Research Article Open Access
Dendrosomal Curcumin Nanoformulation Attenuates Naloxone Precipitated Morphine Withdrawal Signs in Rats
Masoumeh Ghaemi-Jandabi1, Hakime Abdollahi1, Hossein Azizi1, Majid Sadeghizadeh2* and Saeed Semnanian11Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
2Department of Genetics, School of Biological Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
- Corresponding Author:
- Majid Sadeghizadeh
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medical Sciences
Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
E-mail: sadeghma@modares.ac.ir
Received date: February 03, 2015; Accepted date: March 09, 2015; Published date: March 14, 2015
Citation: Ghaemi-Jandabi M, Abdollahi H, Azizi H, Sadeghizadeh M, Semnanian S (2015) Dendrosomal Curcumin Nanoformulation Attenuates Naloxone Precipitated Morphine Withdrawal Signs in Rats. J Addict Res Ther 6:211. doi:10.4172/2155-6105.1000211
Copyright: © 2015 Ghaemi-Jandabi M, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Addiction Research & Therapy
Abstract
Curcuminis known to possess a wide range of therapeutic and pharmacological properties as anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antinociceptive and neuroprotective agents. The recent achievements of nanotechnology illustrate a novel approach in treatment of drug abuse and addiction. Curcumin as a new candidate can be exploited for drug abuse treatment, but its low bioavailability and water solubility is the most important obstacles and limits its application. Here, curcumin was efficiently encapsulated in a nontoxic nanocarrier, labeled dendrosome, to overcome these problems. The present study is designed to investigate the effect of intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) on the behavioral signs of morphine withdrawal syndrome.
Male Wistar rats weighing 250-300 g were rendered dependent on morphine by subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of morphine sulfate (6, 16, 26, 36, 46, 56 and 66 mg/kg, 2 ml/kg) at set intervals of 24 h for 7 days. The animals received i.p. administration of DNC(12.5 mg/kg) immediately after each morphine injection. On day 8, naloxone (2 mg/ kg, i.p.) was injected and behavioral signs of morphine withdrawal were assessed for 25 min. Our results show that i.p. injection of DNC significantly decreases naloxone precipitated morphine withdrawal signs. The present study indicates that intraperitoneal administration of Dendrosomal curcumin exerts a significant effect on morphine dependency in rats.
Keywords
Dendrosomal curcumin; Morphine withdrawal; Rat
Introduction
Chronic use of opioid drugs leads to the development of dependence and tolerance which in turn limits their therapeutic application and brings about serious social and health issues [1]. In many models of drug dependence, positive and negative reinforcement are two major components. Positive reinforcement of euphoric effects results in a compulsive and relentless desire for drug taking while negative reinforcement of withdrawal signs occurs following cessation of opioid receiving [2]. Opiate withdrawal syndrome is a multifaceted phenomenon involving various regions of the brain and is characterized by physiological and behavioral symptoms [3–7]. Curcumin is a hydrophobic compound derived from the rhizome of Curcuma longa, which is commonly used as a spice in most Asian countries [8]. Curcumin has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, antinociceptive and neuroprotective activities [9,10]. The findings have been shown that daily administration of curcumin could prevent morphine analgesic tolerance [11]. However, low water solubility, poor uptake and tissue distribution remain major impediments, limiting the application of curcumin as treatment agent [12]. Recently, scientists have exposed several strategies, such as loading synthetic analogs from turmeric, designing metabolic inhibitors and liposomal formulations, and nanoparticles of curcumin, to overcome these problems [13-15]. Dendrosome was presented as a novel neutral, amphipathic, and biodegrad¬ablenanocarrier for a gene delivery system [16,17]. The high potential of dendrosome as a gene porter has led to the hypothesis that it can be applied as a vehicle for curcumin delivery. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) on the behavioral signs of morphine withdrawal syndrome.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Male Wistar rats weighing 250–300 g (Pasteur Institute, Tehran, Iran) were used in this study. They were housed three per cage in a temperature-controlled colony room with a regular 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on at 07:00 am) and free access to food and water. This study was performed in accordance with ethical guidelines of the Faculty of Medical Sciences Ethics Committee, Tarbiat Modares University, which are based on NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Drugs
The main drugs used in this study are as follows: Morphine sulfate (Temad, Tehran, Iran), naloxone hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA), Curcumin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO).
Preparation of the DNC
DNC preparation was performed using optimized protocol in the authors’ lab [18,19]. Briefly, different weight/weight ratios of dendrosome/curcumin ranging from 50:1 to 10:1 were examined before settling on a suitable ratio of 25:1. Curcumin was dissolved in various amounts of dendrosome and checked for absorbance spectra by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (Infinite® 200 PRO, Tecan, Mannedorf, Switzerland). Then, the appropriate mixture of dendrosome and curcumin was evaluated for excitation/emission value in comparison with curcumin dissolved in PBS and 1% methanol as the control samples [18]. The loading of dendrosome nanocarriers with curcumin molecules was performed using Gou et al’s protocol [20]. Briefly, curcumin and dendrosome were co-dissolved in 5 mL acetone; this solution was added into 5 mL PBS while stirring constantly. Then, the acetone was evaporated in a rotary evaporator. The curcumin/ dendrosome micelle solution was sterilized using a 0.22 μm syringe filter (EMD Millipore) [20]. Finally, the prepared DNC were stored at 4°C in a light-protected condition until used [18].
Induction of morphine dependency
Animals were rendered dependent by subcutaneous injection of incremental doses of morphine for 7 days (6, 16, 26, 36, 46, 56 and 66 mg/kg, 2 ml/kg) [21]. Non-dependent animals received the same volume of saline. Injections were done at a fixed time during the whole period of study. Opioid withdrawal syndrome was induced by naloxone hydrochloride (2 mg/kg, i.p.) in the day after last morphine injection.
Apparatus
Behavioral signs of morphine withdrawal were assessed in a transparent cylindrical Plexiglas test chamber (30 cm diameter, 50 cm height and bedded with wood chip) for 25 min[22]. All animals’ behaviors were evaluated by the same observer and statistical analyses were performed by an experienced researcher who was blind to the treatment.
Experimental groups
Animals were randomly divided into 4 experimental groups; Group 1, saline treated rats received naloxone to find out if there is any withdrawal sign (n=6); Group 2, morphine treated rats received naloxone to evaluate morphine withdrawal signs (n=7); Group 3, animals received concurrent injection of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC, 12.5 mg/kg, i.p.) with morphine injection for 7 days (n=6). They received naloxone 24h after last morphine injection. Animals in group 4 received concurrent injection of dendrosome (vehicle) with morphine injection and received naloxone 24h after last morphine injection (n=7).
Statistical analysis
Morphine withdrawal symptoms were compared in different experimental groups using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test or the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test when necessary (when counts were not normally distributed). Quantal (all or none) behavioral data were analyzed by the chi-square test. Differences amongst means were considered statistically significant if the p-value was less than 0.05. The results are shown as mean ± SEM.
Results
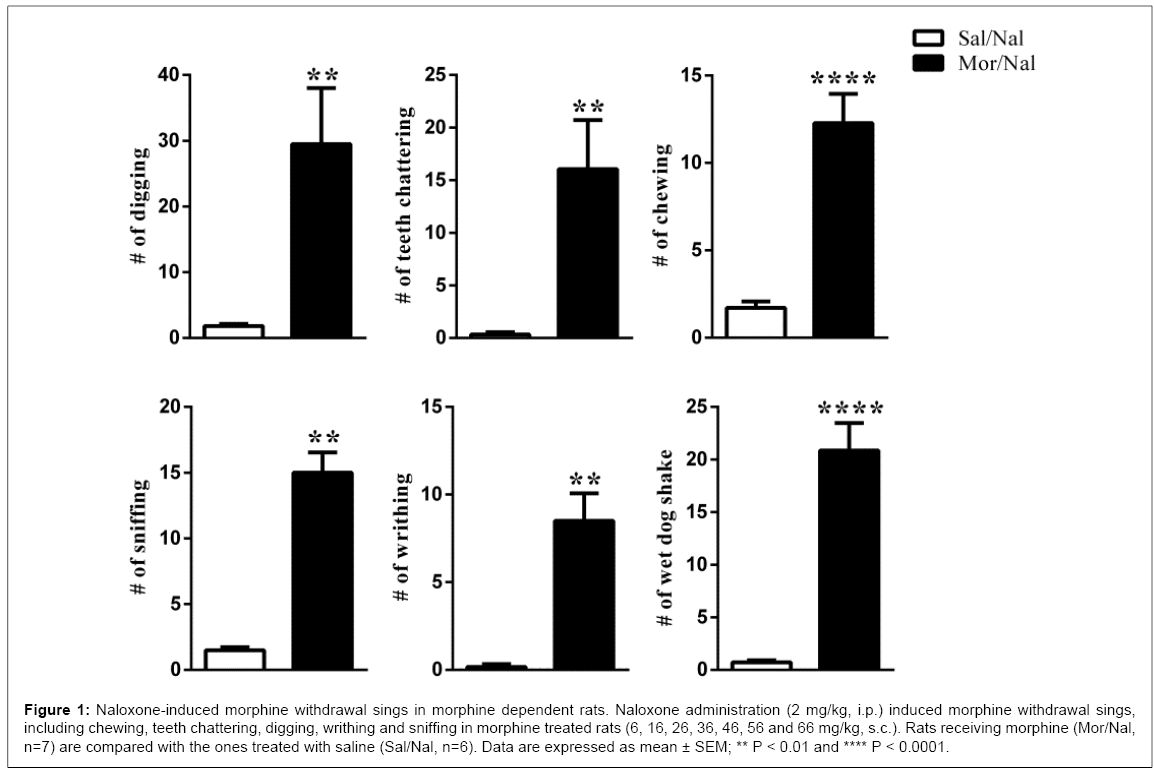
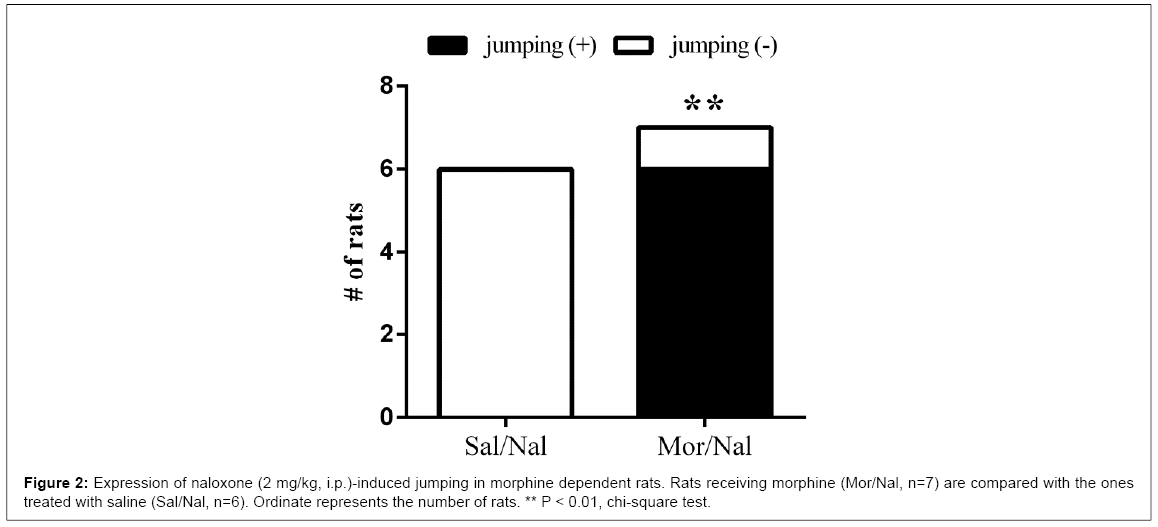
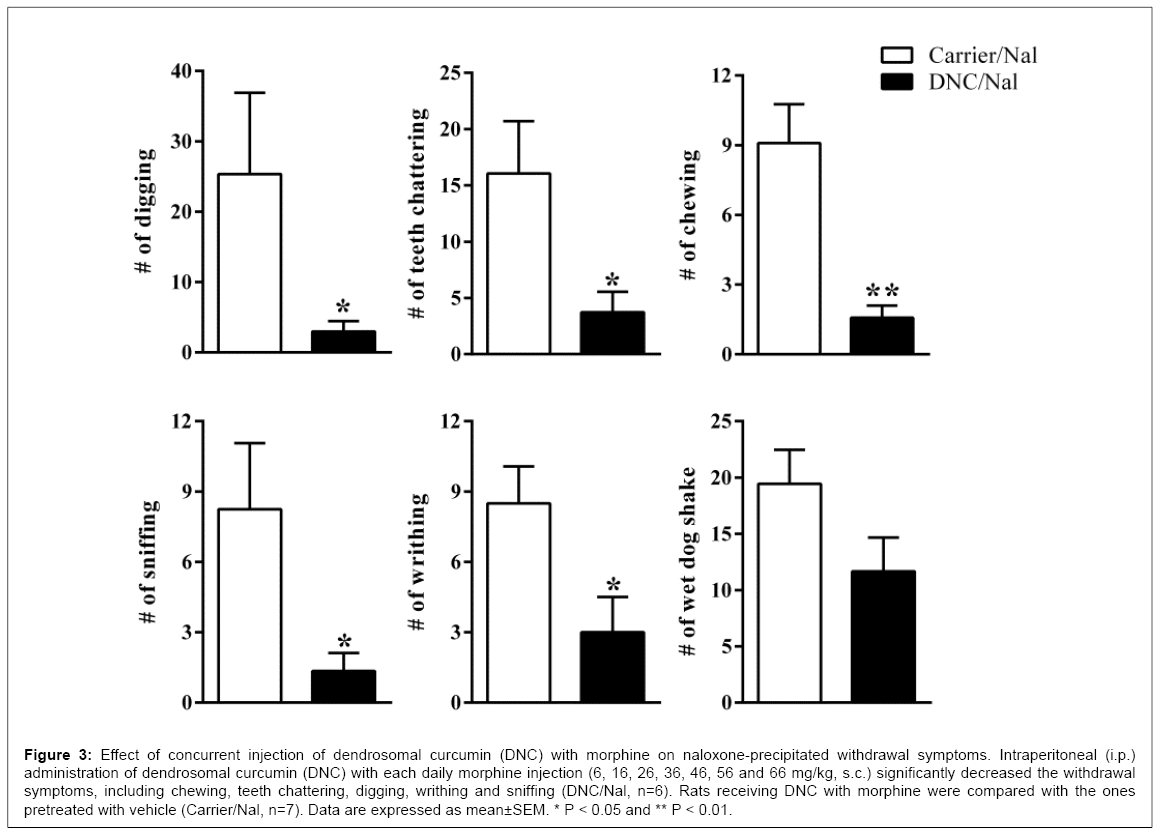
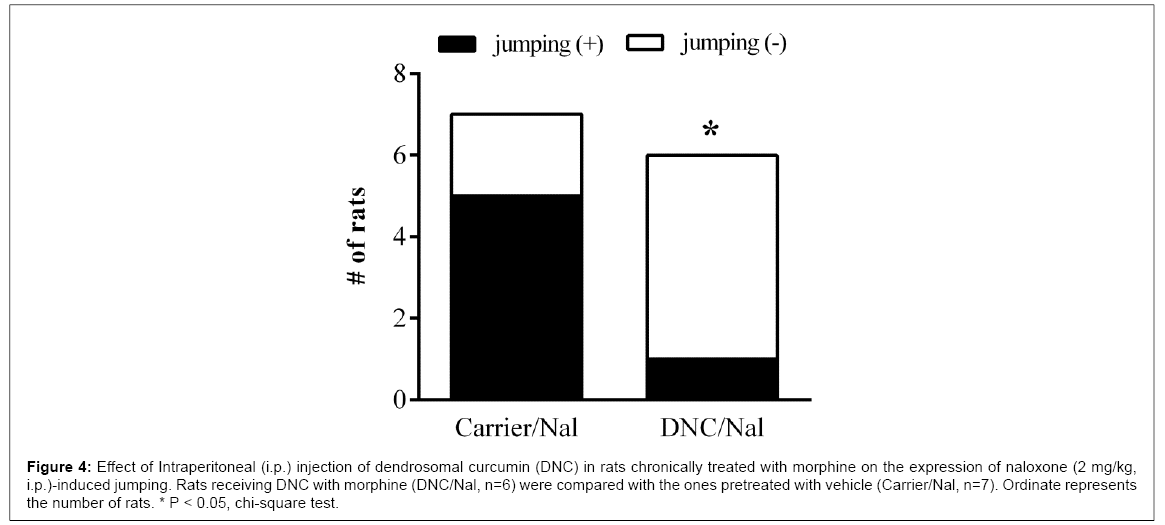
Morphine withdrawal was precipitated by intraperitoneal injection of naloxone hydrochloride (2 mg/kg, i.p.) in morphine dependent rats. These rats showed pronounced withdrawal signs including chewing, digging, jumping, sniffing, teeth chattering, wet-dog shake and writhing following naloxone injection. Non-dependent or saline treated rats (Group 1) exhibited no withdrawal signs following naloxone administration (Figures 1 and 2). Moreover, morphine pre-treated vehicle animals also exhibited pronounced withdrawal signs following naloxone administration. There were no significant differences between morphine pre-treated vehicle animals and morphine treated ones (the data is not represented). Animals received concurrent injection of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) with morphine injection (Group 3) showed significant reduction in several signs of naloxone induced morphine withdrawal symptoms. Some withdrawal signs, including chewing, teeth chattering, digging, writhing and sniffing were reduced significantly (Figure 3). Wet dog shake sign was also reduced but its reduction was not statistically significant. The number of rats that exhibited jumping reduced significantly (Figure 4).
Figure 1: Naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal sings in morphine dependent rats. Naloxone administration (2 mg/kg, i.p.) induced morphine withdrawal sings, including chewing, teeth chattering, digging, writhing and sniffing in morphine treated rats (6, 16, 26, 36, 46, 56 and 66 mg/kg, s.c.). Rats receiving morphine (Mor/Nal, n=7) are compared with the ones treated with saline (Sal/Nal, n=6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; ** P < 0.01 and **** P < 0.0001.
Figure 3: Effect of concurrent injection of dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) with morphine on naloxone-precipitated withdrawal symptoms. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) with each daily morphine injection (6, 16, 26, 36, 46, 56 and 66 mg/kg, s.c.) significantly decreased the withdrawal symptoms, including chewing, teeth chattering, digging, writhing and sniffing (DNC/Nal, n=6). Rats receiving DNC with morphine were compared with the ones pretreated with vehicle (Carrier/Nal, n=7). Data are expressed as mean±SEM. * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01.
Figure 4: Effect of Intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) in rats chronically treated with morphine on the expression of naloxone (2 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced jumping. Rats receiving DNC with morphine (DNC/Nal, n=6) were compared with the ones pretreated with vehicle (Carrier/Nal, n=7). Ordinate represents the number of rats. * P < 0.05, chi-square test.
Discussion
There are various methods for induction of morphine dependency; it seems that injection methods allow more precise control over morphine administration [21]. The present study demonstrates that the concurrent injection of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) with morphine attenuates the development of morphine dependency in rats. These results indicate that i.p. administration of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) significantly decreases the somatic signs of naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal syndrome, including chewing, teeth chattering, digging, writhing, sniffing and jumping.
The remodeling of chromatin structure is implicated as epigenetic mechanisms play a regulatory role in gene expression and behavioral abnormalities that characterize drug addiction [23]. Many drugs of abuse induce modifications in histone acetylation and methylation in the brain, and evidences have been reported that these changes underlie some of the functional abnormalities found in addiction models [24,25]. It has been identified some alterations in histone acetylation and methylation in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) after acute or chronic exposure to cocaine [26–28]. Curcumin as an inhibitor of histone acetyl transferases (HATs) and DNA methyl transferases (DNMTs) activity may disrupt gene transcription and affect drug dependency.
Chronic exposure to drugs of misuse has been reported to cause adaptations in some intracellular messenger pathways. One of the best well-known adaptations is the upregulation of the cAMP pathway after chronic opiate application [29]. This upregulation and the subsequent activation of the transcription factor CREB seem to mediate features of tolerance and dependence [30,31]. The BDNF mutant mice showed marked attenuation of morphine-induced physical dependence, manifested as naloxone-precipitated withdrawal symptoms after repeated morphine treatments [32]. Matsushita and Ueda [11] have reported that daily administration of the CREB-binding protein inhibitor curcumin could prevent upregulation of BDNF transcription and morphine analgesic tolerance. It has also been shown that curcumin could decrease the activation of p-CREB in dorsal root ganglion [33]. With respect to the mentioned findings we can conclude that curcumin might affect morphine withdrawal and tolerance through reduction in CREB Activity and BDNF transcription.
The present study indicates that i.p. administration of Dendrosomal curcumin exerts a significant effect on morphine dependency in rats. Further studies are required to determine molecular and anatomical mediators which are thought to be involved in this phenomenon.
The integrated preparation process of Dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) has been characterized in our previous studies to generate polymeric nanoparticles with high drug loading, narrow size distribution and long-term stability [18,19].The well-defined and controlled nanoparticles provide the platform for drug delivery and drug discovery.
Conclusion
Our results show that intraperitoneal administration of Dendrosomal curcumin attenuates morphine physical dependency. The recent achievements of nanotechnology illustrate a novel approach in treatment of drug abuse and addiction.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University.
References
- Zhu H, Zhou W (2010) Discharge activities of neurons in the nucleus paragigantocellularis during the development of morphine tolerance and dependence: a single unit study in chronically implanted rats. Eur J Pharmacol 636: 65-72.
- Koob GF, Sanna PP, Bloom FE (1998) Neuroscience of addiction. Neuron 21: 467-476.
- Abood LG (1984) Mechanisms of tolerance and dependence: an overview. NIDA Res Monogr 54: 4-11.
- Kantak KM, Miczek KA (1988) Social, motor, and autonomic signs of morphine withdrawal: differential sensitivities to catecholaminergic drugs in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 96: 468-476.
- Koob GF, Maldonado R, Stinus L (1992) Neural substrates of opiate withdrawal. Trends Neurosci 15: 186-191.
- Maldonado R, Stinus L, Gold LH, Koob GF (1992) Role of different brain structures in the expression of the physical morphine withdrawal syndrome. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261: 669-677.
- Redmond DE Jr, Krystal JH (1984) Multiple mechanisms of withdrawal from opioid drugs. Annu Rev Neurosci 7: 443-478.
- Sharma RA, Gescher AJ, Steward WP (2005) Curcumin: the story so far. Eur J Cancer 41: 1955-1968.
- Motterlini R, Foresti R, Bassi R, Green CJ (2000) Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 28: 1303-1312.
- Thiyagarajan M, Sharma SS (2004) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci 74: 969-985.
- Matsushita Y, Ueda H (2009) Curcumin blocks chronic morphine analgesic tolerance and brain-derived neurotrophic factor upregulation. Neuroreport 20: 63-68.
- Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4: 807-818.
- Ferrari E, Pignedoli F, Imbriano C, Marverti G, Basile V, et al. (2011) Newly synthesized curcumin derivatives: crosstalk between chemico-physical properties and biological activity. J Med Chem 54: 8066-8077.
- Orr WS, Denbo JW, Saab KR, Myers AL, Ng CY, et al. (2012) Liposome-encapsulated curcumin suppresses neuroblastoma growth through nuclear factor-kappa B inhibition. Surgery 151: 736-744.
- Anand P, Thomas SG, Kunnumakkara AB, Sundaram C, Harikumar KB, et al. (2008) Biological activities of curcumin and its analogues (Congeners) made by man and Mother Nature. Biochem Pharmacol 76: 1590-1611.
- Sadeghizadeh M, Ranjbar B, Damaghi M, Khaki L, Sarbolouki MN, et al. (2008) Dendrosomes as novel gene porters-III. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83: 912-920.
- Sarbolouki MN, Sadeghizadeh M, Yaghoobi MM, Karami A, Lohrasbi T (2000) Dendrosomes: a novel family of vehicles for transfection and therapy. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 75: 919-922.
- Babaei E, Sadeghizadeh M, Hassan ZM, Feizi MA, Najafi F, et al. (2012) Dendrosomal curcumin significantly suppresses cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol 12: 226-234.
- Tahmasebi Mirgani M, Isacchi B2, Sadeghizadeh M, Marra F3, Bilia AR2, et al. (2014) Dendrosomal curcumin nanoformulation downregulates pluripotency genes via miR-145 activation in U87MG glioblastoma cells. Int J Nanomedicine 9: 403-417.
- Gou M, Men K, Shi H, Xiang M, Zhang J, et al. (2011) Curcumin-loaded biodegradable polymeric micelles for colon cancer therapy in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 3: 1558-1567.
- Mousavi Y, Azizi H, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J, Javan M, Semnanian S2 (2014) Blockade of orexin type-1 receptors in locus coeruleus nucleus attenuates the development of morphine dependency in rats. Neurosci Lett 578: 90-94.
- Azizi H, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J, Rohampour K, Semnanian S (2010) Antagonism of orexin type 1 receptors in the locus coeruleus attenuates signs of naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal in rats. Neurosci Lett 482: 255-259.
- Feng J, Nestler EJ (2013) Epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23: 521-528.
- Renthal W, Nestler EJ (2008) Epigenetic mechanisms in drug addiction. Trends Mol Med 14: 341-350.
- Maze I, Nestler EJ (2011) The epigenetic landscape of addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1216: 99-113.
- McQuown SC, Wood MA (2010) Epigenetic regulation in substance use disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep 12: 145-153.
- Biliński P, Wojtyła A, Kapka-Skrzypczak L, Chwedorowicz R, Cyranka M, et al. (2012) Epigenetic regulation in drug addiction. Ann Agric Environ Med 19: 491-496.
- Kumar A, Choi KH, Renthal W, Tsankova NM, Theobald DE, et al. (2005) Chromatin remodeling is a key mechanism underlying cocaine-induced plasticity in striatum. Neuron 48: 303-314.
- Nestler EJ, Aghajanian GK (1997) Molecular and cellular basis of addiction. Science 278: 58-63.
- Nestler EJ, Tallman JF (1988) Chronic morphine treatment increases cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in the rat locus coeruleus. Mol Pharmacol 33: 127-132.
- Duman RS, Tallman JF, Nestler EJ (1988) Acute and chronic opiate-regulation of adenylate cyclase in brain: specific effects in locus coeruleus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246: 1033-1039.
- Akbarian S, Rios M, Liu RJ, Gold SJ, Fong HF, et al. (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is essential for opiate-induced plasticity of noradrenergic neurons. J Neurosci 22: 4153-4162.
- Li X, Liu RH, Cao H, Li J (2009) [Effects of curcumin on behavior and p-ERK, p-CREB, c-fos expression in dorsal root ganglion in chronic constrictive injury rats]. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 25: 418-422.
Relevant Topics
- Addiction Recovery
- Alcohol Addiction Treatment
- Alcohol Rehabilitation
- Amphetamine Addiction
- Amphetamine-Related Disorders
- Cocaine Addiction
- Cocaine-Related Disorders
- Computer Addiction Research
- Drug Addiction Treatment
- Drug Rehabilitation
- Facts About Alcoholism
- Food Addiction Research
- Heroin Addiction Treatment
- Holistic Addiction Treatment
- Hospital-Addiction Syndrome
- Morphine Addiction
- Munchausen Syndrome
- Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
- Nutritional Suitability
- Opioid-Related Disorders
- Relapse prevention
- Substance-Related Disorders
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 15303
- [From(publication date):
March-2015 - Nov 24, 2024] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 10865
- PDF downloads : 4438