Joint Replacements Exploits Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Received: 04-Apr-2023 / Manuscript No. roa-23-97034 / Editor assigned: 06-Apr-2023 / PreQC No. roa-23-97034 (PQ) / Reviewed: 20-Apr-2023 / QC No. roa-23-97034 / Revised: 22-Apr-2023 / Manuscript No. roa-23-97034 (R) / Published Date: 29-Apr-2023 DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000441
Keywords
Joint arthroplasty; Radiology; MRI imaging
Image Article
Joint arthroplasty is a clinical procedure that has been performed on millions of patients all over the world with great success, reducing pain and improving function. Embed disappointment, nonetheless, because of such factors as releasing, contamination or unfriendly tissue response, requires amendment medical procedure, which is related with expanded dreariness. Brief acknowledgment of difficulties around equipment is along these lines clinically applicable.
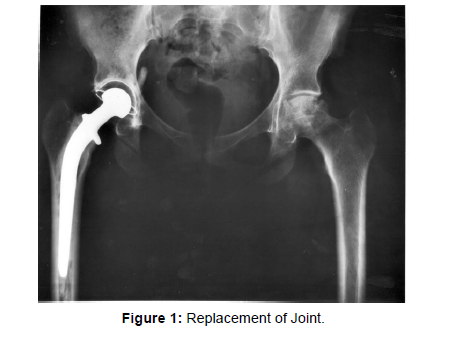
The acquisition of nonfat-suppressed, high resolution, fluidsensitive techniques that permit the detection and characterization of periprosthetic fluid collections is necessary for the optimization of pulse sequences in the presence of regional field inhomogeneity [1]. Susceptibility artifact and low signal-to-noise ratio make it difficult to use conventional MR methods. Susceptibility artifacts, such as T2* dephasing, slice and read-out encoding distortions, signal loss and inplane distortions, will be discussed in detail. Newer pulse sequences designed specifically to reduce artifacts, such as Slice Encoding for Metal Artifact Correction (SEMAC) and Multi-Acquisition Variable- Resonance Image Combination (MAVRIC) will be discussed along with a variety of techniques that reduce artifacts when visualizing both the bone and soft tissue envelope surrounding joint replacements [2]. Examples of typical complications associated with orthopaedic instrumentation and arthroplasty such as infection, loosening, adverse local tissue reaction, and neurovascular impingement, will be provided to illustrate the clinical application of these imaging techniques (Figure 1).
Data demonstrating the high predictive value of MRI as a biomarker of adverse tissue reactions to implants will be presented, as will a discussion of the biology of implant-related adverse tissue reactions.
Acknowledgement
None
Conflict of Interest
None
References
- Naraghi AM, White LM (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging of joint replacements. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 10: 98-106.
- Sofka CM, Potter HG, Figgie M, Laskin R (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 406: 129-135.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Akirha T (2023) Joint Replacements Exploits Magnetic ResonanceImaging. OMICS J Radiol 12: 441. DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000441
Copyright: © 2023 Akirha T. This is an open-access article distributed under theterms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricteduse, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author andsource are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 1006
- [From(publication date): 0-2023 - Mar 29, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 797
- PDF downloads: 209