Irinotecan-Based Regimen as Second-Line Chemotherapy for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Received: 01-Jan-2016 / Accepted Date: 28-Jan-2016 / Published Date: 12-Nov-2016 DOI: 10.4172/2476-2253.1000102
Abstract
Purpose: This study evaluates the clinical outcomes of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients who received Irinotecan-based second-line chemotherapy after platinum-based first-line therapy, especially focused on efficacy and toxicity between single-agent and doublet chemotherapy.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively reviewed 83 patients who given irinotecan-based second-line chemotherapy for extensive-stage SCLC. Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan–Meier method. The Cox proportional hazard model was used for multivariate analysis.
Results: Fifty-nine patients received doublet chemotherapy and 24 with single-agent treatment. The objective response rate (ORR) was 23.7% in the doublet group and 25% in the single-agent group (P=0.90). The disease control rate (DCR) was 65.7% and 58.3%, respectively, (P=0.71). The Progression-free survival (PFS) was 3.10 months in the doublet group and 2.10 months in the single-agent group (P=0.35). In the sensitive recurrence group, 27 patients were with doublet chemotherapy and 10 with single-agent treatment. The Median PFS was 4.73 months (95% CI: 4.37-5.09) and 3.83months (95% CI: 2.65-5.02), respectively (P=0.543). In the refractory recurrence group, there were 32 patients with doublet chemotherapy and 14 with single-agent treatment. The median PFS was 2.57 months (95% CI: 2.19-2.93) and 1.40 months (95% CI: 1.13-1.64), respectively (P=0.048). The grade III/IV toxicity in single-agent group is lower than doublet group (45.8% vs.71.2%, P=0.029). No difference was found in cancerrelated symptoms improvement between the doublet and single group (P=0.36).
Conclusion: Patients with extensive-stage SCLC could benefit from irinotecan-based second-line treatments. The refractory recurrence patients with doublet treatment obtain a moderate PFS advantage than single-agent chemotherapy.
Keywords: Small cell lung cancer; Second-line; Irinotecan; Efficacy
5018Introduction
Although SCLC is a quite chemo sensitive malignancy with overall response rates of 60–80% in patients with extensive stage disease. Most patients relapsed within a year of initial treatment and most of them eventually died from disease progression [1]. Despite the high response rates observed with first-line treatment, the median survival from the time to progression was ranged from 3 to 5 months in the second-line or further-line treatment [2-4]. In an effort to achieve higher survival rates in this destructive disease, the novel agents such as topotecan [5], docetaxel [6], paclitaxel [7], Irinotecan [8], and gemcitabine [9] have been introduced in second-line treatment.
Irinotecan is a hemisynthetic product of camptothecin and shows strong antitumor activity by inhibiting DNA topoisomerase I. A randomized phase III study comparing etoposide-cisplatin (EP) with irinotecan-cisplatin (IP) in first-line treatment Japan patients with extensive-stage SCLC showed that IP was significantly superior to EP in both response and survival [10]. Both of the EP and IP regimen are thought to be standard first-line regimens for extensive-stage SCLC now-a-days. In the second-line setting, irinotecan monotherapy and doublet chemotherapy showed a promising results in several studies. However, most of the trials were from phase II or retrospective study with a small number of patients enrolled [11-13]. The effects and toxicities data comparing the single-agent chemotherapy with doublet chemotherapy as second-line treatment are lacking.
In current study, we compare the effects and toxicities in SCLC patients treated with irinotecan monotherapy versus irinotecan plus platinum combination agent and aim to provide an information for standard second-line chemotherapy.
Methods
Patient eligibility
Two hundred and thirty-three consecutive, unselected SCLC patients, who were admitted to Zhejiang Cancer Hospital between Jan 2000 and June 2011, were received second-line chemotherapy or further treatment. Among the patients, 83 were received Irinotecan monotherapy and Irinotecan-based doublet chemotherapy. The data recorded included demographic information, clinical assessment, chemotherapy regimen and cycle, response and toxicity.
Patients who responded to initial chemotherapy and developed disease recurrence more than 3 months after the completion of chemotherapy were defined as sensitive recurrence cases, whereas patients who did not respond to initial chemotherapy or developed disease recurrence within 3 months were defined as refractory recurrence cases.
Statistical analysis
Survival was recorded from the first day of treatment to the date of death or that of the last follow-up visit. The PFS encompassed the time from the first cycle of second-line therapy to documented progression or death from any cause. The survival curves were calculated according to the method of Kaplan-Meier. The log-rank test was used to compare PFS time between the single-agent chemotherapy and combination chemotherapy. The Cox proportional model was used to evaluate various prognostic factors. Values of p
Treatment
All patients were given Irinotecan 60 mg/m2 as a 10-min intravenous infusion on day 1,8,15 every 21 days. No more than six cycles were used for patients with efficacy. Other drugs concurrent with Irinotecan was according to the package inserts of drug.
Responses and toxicity
Tumor responses were assessed with computed tomography (CT) every two cycles, or were evaluated early when significant signs of progression appeared. Objective tumor responses were according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST 1.1). Objective tumor responses include as complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD) and progressive disease (PD). Disease control rate (DCR) was defined as the addition of objective response and stabilization rates (CR+PR+SD). Objective response rate (ORR) included the CR and PR. Toxicities were checked every cycle throughout the second-line therapy. All toxicities were evaluated according to the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria version 3.0 (CTC3.0).
Follow-up
All the patients that were evaluated for the second-line tumor response had a PFS. Two patients were lost to follow-up, and their overall survival information was not included. Follow-up rate was 97.6%. The median follow-up period was 15.6 months (2.0-48). The last follow-up time was June 31, 2012.
Results
Clinical characteristics
There were 916 SCLC patients who received chemotherapy in our hospital from Jan 2000 and June 2011. Six hundred and fifteen (67.1%) patients had extensive-stage SCLC. Of these patients, 233 (37.9%) patients had received second-line for further treatment. Two hundred and twenty-one could evaluate the clinical efficacy. Irinotecan-based single or doublet accounted for 37.6% (83/221).
Characteristics of irinotecan treatment patients
The baseline patients characteristics are listed in Table 1. The median age of the patients was 57 years. As first-line chemotherapy, 75 patients (90.4%) had received platinum plus etoposide combination chemotherapy, and 8 (9.6%) had received other regimens. Thirty point one percent (24/83) of all patients in second-line received single-agent Irinotecan chemotherapy; 59 with doublet. According to the recurrence time (more than 3 months or less than 3 months), 55.4% (46/83) of the patients who received second-line chemotherapy were refractory recurrence, 44.6% with sensitive recurrence.
| Characteristics | Single-agent chemotherapy (%) | doublet chemotherapy (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| All patients | 24 (100) | 59 (100) | |
| Gender | 0.94 | ||
| Male | 21 (87.5) | 53 (89.8) | |
| Female | 3 (12.5) | 6 (10.2) | |
| Performance status | 0.28 | ||
| 0-1 | 16 (66.7) | 46 (77.9) | |
| 2 | 8 (33.3) | 13 (22.1) | |
| Age | 0.51 | ||
| Median | 58 | 57 | |
| 22 (91.7)51 (86.4) | |||
| ≥ 65 year | 2 (8.3) | 8 (13.6) | |
| Smoking | 0.64 | ||
| Never | 6 (33.3) | 12 (20.3) | |
| Ever or current | 18 (66.7) | 47 (79.7) | |
| Recurrent type | 0.73 | ||
| Sensitive | 10 (41.7) | 27 (45.8) | |
| Refractory | 14 (59.3) | 32 (54.2) | |
Table 1: Comparison between the single-agent and combination chemotherapy in the second-line treatment.
Response data and survival analysis in second-line treatment
Overall, responses included, 1 patients who got CR, 19 with PR and 33 patients had SD; accounting for ORR of 24.1% and DCR of 63.9%. Median duration of second-line treatment was 3.07 months (95% CI: 2.47-3.66), with 2.10 months in the refractory recurrence group (95% CI: 1.36-2.84), and 4.53 months in the sensitive therapy group (95% CI: 3.30-5.76) (P=0.013). The median OS from the starting of secondline treatment was 8.13 and 5.98 months in the sensitive and refractory recurrence group , respectively, (P=0.012).
Efficacy in the single-agent group and doublet group
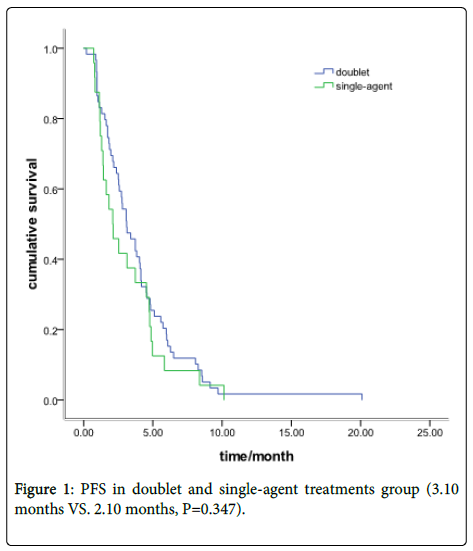
There were 59 patients received Irinotecan-based doublet chemotherapy and other 24 with single-agent treatment. The ORR was 23.7% in the doublet group and 25% in the single-agent group (P=0.90). The DCR was 62.7% and 58.3%, respectively, (P=0.71). The PFS was 3.10 months in the doublet group and 2.10 months in the single-agent group (P=0.347) (Figure 1).
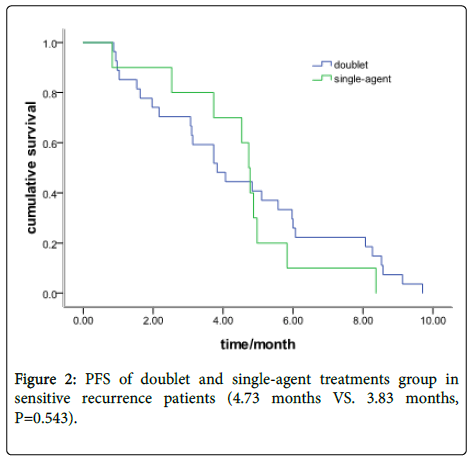
In the sensitive recurrence group, there were 27 patients with a doublet chemotherapy and 10 with single-agent treatment. The Median PFS was 4.73 months (95% CI: 4.37-5.09) and 3.83 months (95% CI: 2.65-5.02), respectively (P=0.543) (Figure 2).
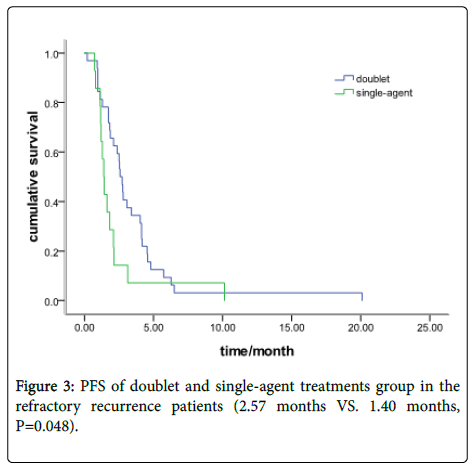
In the refractory recurrence group, there were 32 patients with a doublets chemotherapy and 14 with single-agent treatment. The median PFS was 2.57 months (95% CI: 2.19-2.93) and 1.40 months (95% CI: 1.13-1.64), respectively (P=0.048) (Figure 3). Response data for the single-agent and doublets group are shown in Table 2.
| All the patients (n=83) | Sensitive recurrence group (n=37) | Refractory recurrence group (n=59) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArmA(n=24) | ArmB (n=59) | P | ArmA(n=10) | ArmB (n=27) | P | ArmA (n=14) | ArmB (n=32) | P | |
| ORR | 6 (25) | 14 (23.7) | 0.9 | 4 (40) | 10 (37.0) | 0.87 | 2 (14.3) | 4 (12.5) | 0.76 |
| DCR | 14 (58.3) | 37 (62.7) | 0.71 | 9 (90) | 20 (74.1) | 0.296 | 5 (35.7) | 19 (59.4) | 0.14 |
| PFS | 2.1 | 3.1 | 0.347 | 3.83 | 4.73 | 0.543 | 1.4 | 2.57 | 0.048 |
| OS | 5.51 | 6.93 | 0.39 | 7.56 | 9.21 | 0.54 | 5.11 | 6.79 | 0.45 |
| ArmA: single-agent group; ArmB: doublet group; OS: from start of second-line treatment. | |||||||||
Table 2: Response data for the single-agent and doublet group in second-line treatment. ArmA, single-agent group; ArmB, doublet group; OS, from start of second-line treatment.
Univariate analyses and COX regression analysis in the second-line treatment
Univariate analyses were performed by the Kaplan-Meier method to assess the predictive capability of each variable influencing PFS of second-line treatment. Gender, age, smoking, chemotherapy regimen (single-agent or doublet treatment), were not found to be statistically associated with PFS in second-line treatment. Recurrence type, performance score (PS) and response to first-line were predictive of PFS (Table 3).
| PFS | 95%CI | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.649 | ||
| Male | 2.73 | 2.19-2.93 | |
| Female | 4.07 | 3.09-5.03 | |
| Age | 0.5 | ||
| ≥65 | 2.1 | 0.96-3.24 | |
| ?65 | 3.1 | 2.19-4.01 | |
| Response to first-line | 0.029 | ||
| Yes | 3.6 | 2.50-4.21 | |
| No | 2.3 | 1.79-3.20 | |
| Recurrent type | 0.013 | ||
| Sensitive | 4.53 | 3.3-5.77 | |
| Refractory | 2.1 | 1.36-2.84 | |
| Smoking history | 0.365 | ||
| Yes | 2.77 | 2.20-3.33 | |
| No | 3.73 | 1.72-5.73 | |
| Performance score | 0.015 | ||
| 0-1 | 3.65 | 2.54-4.12 | |
| 2 | 2.15 | 1.25-3.01 | |
| Second-line drug | 0.347 | ||
| Single agent | 2.1 | 1.02-3.18 | |
| Combination | 3.1 | 2.19-4.01 | |
Table 3: Univariate analysis of PFS in second-line treatments.
| HR | 95%CI | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.128 | 0.404-3.150 | 0.819 |
| Age | 1.023 | 0.495-2.115 | 0.951 |
| Response to first-line | 1.22 | 1.02-2.01 | 0.035 |
| Recurrent type | 0.598 | 0.365-0.981 | 0.042 |
| Smoking history | 1.347 | 0.605-2.997 | 0.465 |
| Performance score | 0.457 | 0.398-0.910 | 0.012 |
| Second-line drug | 1.22 | 0.87-1.58 | 0.32 |
Table 4: Multivariate analysis of OS in second-line treatments.
A multivariate Cox regression model was constructed with the incorporation of gender, age, smoking, PS score, response to first-line and recurrence type to evaluated the OS from the starting of secondline treatment. PS score (P=0.012), response to first-line (P=0.035), recurrence type (P=0.042), remained as independent prognostic factors, but, sex (P=0.819), age (P=0.951), smoking (P=0.465) and chemotherapy regimen (P=0.320) did not have significant influence on survival in multivariate analysis (Table 4).
Toxicity of second-line therapy
All patients in second-line treatment were assessed for toxicity. Five patients refused further therapy due to severe toxicities (one anemia, one neutropenia, three diarrhea) and four changed from doublet to single drug treatment. The overall rate of grade III/IV toxicity was 63.9%. Single-agent chemotherapy was 45.8% (11/24), and doublet group 71.2%, (42/59) .There were significant difference between single agent arms and doublet therapy group (P=0.029).
Cancer-Related Symptoms improvement
Of the 83 patients, 56 (41 in doublet and 15 in single arm) had cancer-related symptoms at initiation of second-line treatment. Most frequent symptoms included; cough (57.1%, 32/56), dyspnea (25patients), chest pain (17 patients) and other symptoms that included bone pain, hemoptysis and fatigue. Twenty-seven patients had no symptoms and disease was confirmed by imaging examination. Partial or complete symptom relief was observed in 43 patients (33 in doublet and 10 in single arm) during chemotherapy and 13 patients had no improvement. There were no difference in Cancer-Related Symptoms improvement between the doublet and single arm (P=0.36).
Discussion
The outcome showed that Irinotecan-based chemotherapy had moderated efficacy in second-line chemotherapy. Doublet chemotherapy had advantage in prolongation PFS in refractory recurrence patients, while, increasing toxicity reaction in second-line treatment. To our knowledge, this is the first study for comparing Irinotecan-based single and doublet chemotherapy in the second-line treatment of SCLC.
In practice, clinicians usually would like to use a platinum combination therapy as an option for second-line treatment in order to improve the treatment efficacy when the patients could tolerate the toxicity in non-small cell lung cancer. However, combination agent may lead to more prominent hematological toxicity and gastrointestinal reactions in some patients, which may affect patients quality of life to varying degrees. A meta-analysis in 2009 showed that combination with platinum in the second-line chemotherapy increased the PFS but not OS compared with single-agent chemotherapy in nonsmall cell lung cancer [14]. Considering the different biology characteristics, there may be some difference in second-line treatment of SCLC.
Irinotecan-based doublet chemotherapy has been investigated in several studies [15-17]. In the study conducted by Ando et al, 25 patients who had previously been treated with etoposide and a platinum-containing regimen were enrolled, and 20 patients achieved PR with IP regimen [18]. Naka et al. conducted a phase II study with weekly IC (Irinotecan and carboplatin) regimen, the ORR was 31.0% among the 29 patients, and there was no statistical significance in the response rate between the sensitive and refractory group [19]. In the study conducted by Sevinc et al., patients were treated with irinotecan. Of 46 evaluable patients, the overall response rate of 11.4% and DCR was 17.5% [20]. In current study, there was no significantly difference in ORR and DCR between the single-agent and doublet group. In the refractory recurrence group, there was an advantage in doublet than single-agent chemotherapy in prolonging PFS of second-line chemotherapy. In the sensitive recurrence group, there was no difference regardless of PFS and response rate.
The major limitations of the present study were its retrospective nature and small number of patients. Less than one third patients received single-agent Irinotecan chemotherapy. However, it provides relevant insight into the efficacy of Irinotecan-based second-line treatment of SCLC.
In conclusion, our study showed that Irinotecan-based chemotherapy had moderated efficacy in second-line chemotherapy of SCLC, the refractory recurrence patients may benefit more from the doublet therapy. Further prospective studies are warranted to elucidate any potential differences in toxicity and in efficacy between singleagent and doublet Irinotecan-based chemotherapy in extensive-stage SCLC second-line treatment.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kim DL, Song KH, and Kim SK (2008)High prevalence of carcinoma in ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration cytology of thyroid nodules. Endocr J 55: 135-142.
- Kim EK, Park CS, Chung WY, Oh KK, Kim DI, et al. (2002) New sonographic criteria for recommending fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable solid nodules of the thyroid. AJR Am J Roentgenol; 178: 687-691.
- Peccin S, de Castsro JA, Furlanetto TW, Furtado AP, Brasil BA, et al. (2002) Ultrasonography: is it useful in the diagnosis of cancer in thyroid nodules? J Endocrinol Invest 25: 39-43.
- Chan BK, Desser TS, McDougall IR, Weigel RJ, Jeffrey RB Jr. (2003) Common and uncommon sonographic features of papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Ultrasound Med 22: 1083-1090
- Moon HJ, Kwak JY, Kim MJ, Son EJ, Kim EK (2010) Can vascularity at power Doppler US help predict thyroid malignancy? Radiology 255: 260-269.
- Moon WJ1, Jung SL, Lee JH, Na DG, Baek JH, et al. (2008) Benign and malignant thyroid nodules: US differentiation--multicenter retrospective study.Radiology 247: 762-770.
- Gharib H, Papini E, Valcavi R, Baskin HJ, Crescenzi A, et al. (2006) AACE/AME task force on thyroid nodules. American association of clinical endocrinologist guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. EndocrPract 12:63-102.
- Davies L, Welch HG (2006) Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973-2002. JAMA 295: 2164-2167.
- Papini E, Guglielmi R, Bianchini A, Crescenzi A, Taccogna S, et al. (2002) Risk of malignancy in nonpalpable thyroid nodules: predictive value of ultrasound and color-Doppler features. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 87: 1941-1946.
- Horvath E, Majlis S, Rossi R, Franco C, Niedmann JP, et al. (2009) An ultrasonogram reporting system for thyroid nodules stratifying cancer risk for clinical management. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 94: 1748-1751.
- Cooper DS, Doherty GM, et al. (2009)American Thyroid Association (ATA) Guidelines taskforce on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer; Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 19:1167-1214.
- Baloch ZW, LiVolsi VA, Asa SL, et al.(2008) Diagnostic terminology and morphologic criteria for cytologic diagnostic of thyroid lesions: a synopsis of the National Cancer Institute Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration State of the Science Conference DiagnCytopathol36: 425-437
- Cibas ES, Ali SZ (2009) The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Thyroid 19: 1159-1165.
- Cibas ES, Ali SZ; NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference (2009) The Bethesda System For Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Am J ClinPathol 132: 658-665.
- Lee YH, Kim BH, Suh SI, Seo HS, Seo BK,et al. (2009) Comparison of cytological results obtained by repeated US-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsies of thyroid nodules: focus on the rate of malignancy and diagnostic concordance. Diagncytopathol37: 492-497.
- Sahin M, Gursoy A, Tutuncu NB, Guvener DN (2006) Prevalence and prediction of malignancy in cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules.ClinEndocrinol (Oxf) 65: 514-518.
- Pang T, Ihre-Lundgren C, Gill A, McMullen T, Sywak M, et al. (2010) Correlation between indeterminate aspiration cytology and final histopathology of thyroid neoplasms. Surgery 148: 532-537.
- Yoon JH, Kwak JY, Kim EK, Moon HJ, Kim MJ, et al. (2010) How to approach thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. Ann SurgOncol 17: 2147-2155.
- Miller B, Burkey S, Lindberg G, Snyder WH 3rd, Nwariaku FE (2004) Prevalence of malignancy within cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. Am J Surg 188: 459-462.
- Kim JW, Park IS, Kim BM, Kim YM, Chu YC, et al. (2007) The clinical significance of atypia in thyroid fine-needle aspiration.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264: 1053-1057.
- Chudova D, Wilde JI, Wang ET, Wang H, Rabbee N, et al. (2010) Molecular classification of thyroid nodules using high-dimensionality genomic data. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 95: 5296-5304.
- Haugen BR, Baloch ZW, Chudova D, Cibas E, Friedman L, et al. (2010) Development of a novel molecular classifier to accurately identify benign thyroid nodules in patients with indeterminate FNA cytology. Program of the 14th International Thyroid Congress, Paris, France, p 64. Abstract LB-06.
- Altman DG, Bland JM (1994) Diagnostic tests 2: Predictive values. BMJ 309: 102.
- Alexander EK, Kennedy GC, Baloch ZW, Cibas ES, Chudova D, et al. (2012) Preoperative diagnosis of benign thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. N Engl J Med 367: 705-715.
- Wang CC, Friedman L, Kennedy GC, Wang H, Kebebew E, et al. (2011) A large multicenter correlation study of thyroid nodule cytopathology and histopathology. Thyroid21:243-251.
- Lewis CM, Chang KP, Pitman M, Faquin WC, Randolph GW (2009) Thyroid fine-needle aspiration biopsy: variability in reporting. Thyroid 19: 717-723.
- Alexander EK, Schorr M, Klopper J, Kim C, Sipos J, et al. (2014) Multicenter clinical experience with the Afirma gene expression classifier. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 99: 119-125.
- Ferris RL, Baloch Z, Bernet V, Chen A, Fahey TJ(2015) American Thyroid Association Statement on Surgical Application of Molecular Profiling for Thyroid Nodules: Current Impact on Perioperative Decision Making. Thyroid25:760-768
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, et al. (2015) American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid. Oct 14.
Citation: Cheng G, Shi L (2016) Irinotecan-Based Regimen as Second-Line Chemotherapy for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Cancer Diagn 1:102. DOI: 10.4172/2476-2253.1000102
Copyright: © 2016 Cheng G, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 12579
- [From(publication date): 6-2016 - Apr 03, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 11696
- PDF downloads: 883