Clinical images Open Access
Low Dose Interleukin-10 and Anti-IL-1 Antibody in Modulating Intestinal Inflammation
Fioranelli M1* and Roccia MG21University B.I.S. Group of institutions, Punjab Technical University, Punjab, India
2Marconi University, Rome, Italy
- *Corresponding Author:
- Fioranelli M
University B.I.S. Group of institutions
Punjab Technical University, Punjab, India
Tel: +61 74 9232008
E-mail: massimo.fioranelli@gmail.com
Received date: November 03, 2014; Accepted date: November 20, 2014; Published date: November 22, 2014
Citation: Fioranelli M, Roccia MG (2014) Low Dose Interleukin-10 and Anti-IL-1 Antibody in Modulating Intestinal Inflammation. Interdiscip J Microinflammation 1:i101. doi: 10.4172/2381-8727.1000I101
Copyright: © 2014 Fioranelli M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Inflammation, Cancer and Integrative Therapy
Clinical Image
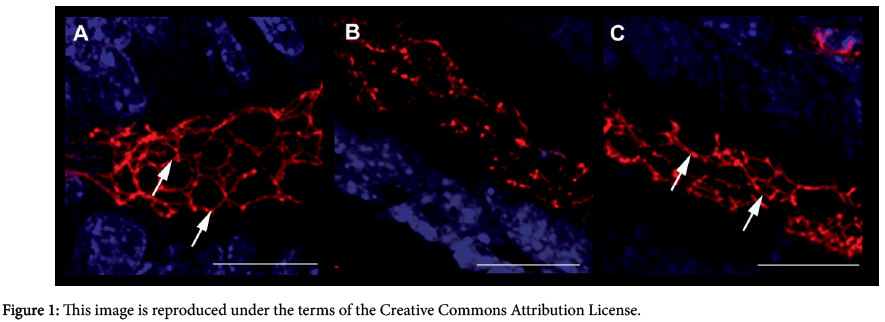
This image exemplifies the qualitative evaluation of the structural integrity of the colon which express the Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1) tight junctions (TJ) protein. The experiment were performed in order to elucidate the effects of the oral intake of a solution containing interleukin-10 and anti-IL-1 antibody in modulating intestinal inflammation induced by (Dextran Sodium Sulphate) DSS oral administration in a validated experimental murine model. Immunofluorescence staining anti-ZO-1 (in red) in colon samples of different treatment groups highlight the different epithelial barrier TJ structural integrity (arrows).
A significative example for each treatment group is shown: A (UNTR; untreated, hydroalcoholic solution only); B (DSS; DSS 2% plus hydroalcoholic solution); C (DSS+IL-10/anti-IL-1; DSS 2%+interleukin-10 plus anti-IL-1 antibody) Bars: 20 µm. This image clearly shows that mice treated with low doses of interleukin 10 and anti-IL-1 antibody were comparable to untreated mice, in terms of maintenance of an healthy epithelial structure.
--Relevant Topics
Recommended Journals
- Journal of Lung Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
- Advances in Cancer Prevention
- Breast Cancer: Current Research
- Cancer Surgery
- Immunology: Current Research
- Current Trend in Gynecologic Oncology
- Journal of Cancer Diagnosis
- Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer and Stromal Tumors
- Cervical Cancer: Open Access
- Journal of Mucosal Immunology Research
- Journal of Oncology Research and Treatment
- Journal of Orthopedic Oncology
- Journal of Prostate Cancer
- Research and Reviews on Pathogens
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 14681
- [From(publication date):
December-2014 - Jul 03, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 10087
- PDF downloads : 4594