Co-Relation between Chronic Psychological Stress and Cancer
Received: 03-Jul-2023 / Manuscript No. jbtbm-23-106063 / Editor assigned: 05-Jul-2023 / PreQC No. jbtbm-23-106063 (PQ) / Reviewed: 19-Jul-2023 / QC No. jbtbm-23-106063 / Revised: 24-Jul-2023 / Manuscript No. jbtbm-23-106063 (R) / Published Date: 31-Jul-2023 DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X.1000334
Abstract
Cancer is a major threat to mankind. Majority of cancer more than 90 percent of all cancers are due to external environmental factors such as smoking or chewing form of tobacco, alcohol, chemicals ingestion, infectious agents such as HPV(Human papilloma virus), EBV (Ebsteinbarr virus). Chronic psychological stress is also one of the etiological factors of cancer. This article highlights about the research findings of co-relation between chronic psychological stress and cancer [1].
Keywords: HPA-Axis; NF-KB; STAT-3
Keywords
HPA-Axis; NF-KB; STAT-3
Co-relation between chronic psychological stress and cancer
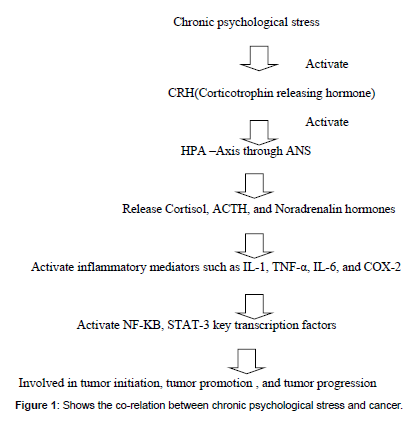
Chronic psychological stress, hatred, jealousy, anger, frustration, depression induced release of CRH (Corticotrophin releasing hormone) from hypothalamus activate HPA-axis (Hypothalamic pituitary axis) through ANS (Autonomic nervous system) release stress releasing hormones such as cortisol, ACTH, noradrenalin activate inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β,TNF-α, COX-2 and IL-6 from inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and mast cells , further activates NF-KB a key transcription factor and STAT-3 transcription factor(1-9). Both NF-KB and STAT-3 transcription factors work together express inflammatory mediators involved in cell proliferation by activation of cyclin D,cyclin E cell cycle regulatory proteins, cell survival by BCL-2,BCL-XL anti-apoptotic proteins , angiogenesis by IL-8,COX- 2,VEGF, genomic instability by ROS,RNS,iNOS,AID (Activation induced cytidine deaminase ) enzyme , Immune suppression by IL- 10,TGF-β,IL-4,IL-13, invasion and metastasis by UPA (Urokinase plasminogen activator),MMP’s 2,9 (Matrix metallo proteinases 2,9) all these changes leads to tumor progression(5,10-16) (Figure 1) [2-4].
Conclusion and future perspective: Chronic psychological stress is one of the neglected etiologies of cancer. Chronic psychological stress should be considered in overall management of cancer, it will improve the patient’s survival rate. Chronic psychological stress induced neurohormones activate inflammatory mediators, which activate NF-KB and STAT-3 key transcriptional factors express inflammatory mediators induced tumor progression. Through understanding of chronic psychological stress and its releasing hormones and it’s mechanism of actions in tumor progression need to be studied for better management of patients [5].
References
- Menachem M,Arie A (2015) Current challenges and future perspectives of plant and agricultural biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 33: 337-342.
- Henry IM (2010) The regulation of agricultural biotechnology: science shows a better way. N Biotechnol 27: 628-634.
- Anthony MS (2003) Considerations for conducting research in agricultural biotechnology. J Invertebr Pathol 83: 110-112.
- Cecilia LCH,Sara B,Rosa FB,Sara B,Josef NG, et al. (2012) An intellectual property sharing initiative in agricultural biotechnology: development of broadly accessible technologies for plant transformation. Plant Biotechnol J 10: 501-510.
- Remziye Y (2019) Modern biotechnology breakthroughs to food and agricultural research in developing countries. GM Crops Food 10: 12-16.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Shrihari TG (2023) Co-Relation between Chronic Psychological Stress and Cancer. J Biotechnol Biomater, 13: 334. DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X.1000334
Copyright: © 2023 Shrihari TG. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 574
- [From(publication date): 0-2023 - Mar 31, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 376
- PDF downloads: 198