Enviro-Technological Perspectives on Climate Change Mitigation in Urban and Rural Environments
Received: 01-Sep-2023 / Manuscript No. . EPCC-23-105016 / Editor assigned: 04-Sep-2023 / PreQC No. . EPCC-23-105016 (PQ) / Reviewed: 18-Sep-2023 / QC No. . EPCC-23-105016 / Revised: 21-Sep-2023 / Manuscript No. . EPCC-23-105016 (R) / Published Date: 28-Sep-2023 DOI: 10.4172/2573-458X.1000351
Abstract
In this article enviro-technological perspectives on climate change mitigation in urban and rural environments are discussed. The entrepreneurship development through green economical model for sustainable entrepreneurship is designed and developed for an efficient and effective solid and hazardous waste management prior to environmental impact assessment (EIA) process. The Resource Conservation and Reecovery (RCRs) and EIAs are designed and developed to protect the environment during the post COVID-19 World. Strategic environmental assessment (SEA) process can be broadly defined as a study of the impacts of a proposed project, plan, project, policy or legislative action on the environment and sustainability. The root cause problem solution for ozone layer depletion potential (OLP) impact, global warming potential (GWP) impact and green house synergic (augmentative) gas (GHG) emissional impacts of 57 Giga tons of Carbon dioxide equivaenent in context to generic, source specific and industrial specific plants are measured, monitored and mitigated by international environmental impact assessment process for the sustainable environmental climate change and control. In this research, SEA process has been aimed in order to incorporate environmental and sustainability factors in to project planning and decision making (PPDM ) process such as project formulation and appraisal of Indo-Matsushita midget electrode (battery carbon rod) plant in 1979 at Tada that included policies, programs, plans and legislative actions. Sustainable entrepresurship development is a kind of development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability and efficacy of future generations to meet their own needs. Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process can be defined as the systematic study and check of the potential impacts (effects) of proposed projects, plans, programs, policies or legislative actions relative to the physicalchemical, biological, bio-physical, radio-active and cultural, and socioeconomic components of the total environment. The primary purpose of the EIA process is to encourage the consideration of the environment in organizational project planning and decision-making process and to arrive at actions that are environmentally compatible. PCPPDM process should include the integrated consideration of technical or engineering, economic, environmental, safety, and health, social and sustainability factors to achieve business excellence. The objective of the study is to conceptualize and develop SEA process for the climate change and environmental pollution control and a course module is developed entitled “BIPARD training and research course module” on pollution, climate change, afforestation and global warming control. The design of the study is cross sectional. Environmental Health Impact Assessment (EHIA) process has been conducted for petroleum and petrochemical, mining and nuclear power plant to consider the environmental quality, safety and health impacts to mitigate psychological health effects on workers and nearby residents. Social Impact Assessment (SIA) process can be defined as the systematic identification and evaluation of the potential social impacts (effects) of proposed projects, plans, programs, or legislative actions such that social consideration is encouraged in process and to arrive at actions that are socially compatible with reference to a sustainable sanitation project. SEA process concerns to environment and sustainability effects in process and arrive at proposed projects, plans, programs, and legislative actions that are compatible with respect to environment and sustainability issues. International EIA process required multi-disciplinary approach that has been conducted very early stage of Japanese Matsushita carbon rod project in 1982 for strategic environmental assessment. The paper highlights SEA process conducted for certain projects that based on operation and process approach and associated studies for sustainable development. Engineering hybrid lifecycle analysis (LCA) has been conducted for identifying and measuring the impact of petrochemical and corroded engineering structural products on the environment and sustain efficacy by means of mass and energy balance methods in M/S Madras Fertilizers Limited, Manali, Chennai, India. LCA considers the activities related to raw materials, transformation, ancillary materials, equipment, method, market, man power, production, use, disposal and ancillary equipment. As far as generic, spurce specific and industrial safety is concerned personal protective equipments and materials (PPEMs) that include garments, clothing, gloves, safety shoes, hard hats, safety glasses, shields, respirators, full aprons, safety belts, and other safety items which have to be used by an individual. Such equipment is important for personal protection and for safety. It is the manager’s and supervisor’s responsibility to ensure that they are used. The enactment of worker’s compensation law and occupational disease law shall increase materially the cost of insurance to industry. The increased cost and the certainty with which it is applied will put a premium on accident-prevention work. This cost can be materially reduced by the installation of safety devices. RCR research experience has shown that approximately 80% of all the generic, source specific and industrial accidents are preventable. EIA and EHIA processes have been conducted for a nuclear power plant to consider the safety and health impacts to mitigate psychological health loadings on workers and nearby residents. SEA system is a potentially useful element of good environmental management and sustainable development; however, as currently practiced in generic, source specific and industries, it is far from perfection. Emphasis should be given in generic, source specific and industries on maintaining economic viability of the operation, while in turn taking care to preserve the ecological and social sustainabilities of the country. International EIA process required multi-disciplinary approach that has been conducted very early stage of Indo-Matsushita Midget electrode project 1982 at Tada for technical, economic, ecological and social sustainablities.
Keywords
Conservation; Resource; Recovery; Education; Embed; Enetreprenership; Environment; Generic quality; Industry; Management; Source; Sustainability
Introduction
In this article enviro-technological perspectives on climate change mitigation in urban and rural environments are discussed. RCR method has been devised prior to the conduction of environmental impact assessment (EIA) process. The RCRs and EIAs are hybrid methods to protect the environment during the post COVID-19 World. Three of the significant terms while complying with the requirements of NEPA process are “environmental inventory”, “environmental impact assessment process”, and “environment impact statement”. EIAs of resource conservation and recovery of industries were undertaken in order to protect environment during the year 1950 in Japan, Europe and North America [1, 2]. The purpose of the EIA process is to encourage the consideration of the environment in organizational planning and decision-making process. Historically, the choice of proposed projects, policies, plans, programs, permits, procedures or legislations was primarily based on only one criterion called economic viability. Today, it is necessary to consider three criteria of economic, environmental and social viabilities in order to prevent global warming and ozone layer depletion potential. Integrated solid and hazardous waste management method for recycling of generic, source specific and industrial waste is recommended for climate change and control. Environment quality management (EQM) is a generic, source specific and industrial integrated solid waste management approach that was the targeted research area in order to achieve sustainable socioeconomic based on the triple bottom-line approach (economical, environmental and social) feasibility studies .
Climate and weather changes are serious threats and should be controlled effective, efficient and combined managerial approach. The world has been experiencing extreme weather events due to climate crisis for about 90% of the days. Though the year, different parts of the world reeled in floods, heat waves, and cyclones giving adverse environmental health effects on plant, animal and human health. Global temperatures are now not to breach 1.5 ℃ of warming within the next five years as per the EI Nino, Neutral and La Nina phenomena.
In 2023, India experienced 365 days of extreme weather events like heat waves, cold waves, heavy rains, floods, cyclones, landslides, thunderstorms and lightening and others. As per the publication and citation of techno-economic-environmental impact study and check conducted, extreme climate and weather will become increasingly intense and frequent. The damage that this would cause to our ecosystems will be irreversible. National climate policy act (NCPA) process is suggested that will integrate different policies and laws to protect environment, climate, weather, biodiversity and sustainable development of its people as the climate change is real and need to be controlled.
Climate Change is a serious threat and should be controlled effectively and efficiently by conducting Environmental Health Impact Assessment (EHIA) process. Green chemistry is discussed titled ‘Indian cotton double roller (DR) ginning industries using chrome composite leather clad (CCLC) rollers and design and development of green chemistry rollers towards sustainable industrial development (SID)’. SID can be defined as the industrial development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability and efficiency of future generations to meet their own needs. “Environmental Impact Assessment Process “(EIA process) can be defined as the systematic identification and evaluation of the potential impacts (effects) of proposed projects, plans, programs, or legislative actions relative to the physical-chemical, biological, cultural, and socioeconomic components of the total environment. The objective is to conduct Environmental health impact assessment (EHIA) process that is to systematically identify and evaluate potential environmental health impacts of CCLC rollers used in Indian CCLC double roller (DR) ginning industries with relative to the physical -chemical and biological can be referred as entitled “natural or biophysical environment” and the cultural and socioeconomic environment represents entitled “manmade environmental components” of the total environment. The systematical identification and evaluation of bio-accumulation and biomagnification environmental health effects of climate change on soil and plants including cotton seed plants completed. Investigation has been done for such health effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) such of those harmful substances in Pumpkins, Bt Cotton , viz., Fluorene, Phenanthrene, Acenaphthylene, Acenaphthylene and Acenaphthene of about 10 ppm in mg/Kg as PAHs (MAC : 0.1 mg/kg) .
Most of the cotton ginning operations are performed by using DR ginning machines which serve an important role in the Indian cotton ginning industries. The rollers used are made of CCLC covering fixed to a shaft. The CCLC contains about 18,000 to 36,000 mg/kg (ppm) (1.8%-3.6%) of chromium particles. The chromium stabilizes the CCLC by cross linking the collagen fibres in chromium leather tanning industries. Chromium salts, especially chrome alum and chromium (III) sulfate are used in chromium-tanning of leather. Chromium tanned leather contains between 3 to 5% of chromium, which is tightly bound to the proteins. For certain types of projects, such as nuclear power plants, it may be necessary to address psychological impacts on nearby residents as per reference entitled “Can Change Damage Your Mental Health?” Nature, Volume 295, January 21, 1982, pp.177- 179 for the necessity to address psychological impacts on nearby residents and reference entitled “An Environmental Health Impact Assessment (EHIA) process” published by World Health Organization (WHO) titled ‘Health and Safety component of Environmental Impact Assessment ‘from WHO publication, Copenhagen in 1987”. Although the form of chromium used for tanning is not toxic hexavalent variety, there remains interest in the management of chromium in the tanning industry such as recovery and reuses, direct / indirect recycling, use of less chromium or ‘chrome-less tanning is need to be practiced to better manage chromium in tanning with respect to green chemistry. Chromium salts or chromates in contact with skin, lungs and stomach result in dermatitis and lung and esophagus cancer and brain tumor among Indian gin and textile mill workers. Brief or occasional contact may not pose a problem. Potassium dichromate is a chromium salt or chromate and is a common metal making up a significant part of the earth’s crust. The most common home exposure of chromate is leather. The majority of leather goods, including shoe and gloves, are tanned with chromates. It is necessary to avoid chromate tanned leather gloves, and shoes. Vegetable tanned leather gloves and shoes or plastic shoes and Oak Bark -Tanning in the traditional manner is recommended compare to chromate tanned leather. For those with shoe dermatitis from chromate and leather, wearing heavy socks or reducing perspiration and moisture may help to reduce dermatitis. The amount of chromium found in all skin layers due to chromium permeation through human skins in diffusion cells. In ginning factories, when the seed-cotton is processed in DR ginning machine, the lint cotton is contaminated with hexavalent and trivalent chromium dust of about 140 to 1990 mg/kg (ppm) , Cr (VI) and Cr(III) which is carcinogenic substance against the safe limits of 0.1 ppm. Ion chromatographic method and atomic absorption spectrometry method are employed for determining chromium content in all samples and Chromium (VI) found more with increased total chromium concentration in samples due to increasing level of application of potassium dichromate and is found cancer among all skin dermatitis workers. The percentage of chromium found During the cotton ginning process due to persistent rubbing of CCLC over stationary knife the chromium particles are adsorbed into lint cotton such that the spun yarns and woven fabrics get contaminated about 100 to 200 ppm which according to ecostandards should not be more than 0.1 ppm. The CCLC rollers used in cotton roller ginning machines get powdered during the ginning process. As chromium is a specific dust, gin and mill workers and residents are directly exposed to this carcinogenic substance and are vulnerable to environmental health hazards. To offset this problem, pollution-free eco-friendly washers/rollers both for laboratory and commercial studies have been fabricated and experimented. Green chemistry attempts are made to alternate dust-producing grinding CCLC ginneries. Environmental health inventory (EHI) serves as the basis for evaluating the potential environmental health impacts both beneficial and adverse of a proposed action. Environmental health impact statement (EHIS) describes the affected environmental health or environmental health setting without the project.
Green Design and development of the EHI is an initial step in the EHIA process of climate control as the climate change is real.
It is concluded that EHIA process (CCPA) as green chemistry is conducted for certain projects, plans, programs, legislative actions, policies in the project planning and decision-making process.
Materials and Methods
SEA process is a predictable process that is devised in to two phases. The first phase is called initial environmental and sustainability evaluation (IESE) and the second phase is environmental and sustainability impact studies (ESIS). IESE has been carried out for Japanese Matsushita carbon company’s proposed project, plan, program, policy, permit, procedure, and legislative action in India to determine whether potentially adverse effects on environment and sustain efficacy with respect to physical, chemical, biological, petrochemical , economical, socio-economic environment and on human health and well-being are significant or whether mitigation measures can be adopted to reduce or eliminate adverse environmental and sustainability impacts. Detailed SEA procedure can be called as ESIS that was applied to identify and evaluate the environmental and sustainability consequences both beneficial and adverse impacts in order to ensure that the environmental and sustainability impacts were taken in to consideration in organization’s planning and decision making process. SEA process is designed to identify and predict the potential impacts of the physical, biological, ecological, socioeconomic, cultural environment and on human health and wellbeing are adequately protected. Given below some of the methods and techniques applied for the sustainable project formulation for the various projects such as midget electrode (Battery carbon rod) project, generic, source specific and industries, nuclear power plant integrated solid and hazardous waste management approach.
1. Expert judgment and stakeholders’ sentiments
2. Check list and matrices
3. Multi criteria analysis
4. Case comparisons
5. Simulation models
6. Software and information system
7. Questionnaires
8. Group discussions
9. Delphi approach
10. Flow charts and decision trees
11. Contingency analysis
12. Overlays
13. Fuzzy logics
Environmental quality and sustainability compliance requirements have been identified and evaluated systematically in these projects.
Step-wise structure of sea process
SEA Process is given by the following nine steps.
1. Preliminary activities and decision of Terms of References (TOR)
2. Scoping
3. Study of baseline data
4. Strategic environmental assessment and evaluation,
5. Evaluation of alternative measures
6. Assessment of alternative measures
7. Preparation of final documents
8. Decision-making
9. Monitoring, measurement and control opportunities for resource transformation and project implementation and its strategic environmental assessment process.
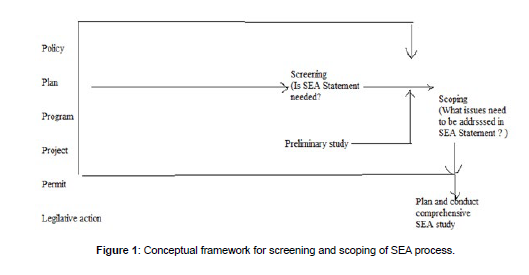
Conceptual framework for screening and scoping of sea process
Screening and scoping processes are the items which are employed in the SEA processes.
(Figure 1)
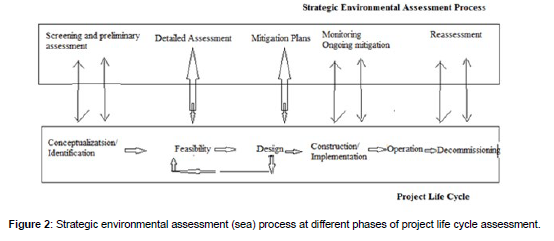
Three most significant items are,” Strategic environmental assessment inventory, environmental impact assessment, strategic environmental impact assessment statement. Generic, source specific and industrial planning and decision making process should include the integrated environmental quality consideration of technical, economic, environmental quality, social, safety, health and sustainability factors (Figure 2).
Strategic environmental assessment management plan (SEMP)
A strategic environmental assessment management plan is a detailed plan and schedule for measures to minimize and mitigate any potential environmental and sustain efficacy impacts. SEMP should consists of a set of measurement , monitoring, control (climate change and mitigative action) and institutional measures to be taken during the implementation and operation of the proposed projects to eliminate adverse environmental and sustainability impacts, offset them or reduce them to acceptable levels. Strategic environmental assessment process aims to incorporate environmental and sustainability considerations in to strategic planning and decision-making processes of the project formulation and appraisal. International EIAs are important considerations in project planning and decision-making process as an integrated solid waste management approach. It has been imperative to consider international EIAs in generic, source specific and industrial projects to mitigate hydro carbons and volatile organic compounds cum Methane and CO2 -induced climate warming and stratospheric ozone layer depletion problem. International EIA process is a potentially good environmental quality management [3].
Results and Discussions
During the last two centuries due to the fast urbanization and industrialization along with advancement of generic, source specific and industrial Science, Engineering and Technology, there have been considerable developments in generic, source specific and industrial sector with the resultant 80% wastage of copious number of resources and tremendous environmental stress due to greenhouse gas emission of 57 Giga tons of Carbon dioxide equivalent, petrochemical ozone layer depletion gases and RCR possibilities. Subsequently, it was realized that there were many adverse impacts on environment and society. These unsustainable petrochemical developments have sustained the environmental growth [4]. Environment and Sustainability of design and development of petrochemical sector, quality of life, safety on earth and continuous process improvement of our environment quality (EQ) is of utmost important. Sustainable development be defind as a kind of development that should be occurred without damages to the environment. Hence, hectic developmental activities during the last two centuries have caused considerable environmental and social impacts as. mentioned that the root cause problem solution for ozone layer depletion potential (OLP) impact, global warming potential (GWP) impact and green house synergic (augmentative) gas (GHG) of 57 giga tones of carbondioxide emission impact in context to petroleum and petrochemical industrial plants are measured, monitored and mitigated by international environmental impact assessment process for the sustainable environmental climate change and control.
International RCRs and EIAs are important in international project planning and decision-making process that mitigates potential environmental impacts in more than one country. The use of sustainable technology and management in environmental and sustainability matters in two areas that is sustainable development with global problems and prevention technologies that are designed to reduce the environment quality effects of products and processes (Figure 3).
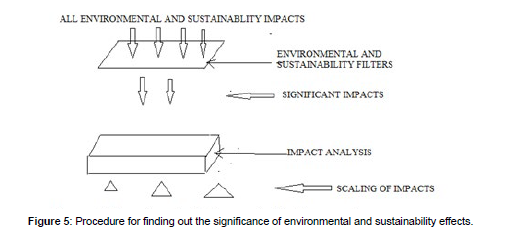
The integration of environmental quality protection and sustainable economic development is the most important strategic environmental assessment tool in achieving sustainable development (Figure 5).
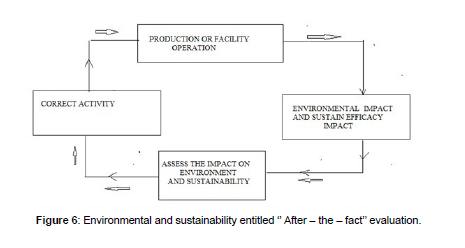
Project planning and decision-making should include the integrative consideration of engineering or technical, economic, environmental, ethical and social factors. A midget electrode project was taken as a case study for the strategic environmental assessment process. International EIA process has been designed for the sustainable midget electrode project design and sustainable plant design to identify and predict the potential effects of the physical, biological, ecological, socio-economic, cultural environment and on human health and wellbeing are adequately protected. Environmental Impact Statements (EIS) have been prepared for the project which considering environmental and socio-economic factors with respect to development and other proposed actions. Therefore, the EIA system is a potentially useful component of good environmental quality management (Figure 6).
In chromium tanning industry, chromium environmental contamination and pollution has discharged beyond safe limits which seriously affects the life on the earth . Toxic emissions from industries, thermal power plants, smelting pollution, auto exhaust pollution in large metropolitan areas, photo chemical smog have been poisoning (-log LD50 ), kg/kg) the atmosphere beyond the permissible levels which causes serious health hazards. Air pollution causes adverse environmental health and social impacts. Solid and hazardous waste disposal of untreated generic, source specific, industrial wastes and Odissa chromite mines and other radio-active wastes in nuclear power plants, petrochemical debris, sanitary wastes, hazardous wastes, municipal solid wastes, agricultural wastes, domestic wastes have contaminated and polluted the water, soil and land beyond the tolerable limits, which adversely affects land fertility, water quality, vegetation, aquatic and marine life. This is proving more and more non-hazardous greenhouse emissions and hazardous ozone layer depletion as this development continuously damaging the environment quality viz., melting of glaciers to 50 inches, increase of hybrid disaster risk, petrochemical smog, greenhouse gas emission, and ozone layer depletion. For example, due to continuous increase in CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide concentration in the atmosphere due to industrial emission of about 420 ppm CO2 which lead to climate change, climate heat change to 15.2 degree centigrade. Addition of greenhouse gasesto the atmosphere, the average sea level around the World by the 2023 and melting glaciers contributes to about 29.5% of mean sea level rise since 1991.
Water supplies stored in the glaciers were projected to decline. Besides contaminating and polluting air, water, soil and land, the intensive technological activities lead to depletion of natural resources.. Sustainable solid and hazardous waste management method is recommended. This must have been required to bring our energy and intellectual capacity in tandem whereby that can meet the challenge efficiently without major disruption as well as without compromising on the livelihood of future generation of their needs. Development would have occurred without damages to the environment and major disruption, and the process of urbanization and industrialization would have occurred in sustainable manner by utilizing the resources efficiently. Now, these environmental quality problems are the present environmental challenges and opportunities for improvement. In order to overcome these environmental problems that shall require new and more efficient solutions, technologies, processes and products alongside behavioral change.
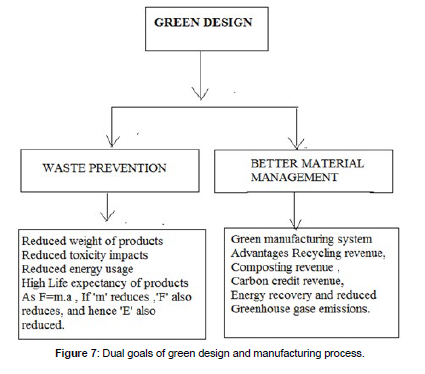
Low carbon and energy efficient technology of generic, source specific and industries can make contributions to mitigating impacts of economic growth on global warming [5]. The resultant output of green products and services which are environmental quality advantages with good performance and cheeper prices. The dual goals of green design are the waste prevention and better material management as depicted in Figure 7. Design and development of green buildings that has considerably reduced the environmental impacts associated with manufacturing, use and disposal (Figure 7).
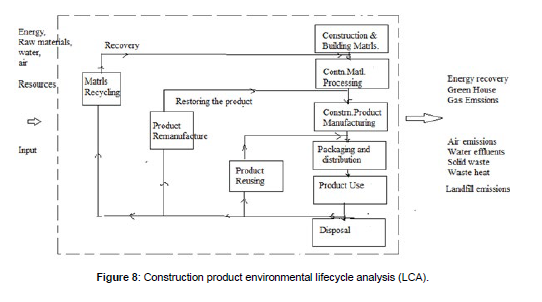
As per the research results that project planning and decisionmaking process must include the integrated consideration of engineering or technical, economic, environmental, safety, ethical, social and sustainability factors. This important consideration can be referred to as “Concept of the Four Es and 1 S” in organizational planning and decision- making process. There are ecological and biogeochemical principles and tools such as energy flows and material cycling, element ratios, mass and energy balance, element cycling, product environmental life cycle assessment (LCA) are available in order to solve major environmental problems that we face in our world today such as global warming, acid rain, environmental pollution and increasing greenhouse gases (Figure 8).
Hybrid life cycle assessment in engineering product and process / hybrid environmental lifecycle analysis (LCA) is used for identifying and measuring the impact of industrial products on the environment and sustain efficacy by means of mass and energy balance methods including resource conservation and recovery (RCR) and solid and hazardous waste management and environmental impact assessment process . LCA consider the activities related to extraction of raw materials, ancillary materials, equipment production, use, disposal and ancillary equipment.
Environmental health impact assessment (EHIA) process for petrochemical and nuclear power plant project towards sustainable petrochemical development
An environmental health impact assessment (EHIA) process is proposed in this research for nuclear power plant project during the petrochemical phase in order to address psychological health impacts on workers and nearby residents. Environmental health impact assessment can be defined as the systematic identification and evaluation of the potential environmental health impacts or effects of proposed nuclear power projects, plans, programs, policies or legislative actions relative to the physical-chemical, biological, cultural and socioeconomic components of the total environment. At present there are more than four hundred thirty-seven nuclear power plants situated in the World. It may be worth mentioned that none of the nuclear power projects, plans, programs, policies, or legislative actions in the World have got sustainable practice in conduction of EHIA process. Nuclear power plants generate electricity using heat generated in pressurized water reactors where nuclear reaction takes place. During the petrochemical phase of nuclear power plants which use Uranium-235, Thorium-232 and Plutonium-239 as fuels in nuclear reactors causing nuclear fission. That time copious amount of radiation dose due to radioactive pollution escaping out in the order of about 120 billion Becquerel (120 GBq) to 240 billion Becquerel (240 GBq) that is 50 grams to 100 grams, radiation activities viz., Alpha (α), Beta (β) and Gamma (γ) as against the safe limits of 0.1 Bq /l or Bq/kg (ppm) in land, air and water when operation , repair and maintenance of replacing old nuclear fuels with new fuels taken place . High exposures to radioactive pollution damage mental health and psychological burden on workers and nearby residents. As per a psychological health impact survey conducted by the author in a nucelar power plant at Quinson, China, severe psychological disorders including radioactive poisoning, depression and post-traumatic stress have been investigated to an extent among 49% of the nearby residents in and around 82% of the nuclear power plants in the World (World Engineers’ Convention, Shanghai, China-2004). Psychological health impact loadings due to radioactive environment on workers and nearby residents have been studied in this research during the test run phase using computer simulation models. Psychological health impact assessment (PHIA) on workers and nearby residents have been addressed to mitigate psychological health impact loadings on workers and narby residents.
Environmental health impact assessment (EHIA) process for sustainable petrochemical industrial development
In this research, sustainable petrochemical process, efficient integrated solid and hazardous waste management practice, EHIA process have been investigated. Reseacrh work has been done on cotton double roller (DR) ginning industries using chrome composite leather clad (CCLC) washers and design and development of an eco-friendly alternative The objective is to assess the environmental health impacts of Indian cotton ginning industries. Most of the cotton ginning operations are performed by using DR ginning machines which serve an important role in the Indian cotton ginning industries. The rollers used are made of CCLC covering fixed to a shaft. The CCLC contains about 18,000 to 36,000 mg/kg (ppm) of chromium particles. When the seed-cotton is processed in DR ginning machine, the lint cotton is contaminated with hexavalent chromium dust of about 140 to 1990 mg/kg (ppm) which is carcinogenic substance against the safe limits of 0.1 ppm. During the cotton ginning process due to persistent rubbing of CCLC over stationary knife the chromium particles are adsorbed into lint cotton such that the spun yarns and woven fabrics get contaminated about 100 to 200 ppm which according to World Health Organization (WHO) eco-standards should not be more than 0.1 ppm. The CCLC rollers used in cotton roller ginning machines get powdered during the ginning process. As chromium is a specific dust, gin and mill workers and residents are directly exposed to this carcinogenic substance and are vulnerable to environmental health hazards. To offset this problem, pollution-free eco-friendly washers/ rollers both for laboratory and commercial studies have been fabricated and experimented. Environmental health inventory (EHI) serves as the basis for evaluating the potential environmental health impacts both beneficial and adverse of a proposed action. Environmental health impact statement (EHIS) describes the affected environmental health or environmental health setting without the project. Design and development of the EHI is an initial step in the EHIA process. It is concluded that EHIA process should be conducted for projects, plans, programs, legislative actions, policies in the project planning and decision-making process.
International EIA process
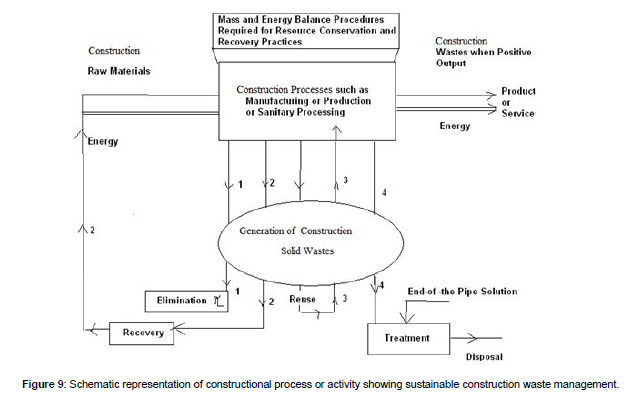
International EIA process is a potentially good environmental management system (EMS). International organization for Standardization (International Electro technical Commission) (IEC) / (ISO)’s 45000 and 14000 and 9000 standards focus on Occupational Health and Safety Management (OHS) and Environmental Management System (EMS) and Quality Management System (QMS) of all sorts of organizations apart from more than 19500 published standards. Environmental Management System (EMS) and Quality Management System (QMS) have been separately featured in ISO (IEC). Environmental Management System (EMS) standards apply to the management system concepts of an organization’s environmental issues and opportunities (Giri.,C.C. et.al.,2003). It defines the features of an EMS that need to be in place to ensure that the organization identifies and focuses on improving areas where they have significant environmental impacts. This system can be integrated with ISO 9000 Quality Management System (QMS) and (International Electro technical Commission) (IEC) standards to achieve excellence in quality as well as environmental obligations. The overall aim of the EMS is to provide protection to the environment and to prevent pollution so as to manufacture eco-friendly products and services. EMS focuses on key drives of performance excellence in products and processes as well as organizations that are focused on delivering values to the customers, internal operational processes, and to staff’s learning and ciontinuous improvement environment. Hence, this system approach to the environmental quality management shall achieve excellence in the overall performance of the organization. In the present study about two third of waste was recyclable recoverable due to the conduction intensive on-site integrative training programmes on recycling processes as against the conventional management practices which could able to recover the waste of only 10 from 65% (Figure 9).
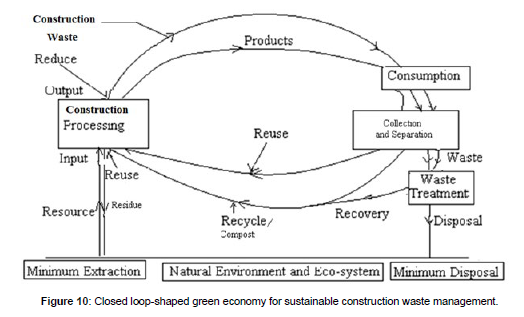
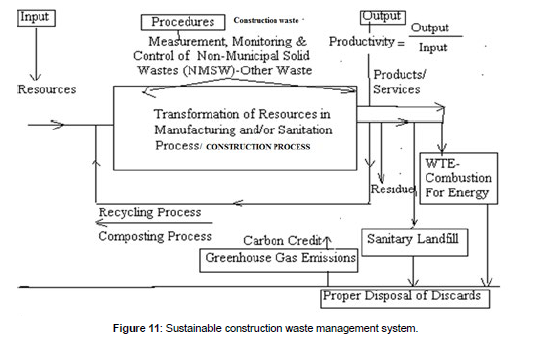
Generic, source specific and industrial wastes are produced by sectors. The study has been attempted to identify and evaluate special waste minimization hierarchy of waste management for properly managing waste including minimizing generation and treatment that have been generated, and disposing of waste residuals. A case study has been included on generation of wastes and potential waste management strategies for a group or generic processes. All processes generate wastes in the form of liquids, solids or gases. Some wastes are considered as hazardous. The waste minimization hierarchy of waste management is duly ranked from most desirable to least desirable. 1. Eliminating waste generation –Most desirable, 2. Reducing waste generation- Most desirable, 3. Reuse, recover or recycle waste materials- Most desirable, 4. Treating waste to diminish quantity and to detoxify the hazardous and non-hazardous solid wastes --Least desirable, 5. Disposing of waste residuals- Least desirable. Waste minimization includes only elimination, recovery, reduce, reuse and recycle hierarchies. Waste minimization does not include treatment of wastes as well disposal that is point number 4 and point number 5 because, these are traditional waste control strategies involves treatment and disposal which are called end-of-the pipe solutions and are costly affairs as well as involve control of high discharge standards. Modern waste control strategies involve point number 1, point number 2 and point number 3 which are not requiring end-of- the pipe solution for the waste management problems. Solid and hazardous waste generation is the sum of material recovery and discards. Report on waste audit conducted for a generic, source specific and industry is presented for recovering two-third of municipal solid wastes (MSW) by recycling and composting processes (Figures 10 and 11).
To achieve the sustainable economic improvement, natural resources to be utilized at optimum levels such as resource conseration and recovery as to maximize efficiency as per the result analysis of optimum competitive and social markets. The efficiency of a kind of sustainable economic system is referred in “A.K” sustainable economic model that is the product of engineering or technical factor level (A) and the capital (K). The sustainable economic improvement is explained by three factors which are given below:-
The natural increase in the accumulation of labor potential, Capital accumulation or money with which a business is started and run, and Sustainable technological momentum can be referred as total factor productivity (TFP) or efficiency in an engineering process.
Such momentum keeps the capital development dynamic which emerges from the sustainable woman enterprise creation process, green products or services, new methods of production and processes, new management and transportation, new markets and new forms of organization.
Standard Production Function (SPF) is expressed based on operation approach as
Y = f (C, L)
Where Y=Output, C=Capital, and L=Labour
As knowledge is a crucial factor for the economic growth,
Standard Production Function (SPF) is modified based on process approach as
Y= A. f (X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6…………..Xn)
‘A’ represents Knowledge on sustainable petrochemical engineering or technical factor,
Y= Output,
Input elements are namely, man power, machinery, materials, method, money and market denoted as
X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6……………Xn,
f = Standard production function.
As per the given standard production function, knowledge is a decisive production variation, sustainable innovation level is required in engineering or technical system. The solution is the development of reformed SEA implemented generic, source specific and industries.
Importance for the conduct of resource conservation and recovery study and environmental impact assessment (eia) and management for the entrepreneurship development projects
Historically, the choice of new entrepreneurial projects was primarily on one criterion, which is economic viability. Presently, second and third choice criteria that is environmental and social impact have become a strong yardstick, therefore a triple bottomline approach that is economic, environmental and social factors to entrepreneurship project viability through green economy model. Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process is a systematic identification and evaluation of potential effects of proposed projects, plans, programs, plans or legislative actions relative to the physicalchemical, biological, cultural and socio-economic components of the total environment.
Steps to conduct environmental impact assessment and management
Step-1: Identification of quantity and quality characteristics of concerned environment of Proposed project.
Step-2: Preparation of description of existing environmental resource conditions.
Step-3: Procurement of relevant quantity and quality standards.
Step-4: Impact predictions,
Step-5: Assessment of impact significance,
Step-6: Identification and incorporation mitigation measures.
Conduct of environmental impact assessment (eia) study for the efficient generic, source specific and industrial projects
1. Prediction and assessment of impacts on surface water environment,
2. Prediction and assessment of impacts on soil and ground environment,
3. Prediction and assessment of impacts on the air environment,
4. Prediction and assessment of impacts on the noise environment,
5. Prediction and assessment of impacts on the biological environment,
6. Prediction and assessment of impacts on the visual environment,
7. Prediction and assessment of impacts on socio economic environment.
8. Prediction and assessment of impacts on cultural environment,
9. Prediction and assessment of impacts on archaeological environment,
10. Prediction and assessment of impacts on anthropological environment
Benefits of EIA in Considerable reduction in waste and the depletion of resources
1. Considerable reduction and / or elimination of the release of pollutants in to the environment.
2. Green design and green building products to minimize their environmental impact in
Production, use, and disposal.
3. Control the environmental impacts of sources of raw material.
4. Waste minimization and adverse environmental impact of new developments.
5. Promote environmental awareness among employees and the community.
Environmental quality management programs
The organization shall establish and maintain a program(s) for achieving the envirornemntal objectives and targets. It shall include designation of the responsible function, team, or individual and a time frame for achievement [6].
1. State the objective / target.
2. State the purpose (how the objective/target will support the policy).
3. Describe how the objective/target will be achieved.
4. State the program (team) leader.
5. Designate departments and individuals responsible for specific tasks.
6. Establish the schedule for completion of the tasks.
7. Establish the program review, which will include format, content, and review schedule.
Conduct of social impact assessment (SIA) study
Social Impact Assessment (EIA) process is a systematic identification and evaluation of potential social effects of proposed projects, plans, programs, plans or legislative actions relative to the society. The purpose of the SIA process is to bring about a sustainable and equitable biophysical and human environment. SIA process includes the monitoring, measurement and control opportunities including analysis and management of the intended and unintended social consequences whether both positive and negative impacts of planned interventions and any changes takes place in social transformation process invoked by those interventions. The SIA process should include the analysis of the use of land, culture, industrial process, economic development, and their impact on service sectors such as water use, energy use, sanitation and traffic. SIA process is done to ensure that there is no mismatch between the development and socio-cultural and economic development of the project areas.
Sustainable waste water quality management
Water quality is to be maintained in sites such that water supply to consumers is safe and hygiene. Relevant water quality standards are to be followed. Sustainable sanitation facility is to be provided. Sanitation impact assessment study has been conducted for sanitation projects and plans. Sewerage system, storm water drainage systems, waste water treatment system, industrial waste treatment system, sustainable septic tank are important onsite requirements. Relevant waste water discharge standards are to be followed. Process approach for measurement, monitoring and control opportunities for water, waste water and industrial water water quanity and quality has been followed at sites.
Safety engineering and management in industries (safety first)
Safety management is the systematic identification and evaluation of potential safety requirements of proposed projects, plans, programs, plans or legislative actions. The purpose of the safety engineering and management is to bring about sustainable design of projects considering Resource conservation and recovery aspects and EHIAs. It has been observed that traditional methods and machineries used in India are to be obsolete and outdated because they were old which operated on poor performances in terms of productivity, quality, efficiency and safety. Some of the alternative machineries, which are indigenously manufactured, also do not guarantee for the superior performance and necessary safety conditions because of their poor design and materials of generic, source specific and industries. It is mandatory that checking for safety requirements with regard to machineries, bridges, roads and buildings. Safety personnel responsible for overseeing the safety of all operating personnel must be cognizant of the latest laws and regulations pertaining to worker safety and occupational health. These are changed and/or updated from time to time. Checking for Safety (CFS) such that to ensure that the question of safety will not be overlooked, it is well to have all plans, specifications and drawings checked for safety, making special provision for this in each set of specifications and in the title plate of each drawing duly checking periodically for cranes, hoists, ventilation, lifts, tackles, fire protection systems, alarms, buildings, mechanical guarding and electrical and electronic equipment and heavy engineering equiments. Personal protective equipments (PPEs) and materials include garments, clothing, gloves, safety shoes, hard hats, safety glasses, shields, respirators, full aprons, safety belts, and other safety items have to used by an individual. Such equipment is important for personal protection and for safety. It is the manager’s and supervisor’s responsibility to ensure that they are used. As far as occupational-disease prevention is concerned that those persons engaged in or working near operation are exposed to appreciable quantities of dusts, fumes or gas, it is important that adequate control measures must be adopted. Some major considerations involved in the application of effective control to industrial occupational disease are given. Some of the policies, practices, and procedures to prevent exposure of personnel to unsafe materials are also provided. As far as the worker’s compensation law is concerned, it must be enacted strictly in our country. The principle involved is that the worker injured or disabled in generic, source specific and industries should be enabled, through proper medical treatment, to return to wage-earning capacity as promptly as possible and while incapacitated, should receive compensation in lieu of wages, and regardless of fault. The expense of medical treatment and compensation should properly be borne by industry and become a part of the cost of its products. The laws generally provide that workers injured in industry shall be furnished the necessary medical treatment, and, in addition, compensation based on a percentage of their weekly wages, payable periodically. Dependents of employees kill in industry are likewise compensated. Occupational diseases law provides provision for compensation benefits in occupational – disease cases. The enactment of worker’s compensation laws and occupational disease law shall increase materially the cost of insurance to industry. The increased cost and the certainty with which it is applied will put a premium on accident-prevention work. This cost can be materially reduced by the installation of safety devices. .Research experience has shown that approximately 80% of all the generic, source specific and industrial accidents are preventable. As far as the fire loss prevention is concerned, which is an indispensable element in generic, source specific and industry. It exists only with top management direction and the support of labor. The designation fire protection usually encompasses the entire field of prevention of loss by fire, including both the causes for the occurrence of fires and methods for minimizing their consequence. Some of the fire standards of protection to prevent injury and loss of life are given in this paper. Fire protection engineering practices both in building design and in safe operating practices are also included . Generic, source specific and industrial noise safety is concerned; noise is recognized as a pollutant, both as a nuisance and as the cause of hearing impairment. There is evidence in generic, source specific and industrial sites that noise cause ailment such as hearing impairment, physiological and psychological disorders including anxiety and heart disorders. Protection from noise is required when sound levels exceed those standards. When protective equipment is required, it must be provided by a trained person and periodic checks made of the effectiveness.
Total quality management (TQM)
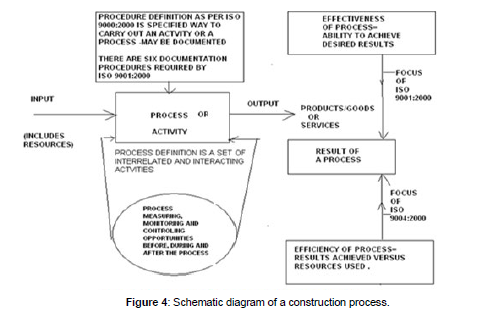
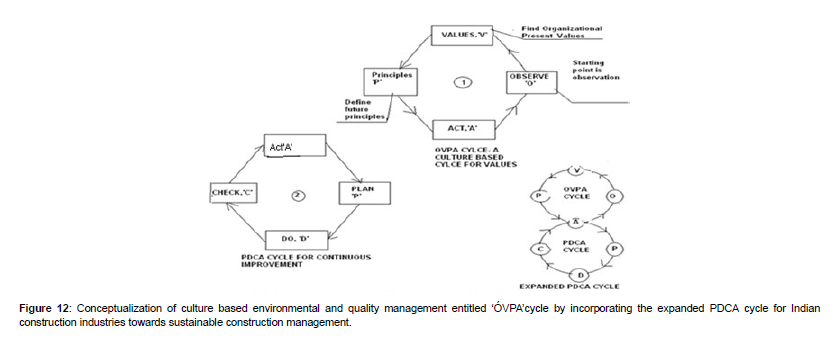
Total Quality Management (TQM) and total safety management (TSM) can be broadly defined as a set of systematic activities carried by an institution to efficiently achieve institutional objectives that satisfies beneficiaries at the appropriate time and price. The definition of quality is “The totality of features and characteristics of products or services that bear on its ability, efficacy and values to satisfy a given or implied need”. TQM is a comprehensive and structured approach to an educational integrated management integrated with environmental quality that seeks to improve the quality of educational services through ongoing refinements in response to continuous feedback. Thus this standard definition of quality is applicable commonly to both products and services that are stated and unstated. TQM has an important role to play in addressing quality issues surrounding the generic, source specific and industrial development. TQM is a comprehensive and structured approach to sector that seeks to improve the quality of services through ongoing refinements in response to continuous feedback. TQM and Total environment quality management (TEQM) leads to sustainable generic, source specific and industrial development. International Organizational for Standardization’s ISO 9000 (International Electrotechnical Commission) (International Electro technical Commission) (IEC) series define TQM and total safety management (TSM) as a management approach centered on quality and safety , based on the participation of all its members and aiming at long term success through customer satisfaction and benefits to all members of the organization and society. Hence, TQM is based on quality management from the customer’s point of view. TQM processes are divided into four sequential categories: plan, do, check, and act. This is also called the PDCA cycle or Deming’s cycle for continuous process improvement. In the planning phase, technologists define the problem to be addressed, collect relevant data, and ascertain the problem’s root cause; in the doing phase, technologists list develop and implement a solution , and decide upon a measurement to gauge its effectiveness and efficiency ; in the checking phase , technologists confirm the result through before-and–after data comparison; in the acting phase, technologists document their results , inform others about process changes, and make recommendations for the problem to be addresses in the next PDCA cycle. ISO 9000 (International Electrotechnical Commission) (IEC) series focus on quality management for all sorts of organizations. It defines the features of quality management system (QMS) and ISO 14000 Environmental Management System standards that need to be in place to ensure that identify and focus on improving the areas where they have significant deficiencies [7,8] (Figure 12).
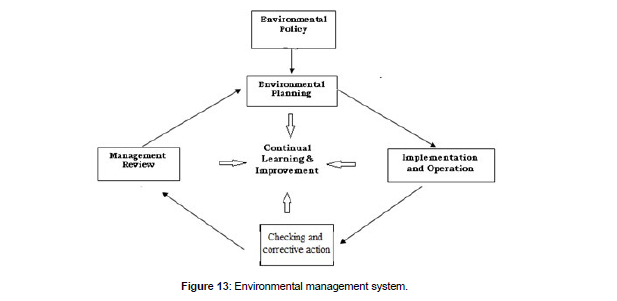
The ISO 14000 Environmental Management System (EMS) standards apply to the management system to manage an organization’s environmental issues and opportunities. It defines the features of an EMS that need to be in place to ensure that the organization identifies and focuses on improving areas where they have significant environmental impacts. This system has been integrated with ISO 9000 Quality Management System (QMS) and TSM standards in order to achieve excellence in quality as well as environmental obligations in midget electrode project. The overall aim of the EMS is to provide protection to the environment and to prevent pollution to manufacture eco-friendly products and services. The ISO 14000 series of standards assist the organizations to excel environmental and economic gains for continuously improving organizational performances. They are used for prevention of pollution, reduction in wastes, enhancement of internal management system efficiency, optimum utilization of resources and compliances for legal and regulatory requirements. EMS can be basically divided into five events which form the sequence of a cycle (Figure 13) . These five events are (1) Environmental Quality Policy, (2) Environmental Quality Planning, (3) Environmental Quality implementation and operations, (4) Checking and corrective actions, and (5) Management Review. The ISO 14000 series of standards have also been designed to cover the areas of environmental issues and opportunities for the organizations to compete the global customer centric markets so that the products and services can be manufactured at par with the international requirements (Figure 13).
EMS focuses on key drives of performance excellence in products and processes as well as organizations that are focused on delivering values to the customers, internal operational processes, and to staff’s learning. It may be mentoned that Environment and Quality Management (EQM) is a managerial approach centered on environment and quality through beneficiary satisfaction in generic, source specific and industries that lead to economic improvement and sustainability. Hence, this system approach to the environmental management shall achieve excellence in the overall performances of the organization [9, 10].
Conclusions and Recommendations
In this article enviro-technological perspectives on climate change mitigation in urban and rural environments are discussed. The resource conservation and recovery (RCR) method has been devised for an efficient and effective solid and hazardous waste management prior to environmental impact assessment (EIA) process. SEA process has been aimed in order to incorporate environmental quality and sustainability factors in to petrochemical project planning and decision-making process, such as project formulation and appraisal of Indo-Matsushita midget electrode (battery carbon rod) plant in 1979 at Tada, sustainable fertilizer project, green sustainable process, resource conservation and recovery (RCR) in generic, source specific and industrial systems, nuclear power plant, cotton roller ginning plant and concrete that included polices, programs, plans and legislative actions. The primary purpose of the SEA process is to encourage the consideration of the environment, safety, health, social and sustainability factors in organizational’s (PCPPDM) process and to arrive at actions that are compatible. IA should be considered as an official tool to protect the environment. Sanitation impact assessment has been investigated for sanitary projects and plans. RCR and EIA processes are multidisciplinary approach that must be necessary in providing a prevention mechanism for environmental quality management and protection in any generic, source specific and industrial process development. EIA process is designed to identify and predict the potential environmental effects of the physical, biological, ecological, socio-economic, cultural environment and on human health and wellbeing are adequately protected.
As per research results, PCPPDM process should include the integrated consideration of technical or engineering, economic, environmental, safety, health, social and sustainability factors to achieve business excellence. The SEA process protocol has been proposed for checking the quality of environmental and social assessments and management plans. This treaty and official government procedures of SEA helpful for making much earlier in the decision-making process than RCR and EIA processes. Therefore, it is key tool for sustainable development. SEA aims to incorporate environmental and sustainability considerations in to strategic decision- making processes, to formulate policies, plans, and programs and legislative actions. Prior to the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) process in 1970 in the USA, technical and economic factors dominance the World’s generic, source specific and industrial projects. The objective of the study is to conceptualize SEA process for the sustainable generic, source specific and industrial sector based on fifteen number of sustainable detailed project reports submitted by the extension learners of Diploma in Entrepreneurship and Business Management course conducted by the Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India during the research year 1999 to 2023 under the author’s counsellorship and BIPARD climate change /control module. The ISO 14000 Environmental Management System standards apply to the management system concepts of total quality management to the management of an organization’s environmental and safety issues and opportunities. It defines the features of an EMS that need to be in place to ensure that organizations identify and focus on improving areas where they have significant environmental impacts. EMS focuses on key drives of performance excellence in products and processes as well as organizations that are focused on delivering values to the customers, internal operational processes, and to staff’s learning. Hence, this system approach to the environmental management shall achieve excellence in the overall organizational performance. Project environmental life-cycle analysis has been conduced for identifying and measuring the impact of generic, source specific and industrial products on the environmental quality means of mass and energy balance methods. Solid and hazardous management method has been devised. LCA considers the generic, source specific and industrial activities related to raw materials, transformation, ancillary materials, equipments, methods, market, production, use, disposal and ancillary equipment. As far as the environmental quality & safety is concerned, personal protective equipment and materials that include garments, clothing, gloves, safety shoes, hard hats, safety glasses, shields, respirators, full aprons, safety belts, and other safety items have to use by generic, source specific and industrial personnel. Such equipment is important for personal protection and for safety. It is the manager’s and supervisor’s responsibility to ensure that they are used. The enactment of worker’s compensation laws and occupational disease law shall increase materially to the cost of insurance to generic, source specific and industry. The increased cost and the certainty with which it is applied will put a premium on disaster prevention work. This cost can be materially reduced by the installation of safety devices. RCR and EIA of petrochemical managerial research experience have shown that approximately 80% of all the generic, source specific and industrial disasters are preventable. It is concluded that environment coupled with quality management is a managerial approach centered on environment and quality through beneficiary satisfaction that leads to economic improvement and sustainability based on the triple bottomline approach. TQM has an important role to play in addressing environmental quality issues surrounding the sustainable generic, source specific and industrial development. Sustainable water and waste water management has been discussed. The author mentioned that the root cause problem solution for ozone layer depletion potential (OLP) impact, global warming potential (GWP) impact and green house synergic (augmentative) gas (GHG) emission impact in context to generic, source specific and industrial plants are measured, monitored and mitigated by international environmental impact assessment process (Figure-3) for the sustainable environmental climate change and control. RCR, EIA and EHIA processes have been conducted for a nuclear power plant to consider the safety and health impacts to mitigate psychological health loadings on workers and nearby residents. SEA system is a potentially useful element of good environmental quality management and sustainable development; however, as currently practiced in generic, source specific and industrial industries, it is far from perfection. Emphasis should be given in generic, source specific and industries on maintaining economic viability of the operation, while in turn taking care to preserve the ecological and social sustainability of the country. International EIA process required multi-disciplinary approach that has been conducted very early stage of Indo-Matsushita carbon rod project in 1982 at Tada for economic, environmental and social viabilities. Strategic environmental assessment (sea) process is devised for entrepreneurship development through economic model towards sustainable environmental entrepreneurship.
Acknowledgements
The author is thankful to Shri K.K. Pathak, I.A.S., Director General, Bihar Institute of Public Administration and Rural Development (BIPARD), Gaya , India for giving permission to publish this research article as a BIPARD Training and Research Development Course Module Number -27 on Sustainable Environmental Climate Change and Control during 2022-2023 research years.
References
- Giri.CC (2003) Importance of the ISO 14000 in Textile Industry and its Implementation Framework. Journal of Textile Association, July-Aug.2003.
- Glynn Hendry J and Gary W.Heinke (2002) Environmental Science and Engineering. Prentice -Hall of India Private Limited Second Edition.
- RalphA.Wurb, (2010) Water Resources Engineering Prentice -Hall of India Private Limited 20edition.
- https://www.academia.edu/61857638/wastewater_engineering_treatment_and_reuse_by_metcalf_and_eddy.
- https://www.scribd.com/doc/180399907/Environmental-Impact-Assessment-by-L-W-Canter.
- Iyer Vijayan Gurumurthy (2015) Environmental and Quality Management for the Higher Education Institutions to Achive Research and Academic Excellence. Journal of Modern Education Review.
- Iyer Vijayan Gurumurthy2015) Social Impact Assessment Process for an Efficient Socio- Economic Transformation towards Poverty Alleviation and Sustainable Development. Global Journal on Advances in Pure and Applied Sciences.
- Iyer, Vijayan Gurumurthy (2007) Design and Production of an Eco-friendly Technology for the Processing of Cotton Fibers . Journal of Textile Association (India).
- Iyer Vijayan Gurumurthy (2007) Eco-Friendly Rubberized Cotton Fabric Roller Development for Cotton Roller Gins. Journal of Agricultural Safety and Health.
- Iyer Vijayan Gurumurthy (2011) Industrial Landfill Sources of Air Water and Land Pollution in India. World Journal of Environmental Research.
Citation: Iyer VG (2023) Enviro-Technological Perspectives on Climate Change Mitigation in Urban and Rural Environments. Environ Pollut Climate Change 7: 351. DOI: 10.4172/2573-458X.1000351
Copyright: © 2023 Iyer VG. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 530
- [From(publication date): 0-2023 - Jan 28, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 447
- PDF downloads: 83