Malnutrition Scenario among School Children in Eastern-India-an Epidemiological Study
Received: 19-Feb-2016 / Accepted Date: 03-Mar-2016 / Published Date: 10-Mar-2016 DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000228
Abstract
Background: Twenty years after the implementation (1995) of the mid-day-meal program to improve nutritional status and academic efficiency among school-children, under-nutrition remained a major concern in India. Efforts to quantify the problem and identify its determinants were handful, especially in the eastern part of the country. Thus the purpose of this study was to determine the burden and predictors of under-nutrition among primary and upper-primary school-children in eastern India.
Methods: Using stratified cluster random sampling with proportional recruitment, a multistage cross-sectional study was conducted involving all twenty educational districts of West Bengal, a highly populous state in eastern India. During 2014-15, using structured questionnaire, standard anthropometry and laboratory testing a representative sample of 24,108 primary and upper-primary students from the whole state of West Bengal were interviewed and assessed. Descriptive and regression analyses were conducted using SAS-9.4.
Results: Among 24,108 recruited students aged between six and thirteen years, prevalence of under-nutrition was alarmingly high (about twenty-three percent). Furthermore, over half of the students (fifty-four percent) were at-risk of developing malnutrition. On the other hand, only seventeen percent students had ideal nutritional status. Odds of being malnourished were higher among male students (compared to females), those belonging to younger age (studying in primary compared to upper-primary classes), Muslim religion (with reference to Hindus), and under-privileged caste (in comparison with general caste) as well as those residing in rural areas (as opposed to urban). Parental education was negatively associated with the likelihood of under-nutrition. Those who had more than three siblings, unemployed father and students whose mother died were more likely to be under-nourished.
Conclusions: Prevalence of under-nutrition was high among school-children in the study area. School-based interventions targeting high-risk, under-privileged children, especially in rural areas with lower parental education and poor level of sanitary practices seemed to be urgently required.
Keywords: Adolescent nutrition; Child nutrition, Malnutrition; Nutritional epidemiology; Indian children; Determinants of malnutrition
164207Introduction
Brain development of a child starts in mother’s womb and continues throughout infancy and up to the age of 2 year, whereas its growth continues beyond that period. Appropriate intake of macro and micronutrients during intra-uterine life as well as first few years following birth are crucial for brain and other organ development [1]. Undernutrition during this period can slow down the physical and mental development of the child and consequences are usually lifelong [2,3].
Poor socio-economic conditions in developing and underdeveloped countries often result in under-nutrition since intrauterine life till early childhood and attempts must be made to ensure their appropriate nutrition during school-age. Under-nutrition and infections like diarrhoea, respiratory infections, malaria, TB etc. are inter-dependent and parts of a vicious cycle [4-6].
On the other hand, chronic infections make children undernourished [5,7]. Prolonged under-nutrition has detrimental effects on all organ-systems including gut, reducing its capacity to maintain homeostasis during under-nutrition and may result into life threatening conditions [8-11].
Dietary requirement of essential nutrients varies with age, gender, physiological status and physical activity [12]. Globally, millions of school-going children suffer from under-nutrition [13]. In India, National Family Health Survey-3 (NFHS-3) estimated that in 2006, 24% under-5 years-aged children were severely malnourished (<3 standard deviation of the reference value suggested by the Indian Academy of Paediatrics) according to the height-for-age scale and 16% according to the weight-for-age values.
Free and compulsory education till the age of 14 year is constitutional right, and institutional commitment in India. Despite these measures, about 40% children drop out during their primary schooling [14].
Low enrolment and higher school dropout rates are attributed to poor socio-economic conditions, thus engaging in child labour; migration of family, helping the family in domestic work and lack of educational motivation compounded by poor nutritional status [14,15]. The scenario worsens further due to superimposition of under-nutrition, anemia and infections among these educationally depleted children. Unfortunately, a sizable portion of Indian children suffer from low food intake induced under-nutrition potentially resulting from poverty, ignorance etc. [16,17].
Preventable infections are also common in India. All these factors undoubtedly hamper their attendance and scholastic performance in school. Nutritional support through school meal program during primary education serves the dual purpose of partial correction of nutritional inadequacies along with reduction in school drop-out rate.
Government-sponsored Cooked Mid-Day Meal Program was rolled-out in 1995 to address the issues of universal coverage of primary education through increased enrolment, improving school attendance, retention and promoting health and nutrition among school children.Affecting 16% population, under-nutrition among primary school children is one of the major public health concerns currently in India.
Studies addressing under-nutrition were mostly restricted to under-5 populations [18-22], whereas very few studies addressed school-going children to assess the magnitude of the problem, role of the mid-day meal programs and factors attributable for undernutrition [23-27]. Hence, a cross-sectional study was conducted among children receiving school meal program (6-13 yrs.) in West Bengal, a highly populous state in eastern India, to understand the malnutrition scenario with special reference to under-nutrition.
Participants and Methods
Research design
A district-wise school-based cross-sectional survey was conducted in each of the 20 educational districts of West Bengal state, using a structured questionnaire. Primary and upper-primary school children (6-13 years) were interviewed followed by anthropometric measurement and hemoglobin estimation to determine the prevalence of under-nutrition and identify its predictors.
Sampling
A multistage cluster sampling technique was employed for this study. In the first stage of sampling, required number of blocks was selected in each district. In the second stage, within each block, one primary and one upper primary schools were randomly selected from the block-wise exhaustive list of schools.
Owing to the possibility that socio-demographic variations were likely to be less among the students in each school compared to the between school variation, it was decided to do clustering at the school level. Thus using schools as the clusters, individual students were then recruited from each selected school through stratified random sampling from age and gender strata-wise list of students in each selected school.
As number of schools in the school-districts was planned in a manner so that each school could cater almost equal number of students, we decided to keep the number of selected students to be fixed for each district. The sample size for each district was calculated based on the formula n = (Z) 2p (1-p)/ε2. The appropriate parameter values for the expected proportion of malnourished children (p) was not available from the study area hence it was assumed to be 0.4 based on the national level [16] estimate along with a desired precision (ε) of 4% or 0.04 and α of 0.05.
An empirical design effect of 2 was considered to adjust for the possibility of variance inflation due to higher inter-cluster (school) and lower intra-cluster variation. Thus 1152 (rounded off to 1200) subjects were required to be evaluated for each district.
Considering average availability of 40 children at each of the primary and upper primary schools, a total of 30 schools (1200/40), [15] primary (grade I to IV: 6-9 years) and 15 upper primary (grade V to VIII: 10-13 years)] were to be selected randomly in each district.
In districts having more than 15 blocks, 15 blocks were selected randomly and in district with 15 blocks all blocks were selected followed by selection of one primary and one upper-primary schools from each selected block. In districts with lesser number of blocks, one school of each type were selected from each block and additional schools were selected from bigger blocks using proportional sampling till selection of 15 primary and 15 upper-primary schools were complete.
Five boys and five girls were randomly selected next in each school from all boys and girls respectively in each grade (I to IV: 6-9 years in primary and V to VIII: 10-13 years in upper primary) thus making it 40 selected students/selected schools.
To have proportionate distribution intact, these schools were selected in a manner (65% rural and 35% urban schools approximately wherever possible) so that the resultant sample was likely to culminate into an appropriate representation of the school-children of West Bengal. Altogether 24,108 students were thus recruited from 20 districts according to this sampling design and strategy.
Ethics Statement
The study protocol was reviewed and approved (No.: A-1/2014-IEC Dated 17.05.14) by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (NICED), Kolkata.
Data collection
Children along with their teachers and guardians were interviewed after collecting their informed consent, using a field-tested, internally validated, semi-structured questionnaire, prepared by an expert group for collection of socio-demographic (including current grade, sex, type of house, caste, religion, family size, major occupation of father and mother, etc.) and other relevant information related to undernutrition.
All relevant information was collected by teams of trained field workers consisting of nutritionist/social workers/field workers and field attendants. Anthropometric measurements such as height and weight were conducted (following Indian Academy of Paediatrics guideline) using anthropometric rods and digital weighing machines with high accuracy.
Instruments were standardized before data collection and once in a week during the study, using standard operating procedures (as per the guidelines of National Nutrition Monitoring Bureau, Indian Council of Medical Research).
Survey form completeness was checked on the same day of fieldwork and sent back to National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (NICED) periodically once a week for entry.
Bio-chemical investigations included blood test for hemoglobin measurement. Hemo-Cue Hemoglobin Analyser (HemoCue Hb 301) was used to determine haemoglobin level in the blood sample collected.
A subsample (grade I and V) of participating subjects were assessed for haemoglobin through pricking of the fingertips using sterile needles [28].
Entire field work was carried out between October -2014 and December 2014.
Nutritional assessment outcomes
Nutritional Assessment was done using guidelines of Indian Academy of Paediatrics (IAP) with their reference values for Height and Weight of 5-18 year Indian Boys and Girls [29].
Under-nutrition was considered as having either weight or height or both less than third percentiles in respect to his or her age and sex as guided by IAP.
Exclusive stunting was considered as having only less than 3rd percentile for height for age and sex similarly exclusive under-weight as less than 3rd percentile for weight for age and sex only.
Anemia is considered as having blood Hemoglobin (Hb) level of less than 11gm%. In view of cost-constraint, hemoglobin estimation was restricted and conducted only for students of grade-I (as representative of primary students) and grade-V standard students (as representative of upper-primary students) of all districts.
Because of high altitude, value of <13gm% was considered as Anemia and <11gm% as moderate anemia for students residing at Darjeeling district (a district with hilly terrains). Children at high risk of malnutrition were identified as those having either height or weight or both measure between 3rd to <10th percentile.
Low risk was considered for children having either height or weight or both measures between 10th to 25th percentiles. Ideal nutritional status was considered for children with both height and weight between 25th to 75th percentiles as per IAP reference population.
Statistical methods
Descriptive analyses of the collected data were conducted to determine the distribution (magnitude of problem is expressed in percentages) of the socio-demographic factors, anthropometric parameters, hygienic practices, clinical history and burden of undernutrition as well as distribution of the factors across the nutritional strata.
To determine the association of these factors with under-nutrition, binary log it models were fitted to the data.
Model fit statistics were checked using Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of fit test.
Variables considered in the final logit model were the common predictors found in literature search from previous studies done in India.
All variables considered in the final model were found to be significant predictors of under-nutrition in bivariate analysis. No transformations of the variables were done. Analysis of data was done using SASv9.4, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
Results
Malnutrition among students
Prevalence of under-nutrition in our study sample was 22.8% (95%CI=22.3-23.4) combining primary (grade I to IV) and upperprimary (grade V to VIII) students as shown in Table 1. Over-nutrition (over-weight & obesity) was observed to be 3% among the studied subjects (grade I to VIII) and mostly prevalent in Kolkata.
| Under-nutrition and types | Primary | Upper-Primary | Overall | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Percentage (95%CI) | n | Percentage (95%CI) | n | Percentage (95%CI) | |
| Under-nutrition | 3134 | 26.1% (25.3, 26.9) | 2368 | 19.6% (18.9, 20.3) | 5502 | 22.8% (22.3, 23.4) |
| Exclusive Stunting1 | 828 | 6.9% (6.4, 7.3) | 685 | 5.7% (5.3, 6.1) | 1513 | 6.3% (6.0, 6.6) |
| Exclusive Under-weight2 | 775 | 6.4% (6.0, 6.9) | 560 | 4.6% (4.3, 5.0) | 1335 | 5.5% (5.2, 5.8) |
| Both stunting and under-weight | 1531 | 12.8% (12.1, 13.3) | 1123 | 9.3% (8.8, 9.8) | 2654 | 11% (10.6, 11.4) |
Table 1: Under-weight and stunting in Primary [N=12020] and Upper-Primary Students [N=12091]. 1 Children <3rd percentile for height only (excluding those who were <3rd percentile for weight also. 2 Children <3rd percentile for weight only excluding those who were less than 3rd percentile for height also.
Among primary students the burden was 26.1% (25.3-26.9) and among upper-primary students it was 19.6% (18.9-20.3).
Anthropometrically, exclusive under-weight was present among 5.5% (5.2-5.8) subjects, exclusive stunting among 6.3% (6.0-6.6) and both were present in 11% (10.6-11.4).
Among primary students 6.4% (6.0-6.9) were exclusively under-weight, 6.9% (6.4-7.3) were exclusively stunted and 12.7% (12.1-13.3) had both.
Among upper-primary students 4.6% (4.3, 5.0) were found to be exclusively under-weight, 5.7% (5.3-6.1) had exclusively stunting and 9.3% (8.8-9.8) had both (Table 1).
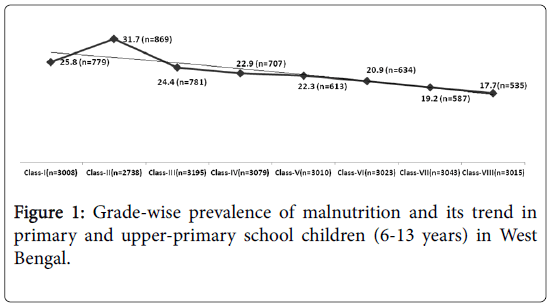
Grade-wise prevalence of under-nutrition varied between 17.7% to 31.7% with highest and lowest burden being observed among student of grade VIII and II respectively (Figure 1).
Figure 2 shows district-wise prevalence of under-nutrition and at high risk children among primary students that ranged from 10% to 38% for under-nutrition and 18% to 35% for at high risk.
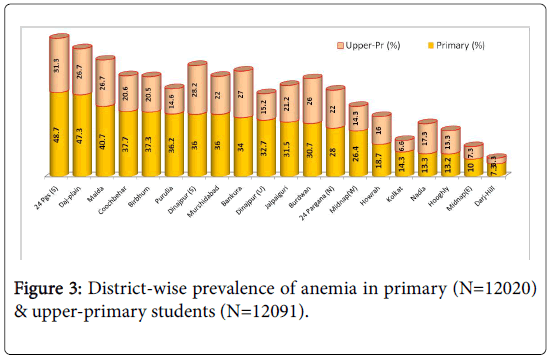
Figure 3 shows district-wise prevalence of anemia among the studied subjects indicating 3 districts had an alarmingly high prevalence of anemia of >40% in primary students.
Demographic characteristics of the individuals
Demographic characteristics of the study subjects are presented in Table 2.
| Variables | Categories | Overall [N (Column %)] | Under-nutrition [N (Row %)] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | P-Value | |||
| Place of residence | |||||
| Rural | 16593 (68.8) | 4184 (25.2) | 12409 (74.8) | <0.0001 | |
| Urban | 7515 (31.2) | 1318 (17.5) | 6197 (82.5) | ||
| Type of School | |||||
| Primary | 12018 (49.9) | 3134 (26.08) | 8884 (73.92) | <0.0001 | |
| Upper Primary | 12090 (50.1) | 2368 (19.59) | 9722 (80.41) | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 12050 (50.0) | 2965 (24.6) | 9085 (75.4) | <0.0001 | |
| Female | 12058 (50.0) | 2537 (21.0) | 9521 (79.0) | ||
| Religion | |||||
| Hindu | 16216 (67.3) | 3461 (21.0) | 12755 (78.7) | <0.0001 | |
| Muslim | 7387 (30.6) | 1942 (26.3) | 5445 (73.7) | ||
| Other | 505 (2.1) | 99 (19.6) | 406 (80.4) | ||
| Caste | |||||
| Scheduled Tribe | 1827 (7.6) | 495 (27.1) | 1332 (72.9) | 0.166 | |
| Scheduled Caste | 6544 (27.1) | 1563 (23.9) | 4981 (76.1) | ||
| Other Backward castes | 2693 (11.2) | 597 (22.2) | 2096 (77.8) | ||
| General | 10301 (42.7) | 2003 (19.4) | 8298 (80.6) | ||
| Siblings | |||||
| None | 2345 (9.7) | 284 (12.1) | 2061 (87.9) | <0.0001 | |
| Having 1 or 2 siblings | 16615 (68.9) | 3792 (22.8) | 12823 (77.2) | ||
| Having ≥3 siblings | 5148 (21.4) | 1426 (27.7) | 3722 (72.3) | ||
| Fathers occupation | |||||
| Unemployed | 143 (0.6) | 43 (30.1) | 100 (69.9) | 0.3769 | |
| Unskilled | 13650 (56.6) | 3551 (26.1) | 10099 (73.9) | ||
| Self-employed | 5949 (24.7) | 1196 (20.1) | 4753 (79.9) | ||
| Skilled | 3407 (14.1) | 498 (14.6) | 2909 (85.4) | ||
| Fathers literacy | |||||
| Illiterate | 2328 (9.7) | 676 (29.0) | 1652 (71.0) | 0.0001 | |
| Primary or Secondary Education | 11414 (47.3) | 2470 (21.6) | 8944 (78.4) | ||
| Graduation and above | 868 (3.6) | 63 (7.3) | 805 (92.7) | ||
| Mothers presence | |||||
| Alive | 23864 (99.0) | 5432 (22.8) | 18432 (77.2) | 0.0282 | |
| Not alive | 244 (1.0) | 70 (28.7) | 174 (71.3) | ||
| Mothers literacy | |||||
| Illiterate | 3543 (14.7) | 961 (27.1) | 2582 (72.9) | <0.0001 | |
| Primary or Secondary Education | 11125 (46.1) | 2291 (20.6) | 8834 (79.4) | ||
| Graduation and above | 450 (1.9) | 20 (4.4) | 430 (95.6) | ||
| Hand washing habit before taking food | |||||
| Always | 11223 (46.6) | 2019 (18.0) | 9204 (82.0) | <0.0001 | |
| Sometimes | 3706 (15.4) | 785 (21.2) | 2921 (78.8) | ||
| Never | 9179 (38.1) | 2698 (29.4) | 6481 (70.6) | ||
| Use of Latrine | |||||
| Open Air | 6217 (25.8) | 1968 (31.7) | 4249 (68.3) | <0.0001 | |
| Dug Well | 6805 (28.2) | 1633 (24.0) | 5172 (76.0) | ||
| Sanitary Latrine | 10992 (45.6) | 1874 (17.1) | 9118 (82.9) | ||
| Other Places | 94 (0.4) | 27 (28.7) | 67 (71.3) | ||
| History of passing of worms (past 6 months) | |||||
| Yes | 7716 (32.0) | 2061 (26.7) | 5655 (73.3) | <0.0001 | |
| No | 16392 (68.0) | 3441 (21.0) | 12951 (79.0) | ||
| Episode of Diarrhea (Past year) | |||||
| Yes | 10936 (45.4) | 2670 (24.4) | 8266 (75.6) | <0.0001 | |
| No | 13172 (54.6) | 2832 (21.5) | 10340 (78.5) | ||
| Received Iron and Folic Acid tablets in School (past 6 months) | |||||
| Yes | 8343 (34.6) | 1686 (20.2) | 6657 (79.8) | <0.0001 | |
| No | 157 (65.4) | 3816 (24.2) | 11949 (75.8) | ||
Table 2: Distribution of the participating school students and their under-nutrition status across the strata of socio-demographic factors in West Bengal, India (N=24108). *Column percentages for the individual categories (in overall distribution) may not sum up to 100% (Total frequency) due to non-response.
Sixty-nine percent of the studied subjects were residents of rural West Bengal.
Sixty-seven percent of the respondents belonged to Hindu families and 30% were Muslims by religion.
Caste-wise, 27% subjects belonged to Scheduled caste (SC), 7% to Scheduled Tribe (ST) and 11% were from other Under-privileged class (OBC).
Family characteristics
About 10% of the participating children had no sibling while 21% had 3 or more.
About 57% of the fathers were unskilled workers, while less than 1% were unemployed at the time of survey.
About 10% fathers and 15% mothers were illiterate, while only 4% and 2% of the fathers & mothers were graduate or above respectively.
Among participants, 1% had lost their mother, 38% never washed their hand before eating, 25% reported that they defecate in open air, 32% had history of passing worms during last six months, 45% suffered from diarrheal episodes during last year.
Determinants of under-nutrition
Considerably high proportion of students was found to be at high risk of being under-nourished. Grade-specific prevalence of students at high risk of being under-nourished varied between 24.1% (grade VIII) and 29.8% (grade III). It was observed an overall prevalence of anemia of 23.7% among students of grade I and V combined. The prevalence of under- nutrition across socio-demographic strata is shown in Table 2. Rural students were more malnourished than their urban counterpart (25% vs. 17.5%). Alarming level of under-nutrition prevalence (=40%) was observed among rural primary students of three Under-privileged school-districts: Darjeeling (plain), Purulia and Jalpaiguri.
Boys had relatively higher prevalence of under-nutrition (25%) compared to the girls. The proportion of malnourishment was also found higher among Muslims (26%) and under-privileged castes (27%, 24% and 22% respectively among ST, SC and OBC) as well as among subjects having three or more siblings (27%), unemployed father (30%), illiterate mother (27%) or father (29%) and those who had lost their mother (29%).
Table 3 shows the results of the bivariate analysis and multiple logistic regression model. While the bivariate analyses presented the odds ratios [OR (corresponding 95%CI)] for each independent predictor, the multiple logistic regression model was prepared to determine adjusted odds ratios [AOR (corresponding 95%CI)] by incorporating multiple predictors in a more complex model. The multiple logistic regression model fitted well having a p-value of 0.3985. The analysis revealed that boys had 25% higher odds of being malnourished than girls [AOR=1.25(1.17-1.33)]. Students from Muslim families had 25% higher odds [AOR=1.25(1.16-1.35)] of being malnourished compared to students from Hindu families. Children who had 3 or more siblings [AOR=1.85(1.59-2.14)] or those who had 1or 2 siblings [AOR=1.64(1.43-1.87)] when compared to those with no sibling, had 85% and 64% higher odds of becoming malnourished respectively. Those living in rural areas had 14% [AOR=1.14(1.06-1.23)] higher odds of being malnourished compared to those residing in urban conglomeration.
| Co-variates | Categories | Under-nourished vs Not under-nourished | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P value | Adjusted OR(95%CI)1 | P value | ||
| Gender (Ref: Girls) | Boys | 1.23(1.15-1.30) | <0.0001 | 1.25(1.17-1.33) | <0.0001 |
| Education (Ref: Upper-primary) | Primary | 1.45(1.36-1.54) | <0.0001 | 1.20(1.10-1.31) | <0.0001 |
| Religion (Ref: Hindu) | Muslim | 1.31(1.23-1.40) | <0.0001 | 1.25(1.16-1.35) | <0.0001 |
| Caste (Ref: General) | Under-privileged caste (including ST, SC, OBC) | 1.31(1.23-1.40) | <0.0001 | 1.25(1.16-1.35) | <0.0001 |
| Place of residence (Ref: Urban) | Rural | 1.59(1.47-1.70) | <0.0001 | 1.14(1.06-1.23) | 0.0007 |
| Siblings (Ref No Sibling) | Having 1 or 2 siblings | 2.15(1.88-2.44) | <0.0001 | 1.64(1.43-1.87) | <0.0001 |
| Having 3 or more siblings | 2.78(2.42-3.19) | <0.0001 | 1.85(1.59-2.14) | <0.0001 | |
| Mothers presence (Ref: Alive) | Not Alive | 1.37(1.03-1.80) | 0.0288 | 1.40(1.04-1.88) | 0.0245 |
| Mothers literacy (Ref: Illiterate) | Primary or Secondary Education | 0.70(0.64-0.76) | <0.0001 | 0.98(0.88-1.08) | 0.669 |
| Graduate and above | 0.13(0.08-0.20) | <0.0001 | 0.39(0.25-0.63) | 0.0001 | |
| Fathers literacy (Ref: Illiterate) | Primary or Secondary Education | 0.68(0.61-0.75) | <0.0001 | 0.87(0.78-0.98) | 0.0163 |
| Fathers Employment (Ref: Skilled or higher) | Graduate and above | 0.19(0.15-0.25) | <0.0001 | 0.52(0.39-0.70) | <0.0001 |
| Unemployed | 2.51(1.73-3.64) | <0.0001 | 1.68(1.14-2.46) | 0.0081 | |
| Unskilled | 2.05(1.85-2.28) | <0.0001 | 1.42(1.27-1.58) | <0.0001 | |
| Self-employed | 1.47(1.31-1.65) | <0.0001 | 1.25(1.11-1.40) | 0.0003 | |
| Episode of Diarrhea during past year (Ref: None) | Yes | 1.18(1.11-1.25) | <0.0001 | 1.05(0.98-1.12) | 0.1184 |
| Episode of worm with stool during past year (Ref: None) | Yes | 1.37(1.28-1.46) | <0.0001 | 1.23(1.15-1.32) | <0.0001 |
| Iron tablets from School (Ref: Received) | Not Received | 1.26(1.18-1.35) | <0.0001 | 1.05(0.96-1.15) | 0.3255 |
| Use of latrine (Ref: Sanitary) | Dug Well | 1.54(1.42-1.65) | <0.0001 | 1.49(1.36-1.62) | <0.0001 |
| Open Air Defecations | 2.25(2.09-2.42) | <0.0001 | 1.36(0.86-2.15) | 0.1851 | |
| Other Places | 1.96(1.25-3.07) | 0.0033 | 1.22(1.12-1.31) | <0.0001 | |
| Hand cleaning habit after defecation (Ref: Always) | Never | 1.90(1.77-2.03) | <0.0001 | 1.35(1.25-1.45) | <0.0001 |
| Sometimes | 1.23(1.11-1.34) | <0.0001 | 1.13(1.03-1.24) | 0.0123 | |
Table 3: Association of socio-demographic variables with under-nutrition among school children in West Bengal, India (N=24108).1Adjusted for other variables in the table. Bold faced figures indicate statistically significant results assuming α=0.05
With father being graduate (with reference to illiterate fathers), odds of being malnourished decreased by 48% [AOR=0.52(0.39-0.70)]. Children whose father was unemployed had 68% higher odds of being malnourished compared to children whose father was skilled worker [AOR=1.68(1.14-2.46)].
Mother’s literacy had a strong impact on nutritional status of children. Participants whose mother was graduate had 61% lower odds of being malnourished as compared to students whose mother was illiterate [AOR=0.39(0.25-0.63)]. Students whose mothers were not alive had 1.40 times [AOR=1.40(1.04-1.88)] odds of being malnourished compared to those who had their mothers alive. Analysis revealed that participants who practiced open air defecation had 1.49 times [AOR=1.49(1.36-1.62)] odds of undernourishment when compared to those using sanitary latrine. Those who did not clean their hands with soap had 35% higher odds of being malnourished [AOR=1.35(1.25-1.45)].
Discussion
Numerous studies were conducted in India to understand the problem of under-nutrition among under-five children but similar studies were rarely undertaken among school going children. This study estimated the burden of undernutrition among school-going children with a prevalence of 23%. Analysis revealed that younger (primary) school-students were more vulnerable to be under-nourished as opposed to the relatively older ones (upper-primary students) while rural students were more vulnerable than their urban counterparts.
We also observed that grade-wise, under-nutrition was most prevalent among second standard students following which a declining trend was observed. In West Bengal state, Coochbehar, Burdwan, Murshidabad, Maldah, Darjeeling (plain), Jalpaiguri and Purulia were the districts with high (>30%) prevalence of under-nutrition among primary students. The situation was found to be worse in the rural areas. Similarly, anemia was highly prevalent (more than 30%) among students of South 24 Parganas, Dakshin Dinajpur, Darjeeling (Plain) and Maldah districts, with an overall state-level prevalence of 23%.
In addition to the under-nourishment, district-level prevalence of students at high risk of developing under-nutrition varied between 18-35%. On the other hand, prevalence of ideal nutritional status (within 25th to 75th percentile of IAP reference level) was observed only among 17% primary and 24% upper-primary students of West Bengal. Thus overall a chronic state of famine was documented particularly among rural school children in almost all districts of this state as large number of children were at various stages of undernutrition, which appeared to be a reflection of India’s ranking (55th) on the Global Hunger Index [30]. This necessitated clubbing the at-risk segment together with malnourished segment while developing an appropriate intervention for improving under-nutrition scenario among school-children of West Bengal.
Corroborating with prior evidences elsewhere [22,27] as well as in West Bengal [21], inferential analyses revealed that boys (reference=girls), relatively young (primary) students (reference=upper-primary),those belonging to Muslim religion (reference=Hindu) or under-privileged (including ST, SC, OBC) caste (reference=Hindu) and students living in rural areas were more likely to be under-nourished [21,22,27].
Additionally, alike others this study also found that having more siblings, mother’s death, father’s unemployment were found to be associated with higher odds of suffering from under-nutrition [21,22,27], while better education of the father and mother were found to be preventive factors. Prior research in Andhra Pradesh [20] and Ludhiana [22] in India did also reveal that father’s unemployment and other predictors of poor economic condition of the household were correlated negatively with the probability of under-nutrition among children. Protective influence of parental literacy on under-nutrition was also evidenced previously among children of this state [21].
Poor sanitation, lack of hygienic practices and recent history of worm infestation were also found to be associated with higher likelihood of developing under-nutrition among school-children. Similar observation was previously reported by other studies conducted among school-children in this state [21,24].
There were some major limitations in our study. Alike any other observational study the associations observed in this study should not be interpreted as causality and owing to the potential for nongeneralizability due to non-response, though very miniscule, any effort to extrapolate the results of the study beyond the study sample, should be done with utmost caution. Similar to any other cross-sectional study, current study suffered from temporal ambiguity, as both malnutrition and their predictors were assessed at the same time, hence we could only measure the correlations but interpretations supporting direct causal association were not possible.
Owing to this cross-sectional design we also could not measure or compare current versus past burden of under-nutrition among schoolchildren. In the cross-sectional design it was also not possible for us to determine the time of occurrence of anemia and its predisposing factors among participating school-children. We could not conduct detailed analyses using anaemia as an outcome owing to the fact that logistic and budgetary constraints did not allow us to measure haemoglobin level of all the subjects. The self-reported nature of the collected information in this study had the potential for information bias and possibilities of residual confounding due to unmeasured confounders were always a possibility.
Nutritional assessment studies needed longitudinal data to infer on causality of the determinants with considerable validity, but considering funding and budgetary constraints, this current study had to be restricted to this cross-sectional design, which was capable of generating at least some evidences. Owing to multistage sampling technique, this sample was considered to be a representative sample of school going children in West Bengal. Despite the aforementioned limitations we believe that based on its large, representative sampling, robust methodology and detailed analyses, this study could provide important evidences regarding the patterns and predictors of undernutrition among school-children of West Bengal.
From the findings of this study, it appeared that an appropriate community-based nutritional intervention is urgently needed in India, especially in the poor-resourced sectors, with the aim of improving community-level childhood nutritional status targeting the foodinsecure population. Corroborating with the findings of the NFHS-3, current study also indicated that parental literacy to be most important and modifiable predictors of under-nutrition among school-children. It is thus the onus on the pillars of the democracy in India to ensure ‘Right to education’ for every child in this country to empower the future generation with appropriate education and ideal nutrition.
Govt. of India need rise to the occasion with a national policy on growth and monitoring of adolescents and school children as there’s none at present. To achieve the goal, a comprehensive program with appropriate policy implication is needed to be complemented with a robust program management. Routine monitoring and analysis in a multi-institutional collaborative approach will help to identify and tackle the enormity of the existing problem. While longitudinal observation appeared to be the need of the hour for studying undernutrition among school-children, to develop a healthy India, these programs need to address gaps identified by this study especially among the young, under-privileged, rural resident, boys, who lost their mothers, had illiterate and unemployed parents, more siblings, suffered from diarrheal infections and worm infestation along with poor hygienic and sanitary practices.
Conclusion
The study explored the district-wise malnutrition scenario among primary and upper primary students in West Bengal. It is a matter of great concern that only less than one-fourth students had appropriate or ideal nutritional status and rest were in various stages of food deprivation. Strengthening of existing school meal program is needed, with emphasis on malnourished and high risk children especially in rural areas with lower parental education and poor sanitary practices. Nutritional surveillance involving above students seems to be beneficial.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Department of School Education, Government of West Bengal, India [KS. 114-ES (CMDMP) Misc 04/12 dated 19-2-2014].
The investigators are thankful to Chief Secretary, Govt. of West Bengal, Secretary, Dept. of School Education, and Project Director, Cooked Mid-Day Meal Program, Govt. of West Bengal, for providing financial and other logistic support. Investigators are also grateful to the spontaneous and sincere participation of the teachers and students and other officials.
Conflict of Interests
None declared.
References
- Pelletier DL, Frongillo EA (2003) Changes in child survival are strongly associated with changes in malnutrition in developing countries. J Nutr 133: 107-119.
- Scrimshaw NS, SanGiovanni JP (1997) Synergism of nutrition, infection, and immunity: an overview. Am J ClinNutr 66: 464S-477S.
- Shankar AH, Prasad AS (1998) Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am J ClinNutr 68: 447S-463S.
- Bhaskaram P (1992) The vicious cycle of malnutrition-infection with special reference to diarrhea, measles and tuberculosis. Indian Pediatr 29: 805-814.
- Katona P, Katona-Apte J (2008) The interaction between nutrition and infection. Clin Infect Dis 46: 1582-1588.
- Yoon PW, Black RE, Moulton LH, Becker S (1997) The effect of malnutrition on the risk of diarrheal and respiratory mortality in children < 2 y of age in Cebu, Philippines. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 65: 1070-1077.
- Schaible UE, Kaufmann SH (2007) Malnutrition and infection: complex mechanisms and global impacts. PLoS Med 4: e115.
- Gupta SS, Mohammed MH, Ghosh TS, Kanungo S, Nair GB, et al. (2011) Metagenome of the gut of a malnourished child. Gut Pathog 3: 7.
- Waterlow JC, Tomkins A, Grantham-McGregor SM (1992) Protein-energy malnutrition: Edward Arnold, Hodderand Stoughton.
- Manary MJ, Sandige HL (2008) Management of acute moderate and severe childhood malnutrition. BMJ 337: a2180.
- Rice AL, Sacco L, Hyder A, Black RE (2000) Malnutrition as an underlying cause of childhood deaths associated with infectious diseases in developing countries. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 78: 1207-1221.
- Hellwig JP, Otten JJ, Meyers LD (2006) Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements: National Academies Press.
- Govindaraju R, Venkatesan S (2010) A study on school drop-outs in rural settings. Journal of Psychology 1: 47-53.
- Abhijan SS (2014) Survey for Assessment of Dropout Rates at Elementary level in 21 States.
- NFHS-3. National Family Healthy Survey 2005-2006 India National Reports, Chapter 10 - Nutrition and Anaemia.
- Bureau NNM (2006) National Nutrition Monitoring Bureau Report -Diet and Nutritional Status of Population and Prevalence of Hypertension among Adults in Rural Areas.
- Mandal GC, Bose K (2009) Assessment of overall prevalence of undernutrition using composite index of anthropometric failure (CIAF) among preschool children of West Bengal, India. Iranian Journal of Pediatrics. 19: 237-243.
- Meshram II, Arlappa N, Balakrishna N, MallikharjunaRao K, Laxmaiah A, et al. (2012) Trends in the prevalence of undernutrition, nutrient and food intake and predictors of undernutrition among under five year tribal children in India. Asia Pac J ClinNutr 21: 568-576.
- Meshram II, Laxmaiah A, Gal Reddy Ch, Ravindranath M, Venkaiah K, et al. (2011) Prevalence of under-nutrition and its correlates among under 3 year-old children in rural areas of Andhra Pradesh, India. Ann Hum Biol 38: 93-101.
- Ray SK, Haldar A, Biswas B, Misra R, Kumar S (2001) Epidemiology of undernutrition. Indian J Pediatr 68: 1025-1030.
- Sengupta P, Philip N, Benjamin A (2010) Epidemiological correlates of under-nutrition in under-5 years children in an urban slum of Ludhiana. Health and Population: Perspectives and Issues 33: 1-9.
- Anand K, Kant S, Kapoor SK (1999) Nutritional status of adolescent school children in rural North India. Indian Pediatr 36: 810-815.
- Deb S, Dutta S, Dasgupta A, Misra R (2010) Relationship of personal hygiene with nutrition and morbidity profile: a study among primary school children in South kolkata. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 35: 280-284.
- Gomber S, Bhawna, Madan N, Lal A, Kela K (2003) Prevalence and etiology of nutritional anaemia among school children of urban slums. Indian J Med Res 118: 167-171.
- Osei A, Houser R, Bulusu S, Joshi T, Hamer D (2010) Nutritional status of primary schoolchildren in Garhwali Himalayan villages of India. Food Nutr Bull 31: 221-233.
- Srivastava A, Mahmood SE, Srivastava PM, Shrotriya VP, Kumar B (2012) Nutritional status of school-age children - A scenario of urban slums in India. Arch Public Health 70: 8.
- Al-Baradie RS, Bose ASC (2013) Portable smart non-invasive hemoglobin measurement system. Paper presented at: Systems, Signals and Devices (SSD), 2013 10th International Multi-Conference.
- Khadilkar V,Yadav S, Agrawal KK, Tamboli S (2015)Indian Academy of Pediatrics Growth Charts Committee, Revised IAP growth charts for height, weight and body mass index for 5- to 18-year-old Indian children. Indian Pediatr 52: 47-55.
Citation: Pal D, Kanungo S, Bal B, Bhowmik K, Mahapatra T, et al. (2016) Malnutrition Scenario among School Children in Eastern-India-an Epidemiological Study. Epidemiology (Sunnyvale) 6:228. DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000228
Copyright: © 2016 Sarkar K, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 15407
- [From(publication date): 4-2016 - Apr 03, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 14163
- PDF downloads: 1244