Research Article Open Access
Descriptive Study on Magnitude of Substance Abuse among Students of Aman Poly Technique College Students, Bench Maji Zone South West Ethiopia
Mesfin Geremew Birega*, Banchlay Addis, Minilk Agmasu and Melkamu TadeleDepartment Public Health, Mizan Teppi University College of Health Science and Medicine, Ethiopia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Mesfin Geremew Birega
Instructor, Department Public Health
Mizan Teppi University College of Health Science and Medicine
Ethiopia
Tel: 251-0911482091
Fax: 251-0473360465
E-mail: mgeremaw@yahoo.com
Received date: October 04, 2016; Accepted date: April 11, 2017; Published date: April 18, 2017
Citation: Birega MG, Addis B, Agmasu M, Tadele M (2017) Descriptive Study on Magnitude of Substance Abuse among Students of Aman Poly Technique College Students, Bench Maji Zone South West Ethiopia. J Addict Res Ther 8:320. doi:10.4172/2155-6105.1000320
Copyright: © 2017 Birega MG, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Addiction Research & Therapy
Abstract
Background: The world drug problem continues to constitute a serious threat to public health and to the safety and well-being of humanity. It is also one of burning public health problem in Ethiopia. There is research evidence that showed increment of trend of substance abuse among high school and college students.
Objective: To assess the magnitude of substance abuse among students of Aman Poly Technique College in 2016.
Methodology: A descriptive quantitative cross sectional study was conducted to assess the magnitude of substance abuse among the students of Aman Poly Technique College.
Results: The overall Prevalence of substance abuse was 42.5%. The commonly used substances were chat chewing 65%, Alcohol 28% and cigarette 4.8%. And the reasons to initiate substance abuse were peer pressure were36.8%, to relive from tension 20% and academic dissatisfaction were 18.4%.
Conclusion: According to this study we conclude that chat was the most abused substance followed by alcohol and peer pressure was the most significant reason to initiate substance abuse.
Keywords
Substance; Use; Chat; Alcohol
Introduction
The world drug problem continues to constitute a serious threat to public health and to the safety and well-being of humanity-particularly children, young people and their families [1]. About 230 million people or 5 percent of the world’s adult population are estimated to have used an illegal drug at least once in 2010. Alcohol and other drug (Khat and tobacco) users number about 27 million, which is 0.6 percent of the world adult population [2].
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime reports while drug use is stabilizing in industrialized countries, it is increasing in developing nations [3]. In Ethiopia a national study reported 23.0% of out-of-school and 7.5% of in-school adolescents use khat [4]. A separate study estimated prevalence of khat use in the general population of Ethiopia was 27.3% among men and 11.0% among women of 15-49 years in 2011 [5]. Heavy consumption of khat is associated with euphoria, hyper activity, anorexia, insomnia, lethargy and depression. In addition to combined use of alcohol and khat could increase sexual risk behavior contributing to spread of HIV [6,7].
In Ethiopia there is research evidence that indicate substance abuse is also increasing among high school and university student [8]. Substance use remains as an important area of research due to the implications of early substance dependence on the future of the youth [9].
Mizan Aman town is one of developing urban center and becoming educational hub of the country, it is expecting that the increasing trend of substance abuse among school student might be similar for our study area. Knowing the current magnitude of substance abuse have importance for future anti substance use behavioral change program, thus this study was conducted with the aim of assessing magnitude of substance abuse among students Aman Poly Technique College, South west Ethiopia.
Methods
Study setting and design
A descriptive quantitative cross sectional study design was conducted among students of Aman Poly Technique College.
Aman Poly Technique College is found at Mizan-Aman town of Benchi Maji zone of Southern nation nationalities and peoples of Ethiopia regional state (SNNPR) which is located 561 km from Addis Ababa; 234 from Jimma and 4.5 km from Mizan town. Aman TVET Collage was established in 1994 E.c and started its work in the same year by four departments with the total number of less than two hundred students. Currently the college has 885 students, studying 8 fields of technique and vocational education with different level; Level I, Level II and Level III.
Study participants
Regular students of Aman TVET College in Aman town obtained by sampling during the specified study period were included in the study.
Sample size and sapling
The formula that we were used to calculate sample size in the study was single population proportion formula. Prevalence of point under consideration was (P=50% because to the extent of our knowledge and searching effort, no P value has been obtained about the magnitude of substance abuse in the study area). So the 384 sample size was computed and after using correction formula hence our total population is less than 10,000 the final sample size became 268.
We were used stratified random sampling method followed by simple random technique to select individual students that are to be included in our sample size. Using stratified random sampling method, the total numbers of students in the college were first divided into different strata based on their departments and level of study. Sample was allocated to each departments and level of study proportionally. Finally, simple random lottery method was used to select study participants using sampling frame of students list (Table 1).
| Department | Number of students by level | Allocated sample by level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | I | II | III | |
| Survey | 47 | 69 | 74 | 16 | 23 | 25 |
| Automotive | 21 | 33 | 42 | 7 | 11 | 14 |
| Masonry | 39 | 55 | 73 | 13 | 18 | 24 |
| ICT | 27 | 33 | 42 | 9 | 11 | 14 |
| GMFA | 8 | 15 | 12 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| Sanitary | 21 | 28 | 30 | 7 | 9 | 10 |
| Auto electric | 52 | 73 | 37 | 17 | 24 | 12 |
| Road and construction | 24 | 9 | 21 | 8 | 3 | 7 |
Table 1: Showing proportional allocation of sample size in each department and level, May 2016.
Data collection
A structured questionnaire were prepared and tested to address all important variables. The questionnaire prepared first in English and then translate in to Amharic and back to English in order to maintain its consistency. Information’s included were socio demographic characteristics, substance use (cigarette, alcohol and Chat chewing) and reasons of substance abuse. Pre-test was conducted on 5% of sample size in similar study context at Mizan Agricultural College. Training and orientation was given for data collector two days in advance of data collection period. Three public health graduating students under supervision were participated in data collection.
Statistical data analysis
The data was processed manually using tally sheets. Each questionnaire was checked for completeness, missing values and unlikely responses and then it was manually clean up on such indication. Data were manually analyzed using scientific calculator. Descriptive statistics and summary measures were employed.
Ethical consideration
Primarily, ethical clearance was obtained from Public Health and Medical Science college ethical review committee. Letter of permission was given to Aman Poly Technic College Dean office and respective departments. All respondents were asked for their willingness for participation in the study and informed verbal consent was obtained after confidentiality of the information assured.
Results
Socio-demographic characteristics
A total of 285 study participants were participated in the study which makes 97% of response rate. One hundred eighty-one (61.5%) of the study participants were males and the rest 38.5% were females. One hundred respondents (49.1%) of the sample in the age interval of 22-26 years. Almost half 146 (49.5%) respondents were Bench by ethnic group. One hundred nine 109 (37.1%) were Orthodox Christian by their religion followers (Table 2).
Concerning academic year 110 (37.4%) were first year students. Majority 192 (65.5%) were came from rural areas. The prominent family occupation was farmer 48.2% followed by Merchant 28.5%. About 145 (49.5%) of respondents had monthly income of greater than three hundred birr and 116 (39.4%) had family income of one thousand to two thousand birr. Eighty six (28.3%) reported that there is habit of substance use in their family.
| Variable | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 181 | 61.50% | |
| Female | 113 | 38.5 | |
| Age category | |||
| 18-22 | 96 | 32.70% | |
| 23-26 | 144 | 49.10% | |
| 27-30 | 54 | 18.20% | |
| Religion | Orthodox | 108 | 37.07 |
| Muslim | 62 | 21.43 | |
| Protestant | 102 | 34.69 | |
| Catholic | 14 | 4.76 | |
| Others | 8 | 2.04 | |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Amhara | 116 | 36.2 | |
| Bench | 146 | 49.5 | |
| Kaffa | 28 | 9.5 | |
| Oromo | 8 | 2.7 | |
| Others | 6 | 2.1 | |
| Resident before | |||
| Rural | 192 | 65.5 | |
| Urban | 102 | 34.5 | |
| Family occupation | |||
| Farmer | 142 | 48.4 | |
| Merchant | 83 | 28.3 | |
| Civil servant | 50 | 17 | |
Table 2: Socio-demographic characteristics of Aman Poly Technique College students, May 2016.
Magnitude of substance use
Of the total of study participants 125 (42.2%) reported that they have experience of using substance at least once in their life time. Among users more than three fourth 107 (85.6%) were males. Concerning type of substance reported by users were chat, alcohol and cigarette by 24.3%, 68.2% and 3.7% study respondents, respectively, as shown in Table 3.
| Variable | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percentage | Frequency | Percentage | |
| Abuse all | 107 | 85.60% | 18 | 14.40% |
| Alcohol dinking | 26 | 24.30% | 7 | 38.90% |
| Chat chewing | 73 | 68.20% | 9 | 50% |
| Cigarette smoking | 4 | 3.70% | 2 | 11.10% |
Table 3: Frequency of male and female substance users among Aman TVTE College students, May 2006.
Current substance users
Of the total 7 (6%) were current users of any substance. Among type of substance alcohol were used by 3 (42.8%), chat 3 (42.8%) and cigarette 1 (14.2%) as shown in Table 4.
| Variable | Current user | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percentage | |
| Any substance | ||
| Yes | 7 | 6% |
| No | 118 | 94% |
| Alcohol | ||
| Yes | 3 | 42.80% |
| No | 4 | 57.20% |
| Cigarette | ||
| Yes | 1 | 14.20% |
| no | 6 | 85.70% |
| Chat | ||
| Yes | 3 | 42.80% |
| No | 4 | 57.20% |
| All | 1 | 14.20% |
Table 4: Frequency of current and ever substance users among Aman Ploy Technique College.
Time of initiation for substance use
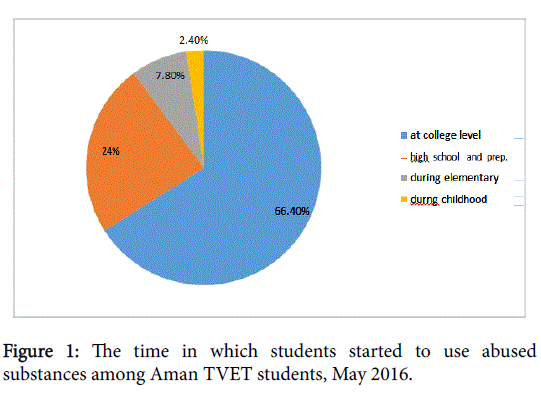
Concerning initiation time of substance use, more than majority 66.40 of substance users reported than they started at college level followed by 24% at high school and preparatory school, as shown in Figure 1.
Patterns of substance abuse
Out of 125 abusers 17 (13.6%), 13 (10.4%), 22 (17.6%), 49 (39.2), 13 (10.4%) and 11 (8.8%) abuse daily, twice a day, once a week, 3-4 times a week, twice a week and sometimes respectively. In case of Duration of substance abuse 32 (25.6%) use less than one year, 39 (31.2%) use 1-2 year, 35 (28%) used 2-4 years and 19 (15.2%) used greater than 4 years. Greater than 62.4% spent 15-20 birr per day, 23.2% spent less than 15 birr per day and 14.4% spent greater than 20 birr per day.
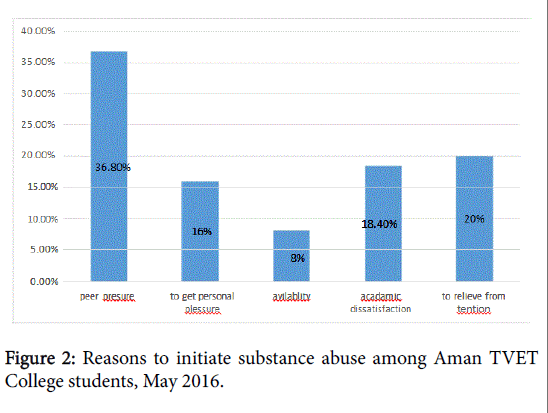
From reason to initiate substance abuse peer pressure accounts 36.8% and academic dissatisfaction, to relive from tension, to get personal pleasure and availability of substance account 18.4%, 20%, 16% and 8%, respectively (Table 5).
| Pattern of substance use | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency of current substance abusing | Daily | 17 | 0.136 |
| Twice a day | 13 | 0.104 | |
| Once a week | 22 | 0.176 | |
| 3-4 times a week | 49 | 39.20% | |
| Twice a week | 13 | 10.40% | |
| Sometimes | 11 | 8.80% | |
| Duration of substance abusing | <1 year | 32 | 25.60% |
| 1-2 years | 39 | 31.20% | |
| 2-4 years | 35 | 28% | |
| >4 years | 19 | 15.20% | |
| Amount of substance abused per day | <15 birr | 29 | 23.20% |
| 15-20 birr | 78 | 62.40% | |
| >20 birr | 18 | 14.40% |
Table 5: Pattern of substance abusing practice among students of Aman Poly Technique SNNPR, Mizan, May 2016.
Discussion
This study was conducted with the aim of assessing magnitude of substance abuse among Aman Poly Technique student. The finding of this study showed that chat was the most abused substance; 65% of study participants ever chew chat. The finding was much higher than other studies in Ethiopia, Adigrat (14.7%) [10], Haramya University (30.3%) [11] and Axum University (28.7%) [12]. Concerning current use of chat, this study revealed that 42.8% of study participants had current use of chat [13]. This finding also higher than study conducted in Adigrat University (9.33%) [10], Jimma University (33.1%) [14], Axum (27.9%) [12] and Mekelle University (25%) [13].
Ever use alcohol among these study participants was 28%. This finding was much higher than study conducted among Iranian student (16%) [15]. But it is lower than Adigrat (56%) [10], Haramaya (53.8%) [11] and Meklle University (82.7%) [13].Concerning the current use of alcohol was 1.05%, this finding was lower than study conducted Adigrat (31.3%) [10], Axum University (32.8%) [12], Mekelle University (41%) [13] and Jimma University (36.4%) [14] (Figure 2).
Ever smoke of cigarette among these study participants was 2.1%. This finding was higher than study conducted Ayer Tena secondary school student in Ethiopia (0.8%) [16] but it much lower than other studies, Preparatory students at Ginner town (8.5%) [17] and Zambia Adolescent (27%) [18].
Conclusion
Substance abuse among Aman Poly Technique College student was prevalent, the most abused was chat chew followed by alcohol and cigarette smoking. The study call up for health education activities for this target groups and the need of further research around the study area.
Authors Contribution
MG was responsible for the study design and implementation, data analysis, and drafting the manuscript. BA & MA reviewed the study design and manuscript revisions. MT participated in the data analysis and manuscript revisions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
References
- United Nations general assembly resolution 67/193 (2013) International cooperation against the world drug problem. New York (NY): United Nations.
- UNODC (2014) World drug report? United Nations publication, New York, pp: 11-25.
- WDR, World drug report. United Nations office on drugs and crime, Vienna.
- Kebede D, Alem A, Mitike G, Enquselassie F, Berhane F, et al. (2005) Khat and alcohol use and risky sex behaviour among in-school and out-of-school youth in Ethiopia. BMC Public Health 5: 109.
- Central statstical agency of Ethiopia (2012) ICF international: Ethiopia demographic and health survey 2011. 2012, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Central statstical agency.
- Volkow ND, Li TK (2005) Drugs and alcohol: Treating and preventing abuse, addiction and their medical consequences. Pharmacol Ther 108: 3-17.
- Kassaye M, Sherief TH, Ghimja F, Teklu F (1999) Drug use among school students in Addis Ababa and Butajira. Ethiop J Health Dev 13: 101-106.
- Gelaw Y, Haile-Amlak A (2004) Khat chewing and its socio-demographic correlates among the staff of Jimma University. Ethiop J Health Dev 18.
- Brook JS, Cohen P, Brook DW (1998) Longitudinal study of co-occurring psychiatric disorders and substance use. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37: 322-330.
- Mossie (2015) Magnitude of psychoactive substance abuse among university students, Adigrat, North Ethiopia: Cross sectional study. J Psychiatry 18.
- Deressa W, Azazh A (2011) Substances use and its predictors among undergraduate medical students of Addis Ababa University in Ethiopia. BMC Public Health 11: 660.
- Gebreslassie M, Feleke A, Melese T (2013) Psychoactive substances use and associated factors among Axum University students, Axum Town, North Ethiopia. BMC Public Health 13: 693.
- Abrha K (2011) Psychoactive substance abuse and intention to stop among students of Mekelle University, Ethiopia.
- Meressa K, Mossie A, Gelaw Y (2009) Effect of substance use on academic achievement of health officer and medical students of Jimma University, South West Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci 19: 155-63.
- Sahraian A, Sharifian M, OmidvarB, Javadpour A (2010) Prevalence of substance abuse among the medical students in Southern Iran. Shiraz E-Medical Journal 11
- Assefa H (2015) Exploring the trends and challenges of substance abuse among Ayer Tena secondary school students in Addis Ababa, Master thesis, Addis Ababa university.
- Ahmed Yasin Mohammed (2014) Assessment of substance use and associated factors among high school and preparatory school students of Ginnir Town, Bale Zone, Southeast Ethiopia. Am J Public Health Res 2: 414-419.
- Odejide AO (2006) Status of drug use in Africa: A review. Int J Ment Health 4: 87-102.
Relevant Topics
- Addiction Recovery
- Alcohol Addiction Treatment
- Alcohol Rehabilitation
- Amphetamine Addiction
- Amphetamine-Related Disorders
- Cocaine Addiction
- Cocaine-Related Disorders
- Computer Addiction Research
- Drug Addiction Treatment
- Drug Rehabilitation
- Facts About Alcoholism
- Food Addiction Research
- Heroin Addiction Treatment
- Holistic Addiction Treatment
- Hospital-Addiction Syndrome
- Morphine Addiction
- Munchausen Syndrome
- Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
- Nutritional Suitability
- Opioid-Related Disorders
- Relapse prevention
- Substance-Related Disorders
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 6485
- [From(publication date):
June-2017 - Jul 13, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 5356
- PDF downloads : 1129