Research Article Open Access
Do Postmenopausal Women Have Higher Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Concentrations Compared to Men or Younger Women?
| Martha A Kaeslin*, Cyril A Fuhrer, Roberto Herklotz and Andreas R Huber | ||
| Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Cantonal Hospital Aarau, Tellstrasse, 5001 Aarau, Switzerland | ||
| Corresponding Author : | Martha A Kaeslin PhD, Institute of Laboratory Medicine Cantonal Hospital Aarau, Tellstrasse 5001 Aarau, Switzerland Tel: +41 62 838 52 90 Fax: +41 62 838 53 99 Email: martha.kaeslinmeyer@ksa.ch |
|
| Received November 18, 2014; Accepted December 08, 2014; Published December 12, 2014 | ||
| Citation: Kaeslin MA, Fuhrer CA, Herklotz R, Huber AR (2014) Do Postmenopausal Women Have Higher Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Concentrations Compared to Men or Younger Women? Autacoids 3:107. doi: 10.4172/2161-0479.1000107 | ||
| Copyright: © 2014 Kaeslin MA, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | ||
Related article at Pubmed Pubmed  Scholar Google Scholar Google |
||
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Autacoids and Hormones
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D deficiency is a widely discussed topic in medicine. However, the phenomenon that postmenopausal women have higher 25(OH)D3 concentrations compared to men or younger women is rarely described in the scientific literature. Therefore the objective was to investigate this phenomenon in a representative population between different life periods and gender in Aarau (Switzerland) at the end of wintertime when the lowest 25(OH)D3 concentrations can be observed from seasonal cycling. Methods: 25(OH)D3 serum concentrations were measured in a volunteer study population (88 women, 26 men;age: 25-82 years) and we compared all 25(OH)D data of patients of the cantonal Hospital of Aarau in the years from 2010 to 2012(2,766 women, 1,532 men; age: 3 month - 99 years) from the end of February to the end of March 2011. Measurements were performed by HPLC and LC-MS/MS routine assays. Further information was obtained from an especially designed questionnaire. Results: Overall vitamin D deficiency (25(OH)D3<50 nmol/L) was more present in men (≥ 50%) than women(<50%). In the volunteer study population and in the hospital patient population elderly women, especially postmenopausal women, had significantly higher mean 25(OH)D3 concentrations (66.5 and 61.0 nmol/L) compared to men (52.3 and 48.2 nmol/L, P<0.05). Conclusions: At the end of wintertime postmenopausal women had the highest 25(OH)D3 serum concentrations compared to younger females and any age cohort of men. Therefore increased testing should be performed for younger women and men to prevent vitamin D deficiency especially during wintertime.
Prevalence; Schistosomiasis; Snail survey; Bulinus; Praziquantel; Gender; Age Group
Introduction
Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia is a parasitic disease caused by several species of trematodes, parasitic worm of the genus Schistosoma. Urinary bilharzia is caused by the Schistosoma haematobium, and the Snails from the genus Bulinus serve as the intermediate host between mammalian hosts. It is common in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in communities with very little or no access to safe drinking water and good sanitation; people involved in routine agricultural, domestic, occupational, and recreational activities which expose them to contaminated water containing the infected snails. When children come into contact with a contaminated water source, the parasitic larvae easily penetrate through their skin and further mature within organ tissues. Schistosomiasis is a chronic disease.
Urinary schistosomiasis causes progressive damage to the bladder, ureter and kidneys. Schistosomiasis has low mortality rate. Although it has a low mortality rate, schistosomiasis is often a chronic illness that can damage internal organs, and in children, impair growth and cognitive development. It is the second most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease after malaria [1]. Many infections are sub clinically symptomatic, with anemia and malnutrition being common in endemic areas. Due to its low mortality rate, the disease is not given as much attention as the other diseases that have a high mortality rate.
According to the Centre for disease control and prevention (CDC) report-(2010), infections with all major Schistosoma species can be treated with praziquantel and that the timing of treatment is important since praziquantel is most effective against the adult worm and requires the presence of a mature antibody response to the parasite. For travelers, treatment should be at least 6-8 weeks after last exposure to potentially contaminate freshwater. One study has suggested an effect of praziquantel on Schistosoma haematobium eggs lodged in tissues, however, limited evidence of parasitic resistance to praziquantel has been reported based on low cure rates in recently exposed or heavily infected populations. In recent studies, no widespread of clinical resistance has been reported, thus, praziquantel remains the drug of choice for treatment of schistosomiasis [2]. Host immune response differences may impact individual response to treatment with praziquantel. Although a single course of treatment is usually curative, the immune response in lightly infected patients may be less robust, and repeat treatment may be needed after 2 to 4 weeks to increase effectiveness. In Zambia, according to the SMART Zambia Institute, ‘‘Mass Drug Administration using praziquantel is done via schools primarily as the target population is school aged children (SAC) 5-14. In areas above 50% prevalence, high risk adults are also treated in a community-based treatment approach of administering drugs going door to door.” The ministry of health has an occasional program of supplying praziquantel (a drug that is used to cure the disease) which is done at least once a year in different primary schools. The drug is given to the children but no post treatment follow-ups are made to evaluate the effectiveness of the drug administration program or check if the burden of schistosomiasis is actually being eradicated or at least reduced; and the sources of infection are not surveyed. This study is therefore important because it will help to determine whether schistosomiasis is present in Sinazongwe district and how prevalent it is if at all present especially with the on-going administration of praziquantel in schools.
Methodology
The methodology that was applied in this study involved the experimental design, i.e. the most reliable technique in this research was the examination of urine samples and a fractional technique was used in the snail survey.
Study area
This study was conducted in Sinazongwe district which is located in the southern province of Zambia. Location map of Sinazongwe district, Zambia, Sinazongwe district, Zambia (Figures 1 and 2).
Bilharzia survey
Three primary schools in Sinazongwe district were sampled by convenient sampling and these were: Mwezya primary, Sinakasikili primary and Maamba private. 542 urine samples were collected from all three schools; 208 from Mwezya primary school, 184 from Sinakasikili primary school and 150 from Maamba private school. The urine samples were collected from pupils in labeled, sterile, wide mouthed, screw capped plastic containers and the pupils were given an instruction to deposit midstream and terminal urine. The urine collection was done between the hours of 10.00 and 14.00 as this is the period in which the female schistosome worm lays its eggs. The samples collected were then processed and examined in the laboratory at Maamba Hospital which is 20 km from Mwezya primary school, 15 km from Sinakasikili primary school and 1 km from Maamba private school.During the processing of the urine samples, 10 ml of the urine in each labeled, sterile, wide mouthed, screw capped plastic container was placed in a test tube and spun in a centrifuge at 3000 revolutions per minute (3000 RPM) for 3 minutes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was decanted, leaving the sediment at the base of the test tube. The sediment, which has a high concentration of the substances contained in the urine was then placed on a glass slide, covered with a cover-slip and examined under a light microscope at 40x objective for the presence of Schistosoma haematobium ova; taking note of the number per sample examined.
Snail survey
Snail survey was carried out along 3 streams that are near the selected schools; Siamaambo stream which is near Mwezya primary school, Kanzinze stream which is near Sinakasikili primary school and another stream also called Kanzinze which is near Maamba private school. 1 km of each stream was surveyed. The length of each investigated area was divided into 10 stations, each station covering 100 m. 10 scoops were conducted at each station using a dip net, and the snails were placed in containers, 1 container per station. The dip net was passed through the water and vegetation at intervals along the shore-lines and sometimes on the upper layer of mud. Snails collected were sorted out according to species; and the number of Bulinus globosus snails collected were counted and further examined to detect cercaria; this was done by putting the snails in test tubes with water, 1 snail in each test tube and then exposed them to a light source (bulb) for two hours. After two hours of exposure to light, the water in the test tube was examined for the presence of cercaria using a magnifying lens. Siamaambo stream in Sinazongwe district, one of the water sources near Sinakasikili primary school. Left-researcher scooping snails on the edges of the river using a dip net; Right- wide mouthed screw capped containers used for sample collection (Figures 3 and 4).
Results
Prevalence rates in school children
Table 1 shows the results of human urine examination for Schistosoma haematobium infection in the three primary schools located in Sinazongwe district that had been selected, namely, Mwezya primary school, Sinakasikili primary school and Maamba private school. 542 urine samples were collected and examined from all three schools, 62 of the 542 were positive, giving 11.44% as a percentage of those that were infected with schistosomiasis. 208 samples of the 542 were collected from Mwezya primary school, 48 were positive, giving 23.08% as a percentage of those infected with schistosomiasis. 184 samples were from Sinakasikili primary school with 12 being positive, giving 6.52% as a percentage of those infected with Schistosomiasis. 150 samples of the 542 were from Maamba private school, 2 were positive, giving 1.33% as the percentage of those infected with schistosomiasis. According to Table 1, Mwezya primary school with 23.08% had the highest percentage schistosomiasis infection, followed by Sinakasikili with 6.52% and Maamba private school with 1.33% having the lowest percentage. (Table 1) Results of human urine examination for Schistosoma haematobium infection in three primary schools located in Sinazongwe district.
| Name of school | Total number of specimen examined | Number of positives | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mwezya primary | 208 | 48 | 23.08 |
| Sinakasikili primary | 184 | 12 | 6.52 |
| Maamba private | 150 | 2 | 1.33 |
| Total | 542 | 62 | 11.44 |
Table 1: Results of human urine examination for Schistosoma haematobium infection in three primary schools located in Sinazongwe district.
Infection rate of Schistosoma haematobium by age group, gender and intensity of infection.
Age group
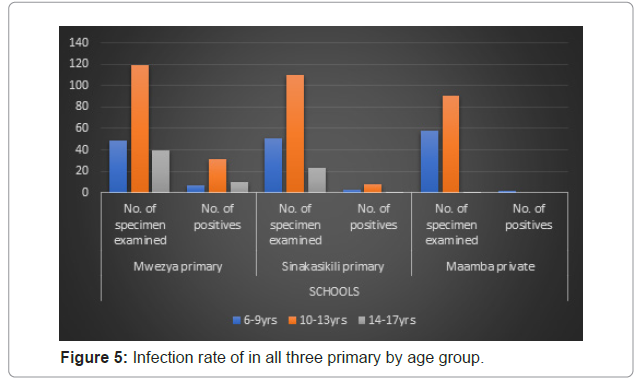
Figure 5 shows the infection rate by age for all three schools. According to this figure, in the 6-9 years age group, 49 samples were collected from Mwezya primary school, 7-(14.29%) were infected; 51 samples were collected from Sinakasikili primary school, 3-(5.88%) were infected and 58 samples were collected from Maamba private school, 2 (3.45%) were infected. Most of the samples collected belonged to the 10-13 years age group and this age group had the highest percentages of infection at Mwezya and Sinakasikili primary schools. 119 were collected from Mwezya primary school with 31 (26.05%) infected, 110 from Sinakasikili primary school with 8-(7.27%) infected and 91 from Maamba private school with 0 infected. The majority of the samples collected in the 14-17 years age group were from Mwezya primary school with a record of 49, and 10-(25%) were infected; Sinakasikili primary school had 23, and only 1-(4.35%) was infected; and Maamba private with 1, who was not infected . Mwezya primary school had the highest infection for all age group. Infection rate of in all three primary by age group (Figure 5).
Gender
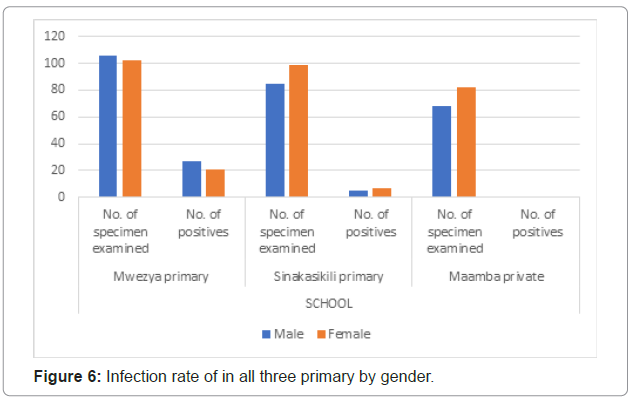
Figure 6 shows the infection rate by gender. Mwezya primary school had 27/106 males-(25.47%) and 21/102 females-(20.59%) with positives results; Sinakasikili primary school had 5/85 males-(5.88%) and 7/99 females- (7.07%) with positive results; and Maamba private school had 1/68 males-(1.47%) and 1/82 females-(1.22%) with positive results. Mwezya primary had the highest percentage of infection in males while Sinakasikili primary and Maamba private schools had the percentage of infection in females higher than that of males. Figure 6: Infection rate of in all three primary by gender.
Intensity of Schistosomiasis infection
Table 2 shows the intensity of schistosomiasis infection in all the three schools, Maamba private school and Sinakasikili primary school had no heavy infections; all infected children in these schools had light infection. Unlike these two schools, Mwezya had 6 children with heavy infection, giving a percentage of 9.68% of heavy infection out of 62 positives. (Table 2) Determination of the intensity of schistosomiasis infection for all three schools had the highest percentage of infection for all age groups. Siamaambo stream, which is closest to Mwezya primary had a high infestation of Bulinus globosus (schistosome intermediate host), this therefore could be the reason for the high percentage of infection among the children at this school. The academic performance of the infected children was found to be below average, in relation to the general class performance. It was noted that the infected children had a lower class attendance; this may be due to the fatigue that accompanies the infection and this could have contributed
| Name of school | Number of Positives | Intensity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light infection (<50 eggs/10 ml) | Heavy infection (>50 eggs/10 ml) | ||||
| No. | % | No. | % | ||
| Mwezya primary | 48 | 42 | 87.5 | 6 | 12.5 |
| Sinakasikili primary | 12 | 12 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Maamba private | 2 | 2 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 62 | 56 | 90.32 | 6 | 9.68 |
Table 2: Determination of the intensity of schistosomiasis infection for all three schools.
Snail survey
For the snail survey, snails collected from Siamaambo stream released cercaria after exposure to a light source for 2 hours. No snails were found in Kanzinze stream, hence none were collected.
Discussion
Prevalence of Bilharzia in primary school children
Praziquantel is the drug of choice for the treatment of schistosomiasis and the drug is administered to primary school children at least once in a year in Sinazongwe district, targeting only the school going children. Administration of this drug should lead to the eradication or at least great reduction in the cases of schistosomiasis in Sinazongwe district. However, from this study, it was found that schistosomiasis is still highly existent in the district despite the ongoing administration of praziquantel; nonetheless, most of the infections are of low intensity.
Most infected gender and age groups
More males were infected than females. This could be the case because the males are usually by the stream fishing and swimming when not at school while the females are home doing house chores and occasionally at the stream to swim, reducing their contact with water because they may only get in contact with the water when cleaning dishes or when taking a bath. Another factor causing the male infection rate to be higher than that of females was found to be that the females are quite shy to undress and swim unlike the boys, hence the reduction of exposure to infection. Nonetheless, the highly infected sex may differ in some areas/places due to culture differences. Different cultures may have different chore allocations for a particular gender, and in an event were a certain chore increases one’s susceptibility to infection, the infection will be high in the sex that is often involved in that chore. From the results obtained from the bilharzia survey, the most affected age group was the 14-17 years age group. This was because the children in this age group are very active and mostly spend time fishing when not at school or at the fields or home helping their parents. They also swim in the stream especially in the hot season. This teenage age apparently is highly explorative and at times may not hind to their parents’ advice which may also be in relation to the disease. Fishing and swimming were found to be the most activities in which the children are involved; and they both involve contact with water, hence increasing the chances of infection if water in infected water. Mwezya primary school to their low performance in class as they are usually absent when a number of lessons are being conducted.
Snail survey
From the snail survey results, Bulinus globosus, which is the intermediate host for Schistosoma haematobium was found to be among the several snail species in Siamaambo stream. The Bulinus globosus snails collected released cercaria when exposed to a light source; therefore they were infected and were/are the source of the bilharzia infection in Mwezya (Mwezya primary school). This infection is therefore obtained in the regions from which the snails were collected, and probably also from the parts of the stream that were not surveyed. Nonetheless, no snails were found in Kanzinze stream. Despite the absence of the intermediate hosts in the streams near Maamba private school and Sinakasikili primary school, some pupils at these were found to be infected with bilharzia. This infection was definitely not acquired from the two surveyed streams, but could have acquired during several migrations to bilharzia infested areas or a stream in within the town/village that was not surveyed. During the survey, it was found that the stream near Maamba private school further connects to the stream near Sinakasikili primary school, causing them to have a common source. Water from the Maamba Coal Mine (Maamba Collieries Limited) washing plant which has a lot of chemicals flow in the Kanzinze stream; therefore this may have been a contributing factor to the absence of snails in this particular stream. Because no snails were found in Kanzinze stream, this stream is therefore not the source of the bilharzia infection in these two area with the respective primary schools; meaning the infected individuals infected at Maamba private school and Sinakasikili primary school got there infection from a different water source/body and not Kanzinze stream which happens to be the nearest water body. The chemicals from the Maamba Coal Mine may contain some potential molluscacides that could be used to eliminate the Bulinus globosus; and this may have to be isolated and proven not to be harmful to the non-disease causing snails so as not to affect the ecosystem [3-8].
Recommendations
Comprehensive control by chemotherapy and snail control to eradicate the disease or at least lower the prevalence. Health education should be given to the communities (targeting parents/adults) with regard to schistosomiasis especially that it is a chronic disease. Targeting school going children is not enough because the children will need to be couched, monitored and reminded from time-to-time. Health officials that are involved in the administration of praziquantel should make follow-ups time-to-time after the drug has been administered to evaluate the effectiveness of prophylactic program. This is very important because there may be adults who are infected but not aware and do not even take even take responsibility to alert the children about the disease. This is very important because a single praziquantel dosage may not be so effective for heavy infections. Tap water must also be made available in most villages; this will reduce frequent contact with contaminated water in streams. Targeting school going children is not enough because the children will need to be couched, monitored and reminded from time-to-time. Health officials that are involved in the administration of praziquantel should make follow-ups time-to-time after the drug has been administered to evaluate the effectiveness of prophylactic program. Research on the chemical composition of the water from the Maamba Coal Mine should be conducted to check for a component that could have hindered the survival of snails in Kanzinze stream, which may be used as a molluscacide.
Conclusion
Despite the administration of praziquantel to school going children, schistosomiasis will still be a problem in Sinazongwe district because the source of infection is not dealt with; as a result, there is continuous reinfection of the treated and untreated children. This is very important because a single praziquantel dosage may not be so effective for heavy infections. Tap water must also be made available in most villages; this will reduce frequent contact with contaminated water in streams.
Limitations
During the bilharzia survey, one of the challenges encountered was the different time tables for the children. Some children reported for school and knocked off before 10:00 am, therefore the sample had to be collected quite earlier than the time when the female schistosome worm is expected to lay most of its eggs. Another challenge was that not all the children followed the instruction to collect terminal urine which is the best sample for diagnosis, this therefore could have affected the results obtained. Nonetheless, the teachers were very helpful in explaining the bilharzia disease in local language, giving the children knowledge about disease and why they had to submit urine samples because some of them were very skeptical about giving their urine to a stranger.
During the snail survey, one of the challenges encountered was the presence of crocodiles in Siamaambo stream. Some areas were not surveyed because they were potential resting regions for the crocodiles during the day, accompanied by several incidences of people being bitten by the crocodiles few days before the snail survey was done.
References
- Mutengo MM, Mudenda V, Mwansa JC, Kaonga K (2009) Presence of Schistosomiasis in Genital Biopsies from patients at the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka Zambia. Medical Journal of Zambia,36:1-5.
- Mubanga FC, Evelyn Funjika, Mohamed AS (2018) Prevalence and intensity of Schistosoma haematobium infection among schoolchildren in central Zambia before and after mass treatment with a single dose of praziquantel. Trop Parasitol 8:12-7.
- Watson JM, Abdel AM, Halawani A (1948) Investigations on the antibilharzial action of miracil D (nilodin). Transactions of The Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 42:37-54.
- Vicente Y Belizario (2008) Efficacy and safety of 40 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg doses of praziquantel in the treatment of schistosomiasis. Journal of Pediatric Infectious Diseases 3:27-34.
- OlogundeCA, Olaoye AB, Olaifa OA, Olowu OY (2012) Schistosomiasis in Ogbese, Re-Infection after Successful Treatment with Praziquantel in Nigeria. Global Journal of Medical Research 12:19-34.
- Schistosomiasis and Soil-Transmitted Helminthes among School children in
- P HIRA P(1969) Transmission of Schistosomiasis in Lake Kariba, Zambia. Nature 224: 670–672.
- Mozambique. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 81:799-803.
Tables and Figures at a glance
| Table 1 | Table 2 | Table 3 | Table 4 | Table 5 |
Relevant Topics
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 13616
- [From(publication date):
November-2014 - Apr 03, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 9055
- PDF downloads : 4561