Case Report Open Access
Ileostomy Site Cutaneous Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma without Visceral Involvement: An Unusual Case
Ilker Ozgur1*, Emre Balik2, Ali Sahin1, Emel Dasgin3 and Ali Akyuz1
1Department of General Surgery, Acibadem International Hospital, Bakirkoy, Istanbul, Turkey
2Department of General Surgery, Koc University Hospital, Topkapi, Istanbul, Turkey
3Department of Pathology, Acibadem International Hospital, Bakirkoy, Istanbul, Turkey
- Corresponding Author:
- Ilker Ozgur, M.D.
Department of Surgery
International Hospital, Istanbul Cad. No: 82
Yesilkoy, Bakirkoy, 34149, Istanbul, Turkey
Tel: +90(536) 829 9992
Fax: +90 (212) 468 4444
E-mail: ilkerozgur@gmail.com
Received Date: July 27, 2015 Accepted Date:September 29, 2015 Published Date:October 5, 2015
Citation:Ozgur I, Balik E, Sahin A, Emel Dasgin E, Akyuz A (2015) Ileostomy Site Cutaneous Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma without Visceral Involvement: An Unusual Case. J Gastrointest Dig Syst S13: S13-003. doi:10.4172/2161-069X.1000S13-003
Copyright: ©2015 Ozgur I, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Gastrointestinal & Digestive System
Abstract
Introduction: The development of cutaneous metastasis during the course of colorectal carcinoma occurs very rarely (4% of patients with rectal carcinoma) and indicates widespread disease. The abdominal wall and perineal area are frequently the sites of cutaneous metastasis.
Case presentation: A 64-year-old woman who received series of daily radiotherapy over 30 days in 1974 due to cervical carcinoma underwent surgery for stage IIA sigmoid colon adenocarcinoma in 1995. In 2001, she underwent abdominoperineal resection, total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and left-sided end colostomy for stage IIIC distal rectal tumor. In 2004, the colostomy site changed to the right lower abdominal quadrant due to unsuccessful parastomal hernia repair in 2003. In 2008, she underwent right hemicolectomy due to stage IIA cecal tumor with end ileostomy in the right lower quadrant. In 2015, she was hospitalized due to the development of a mass at the end ileostomy site; other organ involvement was not observed. The abdominal wall and segmental small bowel were resected and an end ileostomy in the left lower quadrant was performed. Her pathology report revealed middle dermal invasion of moderately differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma at the ileocutaneous junction with clear margins.
Conclusion: Isolated skin metastasis in colorectal cancer after primary surgery occurs rarely but it must be excluded during follow-up visits by careful examination.
Keywords
Colorectal cancer; Cutaneous metastasis
Introduction
The most common sites to which colorectal carcinomas metastasize are the liver and lungs. Skin metastasis is very rare: between 4% and 6.5% of patients with colorectal carcinoma develop skin metastasis [1,2]. Its presence demonstrates widespread disease. The most common skin metastasis sites in colorectal carcinoma are the lower abdominal wall and the perineal area. The present case report describes a patient who was admitted for isolated ileostomy site metastasis 7 years after the last primary surgery.
Case Report
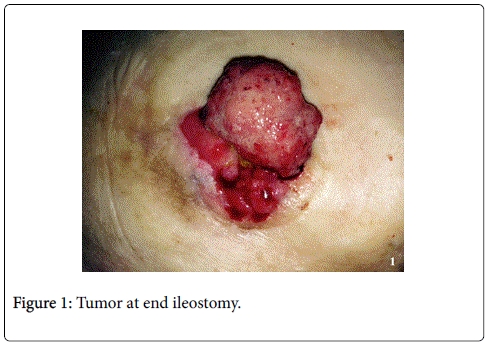
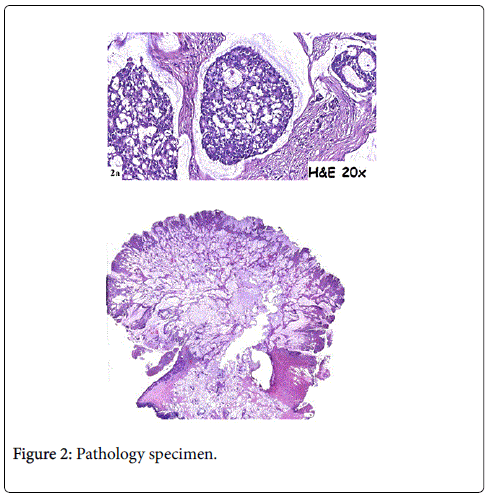
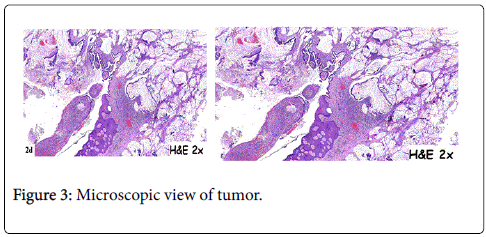
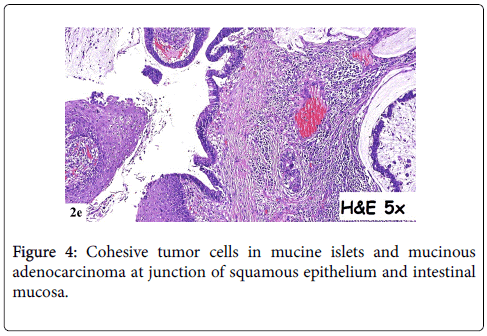
In 2015, a 64-year-old woman was admitted to hospital with a mass at a terminal ileostomy site. She did not have any pain. An examination revealed a round mass at the ileostomy site (Figure 1). Her blood tests results were nonspecific. Radiological analysis did not reveal any other pathological signs. The patient had a history of radiotherapy for cervical adenocarcinoma at 1974. Twenty years later, in 1995, she underwent anterior resection of stage IIA sigmoid colon adenocarcinoma followed by chemotherapy for 6 months. In 2001, she underwent abdominoperineal resection, total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and left-sided end colostomy for stage IIIC distal rectal tumor. This was followed by chemotherapy for another 6 months and close follow-up. In 2004, the colostomy site was changed to the right lower abdominal quadrant due to unsuccessful parastomal hernia repair in 2003. In 2008, a stage IIA cecal tumor was detected and the patient underwent right hemicolectomy with end ileostomy in the right lower quadrant. Finally, in 2015, she was admitted to hospital due to the development of a mass at the end ileostomy site; other organ involvement was not detected. Serum levels of carcinoembyonic antigen was in normal range. A biopsy of the mass revealed metastasis of adenocarcinoma. The patient underwent laparotomy via an infra-umbilical midline incision. No other signs of metastasis were observed during the exploration. The end ileostomy was excised. Moreover, 20 cm of distal ileum and 2 cm clear margins of all abdominal wall layers were included to the pathological specimen by elliptical incision around the ileostomy (Figure 2). An end ileostomy was generated in the left lower quadrant. The patient was discharged from hospital 6 days after surgery without any complications. Histopathology of the resected specimen revealed middle dermal invasion at the ileocutaneous junction by a moderately differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma. The margins were clear and lymph node invasion was not detected (Figures 3 and 4).
Discussion
Cutaneous metastasis during the course of colorectal cancer is extremely rare. The majority of cutaneous metastases occur in the abdominal wall [3], although they have also been reported to occur in decreasing order in the extremities [4], head and neck [5,6], and operative scars [7-9]. Cutaneous presentation of colorectal carcinoma is particularly uncommon when visceral metastasis is absent [8-11]. Alexandrescu et al. [12] previously reported two cases of large cutaneous and subcutaneous metastasis of colon cancer in operative scar tissues. Both cases had above normal serum levels of carcinoembyonic antigen.
To date, several mechanisms of cutaneous metastasis have been proposed. They include hematogenous and lymphatic spread, direct involvement, spread via embryonic ligaments, and seeding of exfoliated tumor cells during surgery. In our case, it remains rather unclear how, despite receiving chemotherapy and radiotherapy, the mucinous adenocarcinoma of the patient metastasized to an operative scar 7 years after multiple surgeries that changed the anatomic structure and lymphatic drainage of the abdominal wall. It seems unlikely that the cancer spread via the lymphatic system and embryonic ligaments because the many surgeries that were performed altered the lymphatic drainage of the abdominal wall. It also seems unlikely that the cutaneous metastasis reflects direct involvement because the patient was followed up for 7 disease-free years after the last surgery. It is possible the cutaneous metastasis arose because of seeding of exfoliated tumor cells during surgery, but it is unclear why it developed so many years later and why other visceral organ involvement was not seen. However, exfoliated tumor cells may turn into resting forms that become activated in the incision scar years later. Notably, Alexandrescu et al. [12] found that the tumor cells of their patients expressed high levels of epidermal growth factor receptors; and concluded that this may explain why the tumor cells adhered to the cutaneous tissue.
Thus, while rare, cutaneous metastasis can arise during the course of colorectal cancer. Patients who have a new diagnosis of colorectal cancer and patients who are being followed up should be assessed meticulously for the presence of nodules that arise in cutaneous or subcutaneous tissue. The presence of these metastatic cutaneous nodules at colorectal cancer diagnosis usually indicates a disseminated disease [4]. However, if these nodules develop in patients who have already been treated for colorectal cancer and other organ involvement is not detected, the patient may have a reasonable chance of diseasefree survival after resection of the cutaneous metastatic tumor [13,14].
Conclusion
Although metastatic lesions to the skin occur rarely in colorectal cancer, it is important to detect them as early as possible, as this will allow proper therapeutic intervention, thereby improving prognosis.
References
- Fyrmpas G, Barbetakis N, Efstathiou A, Konstantinidis I, Tsilikas C (2006) Cutaneous metastasis to the face from colon adenocarcinoma. Case report. IntSeminSurgOncol 3: 2.
- Saeed S, Keehn CA, Morgan MB (2004) Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J CutanPathol 31: 419-430.
- Davis TP, Knollmann-Ritschel B, DeNobile JW (1995) An unusual cutaneous presentation of metastatic colon carcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum 38: 670.
- Gray M, Das S (1989) An unusual presentation of colorectal carcinoma. Br J ClinPract 43: 344-345.
- Luh JY, Han ES, Simmons JR, Whitehead RP (2002) Poorly differentiated colon carcinoma with neuroendocrine features presenting with hypercalcemia and cutaneous metastases: Case report and review of the literature. Am J ClinOncol 25: 160-163.
- Stavrianos SD, McLean NR, Kelly CG, Fellows S (2000) Cutaneous metastasis to the head and neck from colonic carcinoma. Eur J SurgOncol 26: 518-519.
- Reilly WT, Nelson H, Schroeder G, Wieand HS, Bolton J, et al. (1996) Wound recurrence following conventional treatment for colorectal cancer: A rare but perhaps underestimated problem. Dis Colon Rectum 39: 200-207
- Iwase K, Takenaka H, Oshima S, Kurozumi K, Nishimura Y, et al. (1993) The solitary cutaneous metastasis of asymptomatic colon cancer to an operative scar. Surg Today 23: 164-166.
- Wright PK, Jha MK, Barrett PD, Bain IM (2003) Colonic adenocarcinoma presenting as a cutaneous metastasis in an old operative scar. J Postgrad Med 49: 157-158.
- Morton BA, Scholes J, Kral JG (1986) An unusual presentation of colon cancer. J SurgOncol 33: 92-94.
- Kilickap S, Aksoy S, Dinçer M, Saglam EA, Yalçin S (2006) Cutaneous metastases of signet cell carcinoma of the rectum without accompanying visceral involvement. South Med J 99: 1137-1139.
- Alexandrescu DT, Vaillant J, Yahr LJ, Kelemen P, Wiernik PH (2005) Unusually large colon cancer cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases occurring in resection scars. Dermatol Online J 11: 22.
- Rendi MH, Dhar AD (2003) Cutaneous metastasis of rectal adenocarcinoma. DermatolNurs 15: 131-132.
- Hashimi Y, Dholakia S (2013) Facial cutaneous metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. BMJ Case Rep 2013.
Relevant Topics
- Constipation
- Digestive Enzymes
- Endoscopy
- Epigastric Pain
- Gall Bladder
- Gastric Cancer
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Gastrointestinal Hormones
- Gastrointestinal Infections
- Gastrointestinal Inflammation
- Gastrointestinal Pathology
- Gastrointestinal Pharmacology
- Gastrointestinal Radiology
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis
- GIST Sarcoma
- Intestinal Blockage
- Pancreas
- Salivary Glands
- Stomach Bloating
- Stomach Cramps
- Stomach Disorders
- Stomach Ulcer
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 14435
- [From(publication date):
specialissue-2015 - Jul 12, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 9887
- PDF downloads : 4548