Case Report Open Access
Effect of Combined Training Program on Gait Parameters after Bilateral Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Study
| Richa Singh*, Keerthi Rao, Deepak Anap, Chandra Iyer, and Subhash Khatri | |
| College of Physiotherapy, Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Loni, India | |
| Corresponding Author : | Richa Singh College of Physiotherapy Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences Loni, Maharashtra, India E-mail: riichasingh@gmail.com |
| Received August 02, 2012; Accepted August 21, 2012; Published August 24, 2012 | |
| Citation: Singh R, Rao K, Anap D, Iyer C, Khatri S (2012) Effect of Combined Training Program on Gait Parameters after Bilateral Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Study. J Nov Physiother 2:120. doi: 10.4172/2165-7025.1000120 | |
| Copyright: © 2012 Singh R, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Novel Physiotherapies
Abstract
Background and purpose: Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is a common surgery done in rheumatoid arthritis nowa- days. But, post operatively there are various complications seen and the main complaint of such patients is gait rehabilitation. There are many physiotherapy protocols available to prevent the complications, but the effect of combined training program in patients with bilateral total hip arthroplasty not assessed. The purpose of this case study was to find out if combined training program of treadmill and strengthening exercise had an effect on gait parameters.
Method: A 44-year-old male who had undergone bilateral hip arthroplasty referred for gait rehabilitation. Four weeks intervention of combined training has given.
Result: There was significant difference in various gait parameters post intervention.
Conclusion: Combined training is effective in gait rehabilitation after bilateral total hip arthroplasty.
| Keywords | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total hip replacement; Computerized dynography | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic and progressive disorder. Inspite of the various drug (disease modifying antirheumatic drugs) therapy, joint erosion and destruction develops with the passage of time and the major symptom being joint pain. As the disease, progresses there are signs of reduced range of motion, decrease in muscle strength and ultimately a decline in functional activity. Total joint replacement considered a milestone and an important therapeutic option in the management of RA [1]. The indication for surgery is unbearable joint pain with activity or at rest, or a severe functional impairment leading to change in the lifestyle. The aim of total hip arthroplasty (THA) is not only to relieve pain but also to restore hip biomechanics, leading to a minimal functional deficit and to secure the longevity of the implant. Post operative impairments include reduced walking efficiency, pain, muscle weakness of the hip abductors, hip extensors and flexors, contracture of the hip, gait disorders [1,2]. Due to the above problems, it may lead to complications such as loosening of the implant and joint instability. To prevent falls and to avoid limping gait, there should be adequate strength in lower extremity. Post operatively, the rehabilitation program focuses on hip joint mobilization, strengthening of surrounding muscles and gait retraining, initially with a walking aid [2]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| It has already suggested; in neurological rehabilitation, that treadmill training with partial body weight support is effective. It follows modern principles of motor learning and helps the patient to practice complex gait cycles in rehabilitation, before they start walking unsupported and independently on the ground. A preceding biomechanical study of ambulatory total hip arthroplasty patients with a fully loadable implant compared their walking on the treadmill with 15% body weight support (BWS) [3] and walking on the ground with two crutches placed reciprocally. In both the situations, though the patients walked symmetrically, the activation of the affected hip abductor muscle was larger in amplitude and occurred at a more normal time of the gait cycle when walking on the treadmill [3]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Past studies have shown supportive evidence for improvement in gait parameters by using treadmill on unilateral total hip replacement [3]. Other studies have also shown that the strengthening of selective musculature helped in improvement of gait parameters [4,5]. As there is paucity of research in identifying the combined effect of treadmill training and strengthening protocol in bilateral total hip arthroplasty on gait parameters. Hence, the study presenting here, has an aim to find out the combined effect of treadmill and strengthening exercises on gait in bilateral total hip arthroplasty. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suppliers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
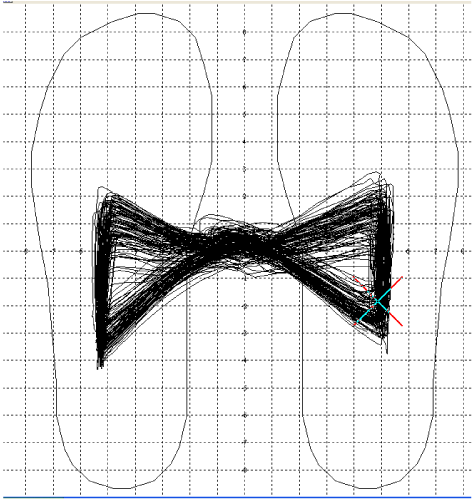
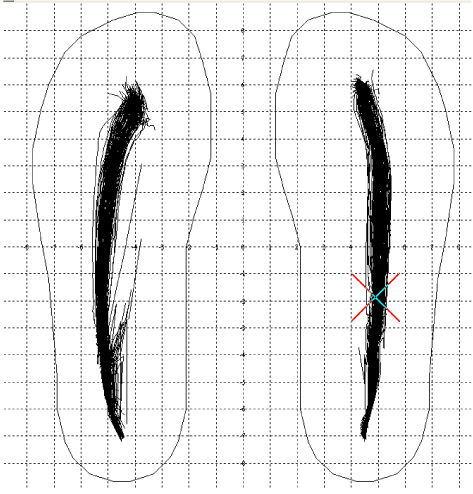
| Computed dynography (CDG® system) manufactured by Infotronic, AB Tubbergen Netherlands, http://www.infotronic.nl. This system measures the vertical ground reaction force distribution during gait, and can be expanded with EMG, joint angle measurements (Goniometer) and video. This system consists of sensor shoes, connecting cables, internal memory unit and computer with ultra tech software. The CDG system provides quantitative data about histogram, cyclogram, gait line, force gait line, step times and force graphics. The system is fully portable, hence not restricted to one specially prepared room. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case Report | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A 44-year-old male who had undergone bilateral THA referred to physiotherapy department for gait rehabilitation after 2 months of surgery. No pain history has observed. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Examination | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient thoroughly assessed by therapist. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manual muscle testing for bilateral hip abductors and extensors was grade 3 (full range of motion against gravity). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resisted isometric contraction for bilateral hip abductors and extensors was strong and painful. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| End feel for bilateral hip abductors and extensor was tissue stretch. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outcome measures: Before and after the intervention the following outcome measures have measured. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gait parameters: It has taken on gait analysis- computer dynography (Figures 1 and 2). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Step time/ step duration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. Single swing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. Single support time | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. Double support time | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. Stance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. Cadence | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxford Manual muscle testing Harris Hip score [6]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The intervention period was of 4 weeks with 5 days per week. The protocol given was strengthening of hip abductors (after calculating 10 RM, the cuff weight of respected weight was applied to ankle joint in supine lying position and Oxford technique was followed) [7]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strengthening of extensors (after calculating 10RM, the cuff weight of respected weight was applied to ankle joint in prone lying position and oxford technique was followed) [7]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For gait retraining on floor- forward walking and side walking for 10 minutes each have given in parallel bars and was progressed with obstacles, 25 minutes of treadmill walking without inclination at participant’s comfortable speed. Stair climbing taught on staircase with the help of railing for 10 minutes. Each session lasted for 45 minutes to 1 hour including rest periods. Before and after the 4 weeks on intervention the participant was made to walk for 60 seconds and average of 3 trails was taken for the distance covered. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In the above table, shows that, there was significant improvement in the affected gait parameters as well as the strength and in the various components of Harris Hip score. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The result of our study shows that combined training of treadmill and muscle strengthening has improved various gait parameters. Isometrics hip strengthening contributes in trunk control and stability, which plays an important role in gait. Sicard-Rosenbaum et al. reported that there is muscle weakness of the quadriceps, hip abductors and hip extensors, which in turn affects the various gait parameters in subjects with total hip arthroplasty [5]. Jan et al. in their study obtained significant improvement in strength and function without including walking in their 12 weeks home exercise program [4]. Sashika et al. and Unlu et al. in their respective studies have shown significant improvement in isometric strength in hip flexors, extensors and abductors in 6 weeks home exercise program [8-10]. In our study, there was significant improvement in the strength of hip extensors and abductors in 4 weeks due to the combined training program, which has given. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| On the other hand, treadmill training improved the various gait parameters. Treadmill training offers a task specific repetitive movement, which helps to practice the complex gait cycle. Participant takes more number of steps on treadmill rather than on ground. Hence, there is improvement in gait pattern. Studies have also shown that well functioning and strong hip muscles are important for walking ability, gait symmetry, and the prevention of implant loosening. Treadmill training also helps in early gait rehabilitation and prevention of complications [1]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The combined effect of treadmill training, gait training and strength training has significantly improved double support time, stance and increase in cadence in 4 weeks of intervention. It has also given better control and strength to the lower extremities and endurance to the participant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conclusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treadmill training combined with hip strengthening exercise is beneficial in improving gait parameters. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Future Scope of Study | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Further studies can be done with large sample size and by increasing the duration of the intervention. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Wolfe F, Zwillich SH (1998) The long-term outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis: a 23-year prospective, longitudinal study of total joint replacement and its predictors in 1,600 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41: 1072-1082.
- Husby VS, Helgerud J, Bjørgen S, Husby OS, Benum P, et al. (2009) Early Maximal Strength Training Is an Efficient Treatment for Patients Operated With Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 90: 1658-1667.
- Hesse S, Werner C, Seibel H, von Frankenberg S, Kappel EM, et al. (2003)Treadmill Training With Partial Body-Weight Support After Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 84: 1767-1773.
- Jan MH, Hung JY, Lin JC, Wang SF, Liu TK, et al. (2004) Effects of a home exercise program on strength, walking speed and function after total hip replacement. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 85: 1943-1951.
- Frost KL, Bertocci GE, Wassinger CA, Munin MC, Burdett RG, et al. (2006) Isometric performance following total hip arthroplasty and rehabilitation. J Rehabil Res Dev 43: 435-444.
- Harris WH (1969)Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am51: 737-755.
- Kisner C, Colby LA (2007) Therapeutic exercises foundation and techniques. (5thedn), Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers, New Delhi, pp: 207.
- Monaco MD, Valllero F, Tappero R, Cavanna A (2009) Rehabilitation after total hip arthroplasty: a systemic review of controlled trails on physical exercise program. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 45: 303-317.
- Unlu E, Eksoglu E, Aydog E, Aydog ST, Atay G (2007) The effect of exercise on hip muscle strength, gait speed and cadence in patients with total hip arthroplasty: a randomised controlled study. Clin Rehabil 21: 706-711.
- Sashika H, Matsuba Y, Watanbe Y(1996) Home exercise program of physical therapy: effect on disabilities of patients with total hip arthroplasty. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 77: 273-277.
Figures at a glance
 |
 |
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
Relevant Topics
- Electrical stimulation
- High Intensity Exercise
- Muscle Movements
- Musculoskeletal Physical Therapy
- Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy
- Neurophysiotherapy
- Neuroplasticity
- Neuropsychiatric drugs
- Physical Activity
- Physical Fitness
- Physical Medicine
- Physical Therapy
- Precision Rehabilitation
- Scapular Mobilization
- Sleep Disorders
- Sports and Physical Activity
- Sports Physical Therapy
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 6665
- [From(publication date):
November-2012 - Apr 03, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 2049
- PDF downloads : 4616
