Developmental Venous Anomaly: Caput Medusae Sign
Received: 04-Jun-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-65933 / Editor assigned: 06-Jun-2022 / PreQC No. roa-22-65933 (PQ) / Reviewed: 20-Jun-2022 / QC No. roa-22- 65933 / Revised: 22-Jun-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-65933 (R) / Published Date: 29-Jun-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000385
Image Article
Developmental venous anomalies (DVAs) are a type of cerebral vascular malformations in addition to arteriovenous malformations, capillary telangiectasia and cavernous malformations. DVAs can be isolated or associated with other cerebral vascular malformations [1, 2].
The exact pathogenesis is still unknown, several hypotheses have been developed some have proposed that DVAs result from a hemodynamic requirement that leads to the recruitment of transhemispheric anastomotic pathways. Others suggest that DVAs develop as a result of a regression anomaly during fetal angiogenesis [1].
Most DVAs have no clinical significance and are discovered incidentally, but they are still a source of complications including hemorrhagic and ischemic infarcts or cerebral edema around the territory of the DVA resulting from acute thrombosis of the collecting vein [2].
Brain CT and MRI can detect the typical “Caput medusa” draining into a collecting vein, which allows the diagnosis of DVAs with certainty without the need to perform a digital subtraction [2]. The brain scan without injection, allows the detection of associated hemorrhage, parenchymal calcifications, atrophy or lesions of the white matter in the drainage territory of the DVA. The collecting vein of the DVA may appear isodense or moderately hyperdense, or markedly hyperdense in acute thrombosis and is enhanced after injection of a contrast agent [2].
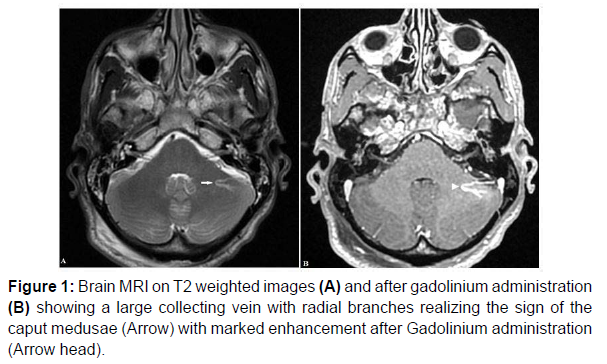
Non contrast T2- and T1-weighted MRI may reveal flow voids and phase-shift artifacts generated by the collecting vein and the larger venous radicles of the Caput medusae. DVA is best assessed after gadolinium administration, especially with 3D-contrast-enhanced echo gradient T1-weighted images [2] (Figure 1).
Figure 1 shows brain MRI of 22 years-old man, on T2 weighted sequence (Figure A) showing a left cerebellar large collecting vein with radial venous branches. MRI with gadolinium (Figure B) showing marked enhancement of the collecting vein and radical branches (caput medusae sign) are corresponding to developmental veinous anomaly.
References
- Gokçe E, Acu B, Beyhan M, Celikyay F, Celikyay R (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging findings of developmental venous anomalies. Clin Neuroradiol 24: 135-143.
- Millán Ruíz DS, Gailloud P (2010) cerebral developmental venous anomalies. Childs Nerv Syst 26: 1395-1406.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Oubaddi T, Izi Z, Imrani K, Billah NM, Nassar I (2022) Developmental Venous Anomaly: Caput Medusae Sign. OMICS J Radiol 11: 385. DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000385
Copyright: © 2022 Oubaddi T, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2373
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Apr 25, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1984
- PDF downloads: 389