method Development and Validation of Rosuvastatin in Bulk Drug Formulation and Stress Degradation Studies by UV. Ind Chem 8:195.
Copyright: © 2022 Gholve S, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Usage
- Total views: 2607
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Nov 29, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 2153
- PDF downloads: 454