Epidemiological Study Investigating the Main Biochemical Profile Related To Neonatal Jaundice in Department of Pediatrics in Zaliten Teaching Hospital in Libya
Received: 01-Nov-2022 / Manuscript No. nnp-22-79908 / Editor assigned: 03-Nov-2022 / PreQC No. nnp-22-79908(PQ) / Reviewed: 17-Nov-2022 / QC No. nnp-22-79908 / Revised: 23-Nov-2022 / Manuscript No. nnp-22-79908(R) / Accepted Date: 23-Nov-2022 / Published Date: 29-Nov-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2572-4983.1000270 QI No. / nnp-22-79908
Abstract
Jaundice caused by indirect neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (INH) is a common and a frequent cause of neonatal cases admitted to health care facilities all over the world. The main aim of this descriptive cross-sectional study is to determine the relationship between biochemical profiles with neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. We examined infants who are admitted to the in Department of Pediatrics at Zaliten hospital for jaundice. Simple random sampling is used to evaluate variables related to maternal and neonatal main biochemical profile related to Neonatal Jaundice based on clinical files. The study found correlation between weight, blood group, haemoglobin and hematocrit with total bilirubin level.
Keywords
Neonatal Jaundice; Hyperbilirubinemia; Biochemical profile; Bilirubin
Introduction
Jaundice caused by indirect neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (INH) is a common and a frequent cause of neonatal admission to health care facilities all around the world.
The main aim of this descriptive cross-sectional study is to determine the relationship between biochemical profiles with neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
The term ‘jaundice’ is used to describe the yellow-orange discoloration of the skin and sclera because of excessive bilirubin in the skin and mucous membranes [1-2]. Jaundice itself is not a disease but rather a symptom or sign of a disease. Bilirubin is mainly formed when the hem component of red blood cells are broken down in the spleen to biliverdin and then unconjugated bilirubin.3 Bilirubin is not water soluble, so that it is transferred via the bloodstream from the spleen to the liver and finally bound to the plasma protein, albumin. This form is known as conjugated bilirubin, that is then secreted into the gall. In the gut it is further metabolized to other gall pigments and then excreted in the faeces [3].
The mechanism of neonatal jaundice is the imbalance between bilirubin production and conjugation, which results in increased bilirubin levels. [4] This imbalance is mainly because of the immature liver of the neonate and the rapid breakdown of red blood cells, which may be multifactorial. [3-6] based on the present evidence, 80% of premature infants have clinical symptoms, including yellowish skin and sclera, caused by serum bilirubin levels [7-9].
It usually occurs on the second day of birth, is not harmful and a self- limiting disease. It mostly improves without the need to medical interference after reaching the normal amount of bilirubin [6-10].
Materials and Methods
A total of 27 infants admitted to the in Department of Pediatrics at Zaliten hospital for jaundice were enrolled in the current study.
Random sampling is used to evaluate variables related to maternal and neonatal main biochemical profile including full blood count, Liver function test, blood group and balancer for weight measurement.
Results
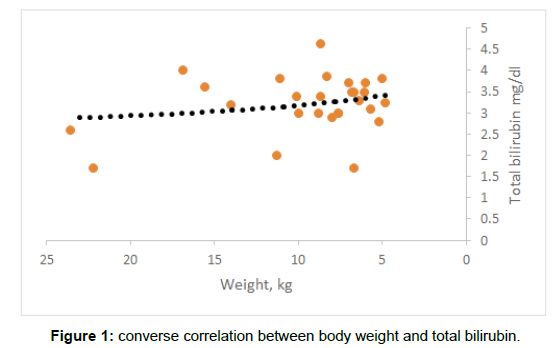
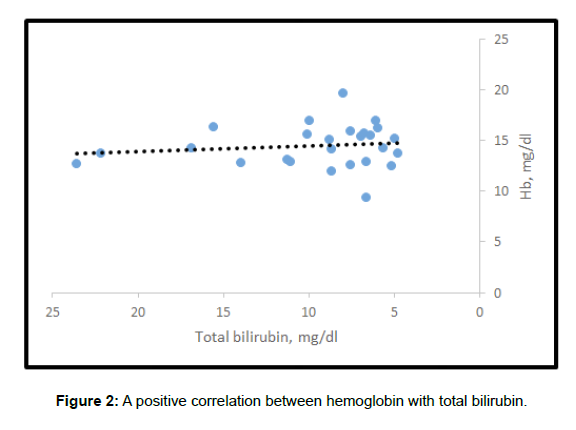
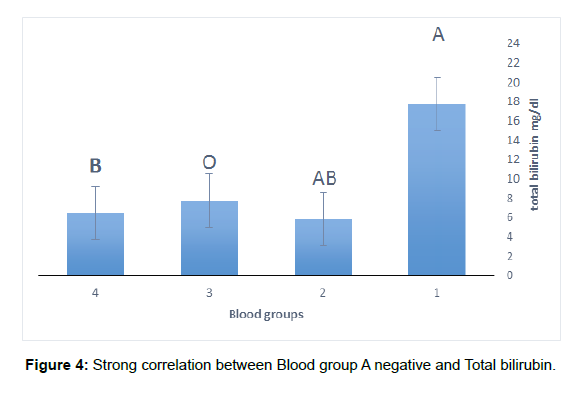
The study found that there is converse correlation between body weight and total bilirubin. As the body weight increases, the total bilirubin decreases. (Figure 1) Additionally, a positive correlation was recoded between haemoglobin with total bilirubin, as the haemoglobin increases the total bilirubin increases (Figure 2). The study found positive correlation between hematocrit and total bilirubin, as the haemoglobin increases the total bilirubin increases (Figure 3). The study showed that then is strong correlation between Blood group A negative and Total bilirubin in comparison with other blood groups in the study (Figure 4) (Table 1).
| Blood groups | A- | AB- | O+ | B+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total bilirubin | 17.68 | 5.8 | 7.7375 | 6.5 |
| Std deviation | 5.428352 | 1.414214 | 2.101658 | 1.609348 |
Table 1: Total bilirubin in comparison with other blood groups.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The study found correlations between body weight, blood groups, haemoglobin and hematocrit with total bilirubin level. Diagnosis, treatment prevention of neonatal jaundice should be considered as the main policy in all health care settings of the country. Therefore, identification of factors affecting the incidence of jaundice can be effective in preventing susceptible predisposing factors in newborns and high-risk mothers. Therefore, we recommend that this study is expanded to include other Libyan cities and increase the sample size.
References
- NICE (2010) Neonatal jaundice. Clinical guideline 98, London: Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists.
- Khan RS, Houlihan DD, Newsome PN (2015) Investigating jaundice. Medicine 43: 573–576.
- Brown SB, King RF (1978) The mechanism of haem catabolism. Bilirubin formation in living rats by [18O] oxygen labelling. Biochem J 170: 297.
- Kaplan M, Muraca M, Hammerman C (2002) Imbalance between production and conjugation of bilirubin: A fundamental concept in the mechanism of neonatal jaundice. Paediatrics 110: e47.
- Rennie J, Burman-Roy S, Murphy MS (2010) Guideline Development Group. Neonatal jaundice: Summary of the NICE guidance. BMJ 340: 2409.
- Maisels MJ, Kring E (2006) The contribution of hemolysis to early jaundice in normal newborns. Pediatrics 118: 276–279.
- Newman TB, Xiong B, Gonzales VM, Escobar GJ (2000) Prediction and prevention of extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in a mature health maintenance organization. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 154: 1140–1147.
- Watchko JF (2009) Identification of neonates at risk for hazardous hyperbilirubinemia: emerging clinical insights. Pediatr Clin North Am 56: 671–687.
- Stoll BJ, Kliegman RM (2007) Jaundice and hyperbilirubinemiain the newborn, Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 18th ed. Philadelphia. Saunders 592-598.
- Fanaroff AA, Martin RJ (1987) Neonatal-perinatal medicine: diseases of the fetus and infant.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at , Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Abushhewa MEL, Alati RMO, Salem AE, Abusittah WRA, Mohsen RW, et al. (2022) Epidemiological Study Investigating the Main Biochemical Profile Related To Neonatal Jaundice in Department of Pediatrics in Zaliten Teaching Hospital in Libya. Neonat Pediatr Med 8: 270. DOI: 10.4172/2572-4983.1000270
Copyright: © 2022 Abushhewa MEL, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Conferences
42nd Global Conference on Nursing Care & Patient Safety
Toronto, CanadaRecommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 1954
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Apr 01, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1603
- PDF downloads: 351