Short Communication Open Access
Clubfoot since Ancient Time Up To Now
Arben Gjonej1*, Risida Gjonej2 and Edvin Selmani11Service of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, University Hospital Center “Mother Theresa” Tirane, Albania
2Department of Nursing, Faculty of Technical Medical Sciences, University of Medicine, Tirane, Albania
- *Corresponding Author:
- Arben Gjonej
Service of Orthopaedic and Traumatology
University Hospital Center “Mother Theresa” Tirane
Albania
E-mail: arben_gjonej@hotmail.it
Received date: January 04, 2016; Accepted date: January 25, 2016; Published date: February 17, 2016
Citation: Gjonej A, Gjonej R, Selmani E (2016) Clubfoot since Ancient Time Up To Now. J Ost Arth 1:108. doi: 10.4172/joas.1000108
Copyright: © 2016 Gjonej A, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Osteoarthritis
Introduction
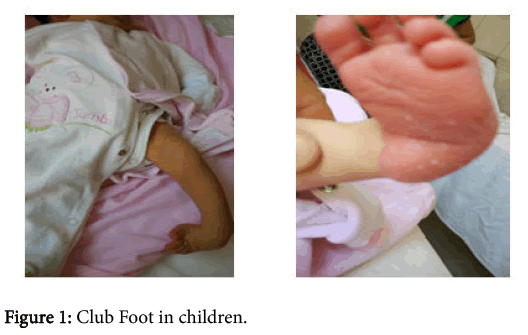
Idiopathic clubfoot or in other words congenital talipes equinovarus which dating too early as a pathology is a birth pathology [1,2]. Is a common deformity but very complex with four components: cavus, forefoot adductus heel varus and equinus. Some authors and researchers add another component which is atrophy of calf muscle associated with foot size and tibia length [3-5]. This bone deformity can affect one foot but also two feet in the same person and inhibits him to walk normally (Figure 1) [6].
Medical texts, but also many studies show that this pathology affects approximately 1 in every 1,000 children worldwide and the most affected gender are male [7-9]. The etiology of clubfoot is almost unknown although it's divided into two major groups: genetic and environmental factors [10].
Genetic factors that contribute in this congenital pathology are unknown. And exactly this dysregulation of genes that affect extremities and muscles development can contribute to clubfoot. While in environmental factors we can mention: oligohydramnios (is a condition in pregnancy characterized by a deficiency of amniotic fluid), incorrect position of the foetus in the womb, placental insufficiency, high temperature, toxins etc. [11-13].
Clubfoot as a pathologyt can vary from middle to an extreme case to treat. But these two big classifications systems which are based at Dimeglio & Pirani scores are related to the clubfoot severity [14-16].
Some Historical Facts
Congenital talipes equinovarus is a pathology which is known since in ancient time. This deformity we find parts in paintings of Egyptians tomb. Meanwhile, the first treatment of this deformity dates approximately 1000 B.C in India. Then, Hippocrates approximately 400 B.C described and begins to treat clubfoot this birth deformity [17]. He threw ideas, how to treat clubfoot which are almost similar like conservative treatment nowadays.
Hippocrates explained the importance of starting treatment as soon as possible after birth but using gentle and repeated manipulations with hands and then application of bandages to maintain the correct position. Then in the end of the treatment the use of special shoes was important to prevent recurrent deformity.
In 1658 was Arcanys, who described his technique and also two mechanical devices in treating and correcting the deformity of foot. After the 18th century, in 1803 Scarpa presented his ideas, which were opposed to the ideas of Hippocrates and other authors until that time [18]. He developed another technique. A forceful manipulation and a mechanical device known as Scarpa's shoe. Anyway he never succeeded.
In 1823, Delpech presented another way to treat patient with clubfoot. This new way was tenotomy, which means the cut of the Achilles tendon in those patients. As a surgical procedure it had its complications like infections. But anyway this technique was improved over time [19-22].
Pathology Treatment
After 1830s many physicians gave a successful contribution to the etiology and treatment of clubfoot, such as: Hugh Owen Thomas, Sir Robert Jones, Denis Browne, Michael Hoke, Kite, Ponseti, Huson etc.
Three main methods of conservative treatments described in literature are: Kite method (described in 1939), Ponseti Method (developed since 1950) and the French Method. In our Country when it was established the treatment of this pathology by Prof Dr. Panajot Boga was used gradual gentle manipulation and correction according to Kite method. This anomaly consists of distortion of the foot with four components: forefoot adduction and supination and heel varus and equinus. Often the cavus element can be added.
The difference between the Kite and Ponseti method is the point of counter pressure. In the Kite method the point of counter pressure is the calcaneocuboid joint and in the Ponseti Method is the talar neck. Also another difference is that in the Ponseti method the first immobilization of the foot is in supination and the Achilles tenotomy instead of Kite method which immobilizes the foot in pronation [23].
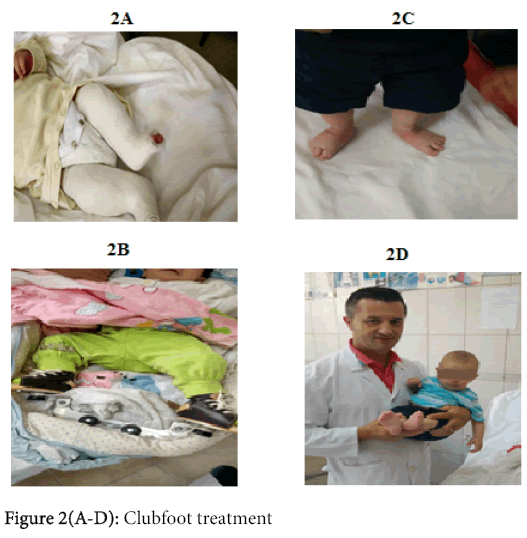
In the last 10 years we are using Ponseti technique (since in 2005) which is more effective than Kite method [24-28]. Conservative treatment consist in the gradual manual manipulation with cast by the cast technician and the orthopaedic doctor (remember that the first physician who describes and began treating the clubfoot with cast was Michael Hoke, medical director of the Scottish Rite Hospital in Decatur, Georgia in 1874-1944). The Ponseti method is the best technique up to now to treat this birth deformity. It consist in using gradually manually and gentle manipulations with cast within the first days after birth. Manipulation performed every 7 days. Cast is placed over the knee for avoiding the cast scroll and correct the internal tibial torsion [13]. At the end of first 2 months of treatment we performed Achilles tenotomy (Figure 2A-2D). Then again placed for approximately 3 to 4 weeks in plaster by changing it for every 2 weeks. When treatment ends, family members were taught about foot stretching exercises and keeping the foot abduction brace. During the first 3 months after the cast treatment has end, the brace should take off only 1 hour during the day. After 3 months these braces should be wearing only in bedtime until the age 4 years old.
Conclusion
Clubfoot is a congenital deformity of the foot that can be treated in the most cases with non- surgical method. Genetic and environmental factors are most accused factors in the cause of this deformity. The evidences show that development of bone, joint, connective tissue, innervation, vasculature and muscle may each be implicated in the pathophysiology [29].
Clubfoot is a congenital deformity of the foot that can be treated in the most cases with non- surgical method. Genetic and environmental factors are most accused factors in the cause of this deformity. The evidences show that development of bone, joint, connective tissue, innervation, vasculature and muscle may each be implicated in the pathophysiology [29].
It is easy to diagnose this pathology because of prenatal ultrasonography when the child is intrauterine and clinic evaluation after birth. Both female and male patients at the age of 60 years or more experience decreased foot and ankle function, the outcome being worse for female patients [30]. The results of treatment vary, depending to early presentation for treatment, severity of the pathology and physician's point of view about clubfoot [31], but in general, clubfoot is a congenital pathology which in the most cases the foot return to normality because of the improvement of the treatment techniques.
References
- Morcuende JA (2006) Congenital idiopathic clubfoot: prevention of late deformity and disability by conservative treatment with thePonseti technique. Pediatr Ann 35: 128-130,132-136.
- Desai L, Oprescu F, DiMeo A, Morcuende JA (2010) Bracing in the treatment of children with clubfoot: past, present, and future. Iowa Orthop J 30: 15-23.
- Singh NJ, Keshkar S, De P, Kumar R (2011) Management of clubfoot by Ponseti technique- our experience. IJPMR 22:12-16.
- Feldbrin Z, Gilai AN, Ezra E, Khermosh O, Kramer U, et al. (1995) Muscle imbalance in the aetiology of idiopathic club foot. An electromyographic study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77: 596-601.
- Dobbs MB, Gordon JE, Walton T, Schoenecker PL (2004) Bleeding complications following percutaneous tendoachillestenotomy in IJPMR. The treatment of clubfoot deformity. J PediatrOrthop24: 353-357.
- Foster A, Davis. N (2007) Congenital talipesequinovarus (clubfoot). Surgery (Oxford) 25: 171-175.
- Weymouth KS (2012) Identifying Genetic Variants And Characterizing Their Role In Clubfoot. Dean, The University of Texas Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. A dissertation 1-150.
- Barker S, Chesney D, Miedzybrodzka Z, Maffulli N (2003) Genetics and epidemiology of idiopathic congenital talipesequinovarus. J PediatrOrthop 23: 265-272.
- Boga P (1977)DisaproblemetetrajtimitteLuksacionitKoksofemoralKongenitaldhePesEquinovarusnevendintonë. PunimeKirurgjikale117-123.
- Dobbs MB, Gurnett CA (2009) Update on clubfoot: etiology and treatment. ClinOrthopRelat Res 467: 1146-1153.
- Scarpa A, Wishart JH (1818) A memoir on the congenital club feet of children. Translated from Italian.
- Sheldrake T (1806) Distortions of the legs and feet in children.
- Little WJ. A treatise on the nature of club-foot and analagous distortions. London: W Jeffs, S Highley; 1839.
- Dobbs MB, Morcuende JA, Gurnett CA, Ponseti IV (2000) Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot: an historical review. Iowa Orthop J 20: 59-64.
- Gjonej A, Gjonej R, Selmani E, ÇaushiG (2014) Results of Clubfoot Treatment with Kite Method.Int Journal of Orthopaedics 1: 122-125.
- Gjonej A, Gjonej R (2015) Ponseti Method or Kite Method. Which Is More Effective For Clubfoot Treatment? A Descryptive Study, Conducted In Orthopaedic Service In Tirana. IntJournal of Sci Res (IJSR) 4: 1250-1252.
- Herzenberg JE, Radler C, Bor N (2002) Ponseti versus traditional methods of casting for idiopathic clubfoot. J PediatrOrthop 22: 517-521.
- Ippolito E, Farsetti P, Caterini R, Tudisco C (2003) Long-term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-85A: 1286-94.
- Segev E, Keret D, Lokiec F, Yavor A, Wientroub S, et al. (2005) Early experience with the Ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot. Isr Med Assoc J 7: 307-310.
- Boga P (1977)DisaproblemetetrajtimitteLuksacionitKoksofemoralKongenitaldhePesEquinovarusnevendintonë. PunimeKirurgji¬kale117-123.
- De Hoedt AM (2013) Clubfoot image classification. University of Iowa1-85.
- Miedzybrodzka Z (2003) Congenital talipesequinovarus (clubfoot): a disorder of the foot but not the hand. J Anat 202: 37-42.
- Wallander HM (2010) Congenital clubfoot. Aspects on epidemiology, residual deformity and patient reported outcome. ActaOrthopSuppl 81: 1-25.
- Nordin S, Aidura M, Razak S, Faisham W (2002) Controversies in congenital clubfoot : literature review. Malays J Med Sci 9: 34-40.
- Diméglio A, Bensahel H, Souchet P, Mazeau P, Bonnet F (1995) Classification of clubfoot. J PediatrOrthop B 4: 129-136.
- Pirani S, Outebridge H, Moran M, Swawtsky B (1995) A method of evaluating the virgin clubfoot with substantial inter-observer reliability. POSNA meeting, Miami, Florida.
- Selmani E (2012) Is Ponseti’s method superior to Kite’s for clubfoot treatment? European Orthop. Traumatolo 3: 83-187.
- Wynne-Davies R (1964) Family Studies and the Cause of Congenital Club Foot. TalipesEquinovarus, TalipesCalcaneo-Valgus and Metatarsus Varus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 46: 445-463.
- Carter CO (1969) Genetics of common disorders. Br Med Bull 25: 52-57.
- Soloman L, Warwick DJ, Nayagam S (2011) Apley’s system of orthopedics and fractures. 8th edn.London: Arnold. The ankle and foot485-520.
- Morcuende JA, Dolan LA, Dietz FR, Ponseti IV (2004) Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics 113: 376-380.
- McKay DW (1982) New concept of and approach to clubfoot treatment: section I-principles and morbid anatomy. J PediatrOrthop 2: 347-356.
- Scarpa A (1818) Memoir on congenital clubfoot in children.Edinburgh: Constable (Wishart JW, Trans).
Relevant Topics
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 13066
- [From(publication date):
February-2016 - Apr 22, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 12204
- PDF downloads : 862