Knowledge about Climate Change Impact and Its Adverse Effect on Household Income: A Study in the Slum Settlement of Dhaka City, Bangladesh
Received: 23-Jul-2019 / Accepted Date: 16-Aug-2019 / Published Date: 22-Aug-2019
Abstract
In Bangladesh, effects of climate change along with hazards and disaster are evident in urban areas. Increased population pressure, unplanned urbanization, and environmental pollution are compounding the risks. Urban poor, particularly children and women are the most vulnerable. Amidst decreasing income level increased the vulnerability of population. This article highlights specifically the perception of households of climate change and tries to reveal its impact on household income.
Keywords: Climate change; Pollution; Environment; Temperature
Introduction
The impact of climate change in Bangladesh is a pressing issue. This impact covers human settlement, lesser the possibility to involve in the different sources of income and at the same time hamper the present access of income source. It increases the household expenditure as well. This article highlights specifically the perception of households of climate change and tries to reveal its impact on household income. A study investigated the impact of climate change on household welfare of US and found that the household costs will increase when human being will take steps to reduce the fatal effect of extreme heat or extreme cold.
Like many other countries Bangladesh also has started to face the negative consequences of climate change and started experiencing the severity of natural hazards like tropical cyclones, landslides, river erosions, and floods [1]. People living in poverty will face a difficulty in coping with changing climate due to their limited financial resources. In the slums of Dhaka around ten thousand people live in huts with roofs made of cardboards and polythene. Higher renting cost will reduce the accessibility of renting area for the people who migrate to cities [2].
Data and Method
The article is based on analysis of data capturing the data of slums in Dhaka city. This was a part of large study held in April to June 2018. Multi-stage (cluster and simple random sampling) sample was applied to select the desired location of study [3]. Two City Corporations in Dhaka city divided where intervention of different large NGOs has been implemented for year with a number of projects. In Dhaka nine slums were selected from twenty-seven intervention slums which were situated at Ward-49 in South City Corporation and Ward 2 and 5 under North City Corporation. In Dhaka total respondents were 100 in 9 slums. Data analysis has been done using SPSS software. The present article only analyzed the data extracted from the responses of respondents of Dhaka city not the other districts.
Results
Perception about climate change impact
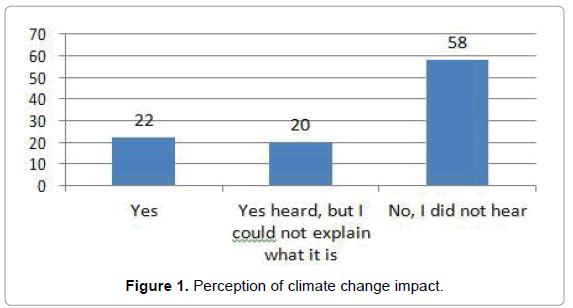
The study revealed that a total 22.1% HHs in slums heard about climate change and mentioned about it. 20% heard about climate change but can’t mentioned properly and rest of 58% never heard about climate change (Figure 1).
There are many awareness sessions were carried out by intervening NGOs in those slums however It was assumed that because they were not attending session on disaster management and climate change adaptation regularly because sessions are mainly happened in day time which was not convenient for them to attend due to involvement of household works and also go outside for their daily job. The sessions were mainly organized by different NGOs like Brac, Caritas, Plan Bangladesh, CCDB. As the respondents largely represent the marginal community so they have no other means to know about climate change. But they feel that increase temperature, increase of rain and cold and heat wave in recent years. According to them climate change impacts are given in Table 1.
| Types of Impact | Dhaka South (%) | Dhaka North (%) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of underground water layer | 4.3 | 23.2 | 13.8 |
| Increased natural calamities and decreased income | 56.5 | 32.3 | 19.2 |
| Irregular rainfall | 78.3 | 71.7 | 42.7 |
| Increased temperature | 30.4 | 87.9 | 52.3 |
| Increased pollution (Water/air) | 14.5 | 44.4 | 26.5 |
| Destroy/loss of Livelihood | 2.9 | 40.4 | 24.1 |
| Climate displacement | 2.9 | 16.2 | 9.6 |
| Increase urbanization | 5.8 | 24.2 | 14.4 |
Table 1: 1% of HHs identified possible impacts/effects of climate change.
According to this table it is observed that increased temperature (52.3%), increased diseases (43.9%), and irregular rainfall (42.7%) are significant impacts of climate change. The increased natural calamities responsible for decreased income in the study areas. The natural calamities include irregular rainfall (42.7%) and increased temperature (52.3%) [4].
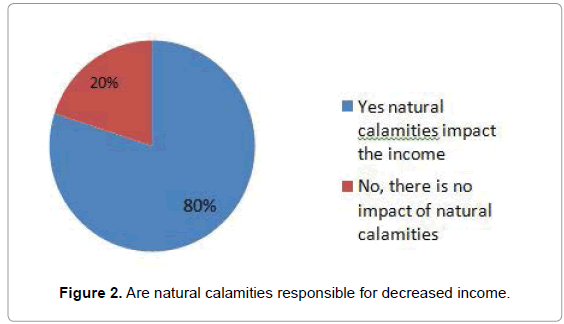
Relation between increased natural calamities and decreased income (respondents’ perception)
Almost 80% respondents agreed that due to increased natural calamities their income level was decreased gradually for years. The rainfall was longer than previous years. This hampered them to go to their job place sometimes there were irregular rainfall. This was associated with spread of different water borne diseases. Figure 2 represents the perception of respondents about the impact of natural calamities on income.
According to study findings most of the community people were not properly aware about climate change issue and they do not have clear idea about climate change, and adaptation mechanism. But they can realize climate change has impacted their income level. They can do trend analysis of impact of climate change (Such as: Increasing temperature, cold wave and irregular rainfall).
Conclusion
There were mainly three types of climate change impacts identified the present study. Perception of communities in climate change impact show that yet now they were not well aware about the impacts. However, the impact of the natural calamities in the income of the study respondents was significant. The adaptation measures taken by communities were not that much improved.
References
- Asfaw S, Arslan A, Karfakis P, Lipper L, Mortari P A (2016) Welfare impacts of climate shocks Evidence from Uganda. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations 1-68.
- Karim MR, Ishikawa M, Ikeda M, Islam MT (2012) Climate Change model predicts 33% rice yield decrease in 2100 in Bangladesh. Agron Sustain Dev 32: 821-830.
- Knox J, Hess T, Daccache A, Wheeler T (2012) Climate change impacts on crop productivity in Africa and South Asia. Environ Res Lett. 7: 034032.
- Mulwa R, Rao KPC, Gummadi S, Kilavi M (2016) Impacts of climate change on agricultural household welfare in Kenya. Clim Res 67: 87-97.
Citation: Sonia SA, Islam T (2019) Knowledge about Climate Change Impact and Its Adverse Effect on Household Income: A Study in the Slum Settlement of Dhaka City, Bangladesh. J Earth Sci Clim Change 10:524.
Copyright: © 2019 Sonia SA, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Usage
- Total views: 2285
- [From(publication date): 0-2019 - Apr 05, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1522
- PDF downloads: 763