Functional Medicine: A Comprehensive Approach to Optimal Health
Received: 01-Sep-2023 / Manuscript No. JHAM-23-106224 / Editor assigned: 04-Sep-2023 / PreQC No. JHAM-23-106224 (PQ) / Reviewed: 18-Sep-2023 / QC No. JHAM-23-106224 / Revised: 22-Sep-2023 / Manuscript No. JHAM-23-106224 (R) / Published Date: 29-Sep-2023 DOI: 10.4172/2573-4555.1000394
Abstract
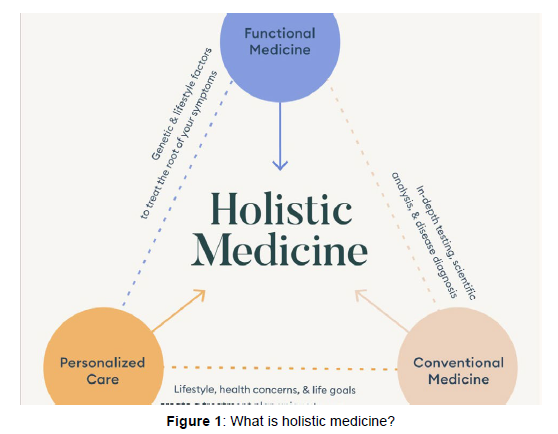
Functional medicine has emerged as a transformative approach to healthcare, offering a comprehensive and personalized framework for achieving optimal health. Unlike traditional medicine, traditional medicine focuses on uncovering and addressing the root causes of illness rather than merely treating symptoms. This article provides an overview of functional medicine, its core principles, and the benefits it offers. It highlights the patient-centered approach, systems biology perspective, and individualized treatment plans that characterize functional medicine. The article also explores the preventive care aspects of functional medicine, emphasizing the importance of proactive lifestyle modifications. Additionally, it examines the integration of conventional and alternative therapies within functional medicine, showcasing the potential for comprehensive healing. The applications of functional medicine in chronic disease management, optimal aging, and mental health are discussed, showcasing its versatility and potential impact. Overall, functional medicine represents a paradigm shift in healthcare, empowering individuals to take an active role in their health and promoting long-lasting well-being. In functional medicine, an individual's genetic and environmental details are obtained thus providing in-depth knowledge of the patient's health status. Holistic medicine is a form of healing that considers the whole person body, mind, spirit, and emotion in the quest for optimal health and wellness
Keywords
Traditional medicine; Functional medicine; Environmental; optimal health
Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, a growing number of individuals are seeking a more comprehensive approach to their well-being. Functional medicine, a discipline gaining significant attention, offers a holistic framework that goes beyond merely treating symptoms. It focuses on uncovering the root causes of illness and aims to restore balance in the body's systems. This article explores functional medicine as a transformative approach to achieving optimal health and addresses its core principles, benefits, and potential applications [1]. Functional medicine views the human body as an interconnected web of biological systems that work together to maintain health. Rather than isolating symptoms or diseases, this approach recognizes the intricate relationships between genetics, lifestyle, environment, and individual health. It embraces the concept of personalized medicine, recognizing that each person's unique biological makeup requires tailored treatment plans [2].
A major premise of Functional Medicine is that, using science, clinical wisdom, and innovative tools, we can identify many of the underlying causes of chronic disease and intervene to remediate the dysfunctions, both before and after frank disease is present [3]. People may wonder why preventing and treating chronic disease effectively requires something different than is usually available in our very expensive healthcare system Perhaps the most urgent reason is that a rapidly spreading epidemic of chronic disease has compromised the effectiveness of our healthcare system and threatens to bankrupt both national and global economies. Alarming projections suggest future generations may have shorter, less healthy lives if current trends continue unchecked. Our current healthcare model fails to confront both the causes of and solutions for chronic disease and must be replaced with a model of comprehensive, personalized care geared to effectively treating and reversing this escalating crisis [4 ].
Methodology
Core principles of functional medicine
Patient-centered care: Functional medicine emphasizes a partnership between patient and practitioner, valuing the patient's experiences, concerns, and goals. This approach encourages active participation in the healing process.
Systems biology approach: Instead of focusing on individual organs or symptoms, functional medicine analyzes the underlying dysfunctions within the body's systems. By addressing the root causes, functional medicine aims to restore balance and promote long-term health [5].
Individualized treatment: Recognizing the uniqueness of each individual, functional medicine practitioners design personalized treatment plans. These plans consider the patient's genetics, lifestyle factors, environmental influences, and specific health challenges.
Integrative approach: Functional medicine integrates the best of both conventional and alternative therapies. It combines evidencebased practices with natural and holistic approaches, seeking to provide the most effective and least invasive treatments [6].
Benefits of functional medicine
Addressing the root causes: Functional medicine strives to identify the underlying factors contributing to illness rather than solely focusing on symptoms. By addressing the root causes, it offers the potential for long-lasting healing and improved overall health [7].
Preventive care: Functional medicine places great emphasis on prevention, helping individuals make lifestyle modifications that promote optimal health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Personalized treatment: With its patient-centered approach, functional medicine recognizes that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. It tailors treatment plans to address the unique needs of each individual, optimizing their chances for success.
Collaboration and education: Functional medicine encourages collaboration between patients and practitioners. It empowers individuals with knowledge about their own health, fostering self-care and proactive decision-making [8].
(Figure 1)
Applications of functional medicine
Chronic disease management: Functional medicine has shown promise in managing chronic conditions such as autoimmune disorders, gastrointestinal issues, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic diseases. By addressing the underlying dysfunctions, it aims to improve patients' quality of life [9].
Optimal aging: Functional medicine offers strategies to promote healthy aging and mitigate age-related conditions. It focuses on preserving vitality, cognitive function, and physical well-being throughout the aging process.
Mental health and wellness: Functional medicine recognizes the intricate connection between mind and body. It provides an integrative approach to mental health, addressing factors like nutrition, gut health, hormone balance, and environmental influences [10].
(Figure 2)
Conclusion
Functional medicine represents a paradigm shift in healthcare, offering a comprehensive and personalized approach to achieving optimal health. By delving into the root causes of illness, it aims to restore balance and empower individuals to take an active role in their own well-being. With its emphasis on collaboration, education, and preventive care, functional medicine holds the potential to transform our healthcare system, leading to improved outcomes and a greater focus on holistic healing. Drug discovery and development is the most important strategy for the prevention and treatments of the complex diseases, functional natural product are currently still dominant players in the kingdom of the patient drugs, approximate 60–70% approval drugs are natural product derived therapeutic preparations . Basically, traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) are basically composed of many medicinal plants, which are well developed by ancient Chinese. The functional medicine model of care offers a patient-centered approach to chronic disease management. It seeks to answer the question, “Why are you ill?” so you can receive personalized, effective care for your needs. Functional medicine providers spend time listening to you and gathering your medical history. Functional medicine aims to optimize the functioning of the individual's organs and tissues and to heal and help prevent diseases associated with aging. This may involve correcting an imbalance of natural substances within the body.
References
- Brito FMS, Bortoletto Júnior G, Paes JB, Belini UL, Tomazello-Filho M (2020) Technological characterization of particleboards made with sugarcane bagasse and bamboo culm particles. Constr Build Mater 262:120501.
- Aydin I, Demirkir C, Colak S, Colakoglu G (2017) Utilization of bark flours as additive in plywood manufacturing. Eur J Wood Prod 75:63-69.
- Rajeshkumar G, Seshadri SA, Devnani GL, Sanjay MR (2021) Environment friendly, renewable and sustainable poly lactic acid (PLA) based natural fiber reinforced composites-A comprehensive review. J Clean Prod 310:127483.
- Pędzik M, Janiszewska D, Rogoziński T (2021) Alternative lignocellulosic raw materials in particleboard production: A review. Ind Crops Prod 174:114162.
- Lee SH, Lum WC, Boon JG (2022) Particleboard from agricultural biomass and recycled wood waste: A review. J Mater Res Technol 20:4630-4658.
- França WT, Barros MV, Salvador R (2021) Integrating life cycle assessment and life cycle cost: A review of environmental-economic studies. Int J Life Cycle Assess 26:244-274.
- Hammiche D, Boukerrou A, Azzeddine B (2019) Characterization of polylactic acid green composites and its biodegradation in a bacterial environment. Int J Polym Anal Charact 24:236-244.
- Couret L, Irle M, Belloncle C (2017) Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from post-consumer wood fiberboard waste. Cellulose 24:2125-2137.
- Haag AP, Maier RM, Combie J (2004) Bacterially derived biopolymers as wood adhesives. Int J Adhes 24:495-502.
- Soubam T, Gupta A, Sharma S (2022) Mechanical property study of plywood bonded with dimethylol dihydroxy ethylene urea crosslinked rice starch-natural rubber latex-based adhesive. Mater Today Proc.
Citation: Rochev Y (2023) Functional Medicine: A Comprehensive Approach toOptimal Health. J Tradit Med Clin Natur, 12: 394. DOI: 10.4172/2573-4555.1000394
Copyright: © 2023 Rochev Y. This is an open-access article distributed under theterms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricteduse, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author andsource are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 564
- [From(publication date): 0-2023 - Dec 22, 2024]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 492
- PDF downloads: 72