Imaging on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration
Received: 02-Feb-2023 / Manuscript No. roa-23-90058 / Editor assigned: 04-Feb-2023 / PreQC No. roa-23-90058 (PQ) / Reviewed: 18-Feb-2023 / QC No. roa-23-90058 / Revised: 21-Feb-2023 / Manuscript No. roa-23-90058 (R) / Published Date: 28-Feb-2023 DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000427
Image Article
Another promising area is the use of BMs represented by magnesium to repair nerve damage. Mg ion is an effective neurotransmission agent because it is involved in in vivo neurotransmission and prevents hypoxic synaptic damage, for example. Mg inhibits the production of glutamatergic excitation signals and blocks the calcium channel of the n-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor, according to the specifics of the mechanism. Numerous disorders of the nervous system, including cerebral vasospasm, Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and migraine, are linked to magnesium deficiency [1,2].
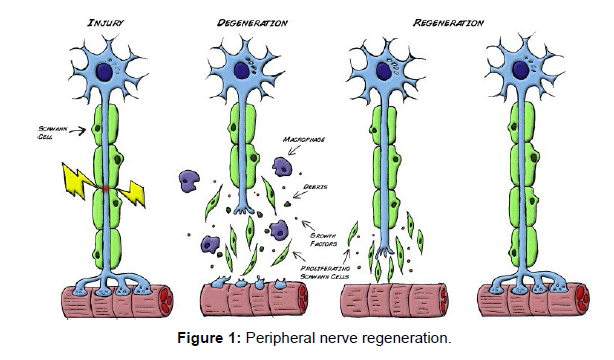
Oral or intravenous magnesium supplementation in horses has been shown to reduce symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia in in vivo studies. Peripheral neuropathy is also linked to lower serum Mg levels in type 2 diabetes. They found that ZN (Mg–2Zn–Nd) and Mg–10Li alloys have the potential to be used for nerve repair and have no obvious neurotoxicity. Mg supplementation inhibited Schwann cell apoptosis, promoted nerve regeneration and nerve structure recovery by down regulating inflammatory responses. In a similar vein, neonatal rats with sciatic nerve axotomy demonstrated that Mg solution injected subcutaneously decreased motor neuron death and increased motor unit survival (Figure 1).
Additionally by regulating mitochondrial function an appropriate concentration of Mg ions could regulate the proliferation of cultured neural stem cells. It is beneficial for nerve repair to place an Mg wire in the hollow nerve growth conduits, particularly in adult rats with injured sciatic nerves that have a small gap. Compared to a single hollow nerve conduit or a Ti wire conduit, Mg wires improved axonal parameters and were anti-inflammatory. During mandibular third molar extraction, nerve injury caused by implant operation is a common complication in the oral and maxillofacial area. Nerve injury recovery has always been a challenging clinical issue. Oral and maxillofacial nerve repair may benefit greatly from the use of magnesium.
References
- Pan HC, Sheu ML, Su HL, Chen YJ, Chen CJ, et al. (2011) Magnesium supplement promotes sciatic nerve regeneration and down-regulates inflammatory response. Magnes Res 24: 54-70.
- Zhang Q, Ji L, Zheng H, Li Q, Xiong Q, et al. (2018) Low serum phosphate and magnesium levels are associated with peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 146: 1-7.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Albert P (2023) Imaging on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. OMICS JRadiol 12: 427. DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000427
Copyright: © 2023 Albert P. This is an open-access article distributed under theterms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricteduse, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author andsource are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 1040
- [From(publication date): 0-2023 - Mar 29, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 797
- PDF downloads: 243