Atmosphere Has No Energy as It is Balanced Between Gravity and Full Vacuum Universe: A Mini Review
Received: 05-Apr-2018 / Accepted Date: 16-Apr-2018 / Published Date: 19-Apr-2018 DOI: 10.4172/2157-7617.1000461
Abstract
It should be agreed that all objects like planets, stars etc. float in the full vacuum universe. It should also be agreed that atmosphere possessed by these objects is due to gravity and the atmosphere is in the open system full vacuum universe. Here, air molecules always try to escape in full vacuum universe against gravity to have uniformity in the universe. Means it is balanced between gravity and full vacuum universe. It is in science textbooks that the Earth’s atmosphere exerts pressure. But, to have pressure in the system, it must be isolated by boundary and its value is same at any point within. Here, Earth’s atmospheric air neither uniformly distributed nor in a closed system. It is known that gravity is holding each air molecule towards the Earth. On surface, air has high-density molecules and as further go away molecules density decreases. This density difference is balanced between gravity and full vacuum universe. This paper uncovers the misconception regarding Earth’s atmosphere exerts pressure due to its air molecules vertical column mass. To prove the argument, the manometer experiment is visited. In this experiment author makes the effort to raise mercury filled tube up against gravity above pot level then inverts it. Here, mercury level drops because of gravity which creates a vacuum in the top of the tube. This causes reduced surface energy inside wall of the tube. To be in the equilibrium state with outer tube wall, inner wall surface tries to suck in all direction that holds mercury up against gravity that means tube mercury weight is balanced by vacuum and that is demonstrated.
Keywords: Atmosphere; Gravity; Open system earth; Air molecules; Homogeneous state; Manometer; Surface energy; Absolute pressure; Vacuum intensity; Full vacuum universe
Introduction
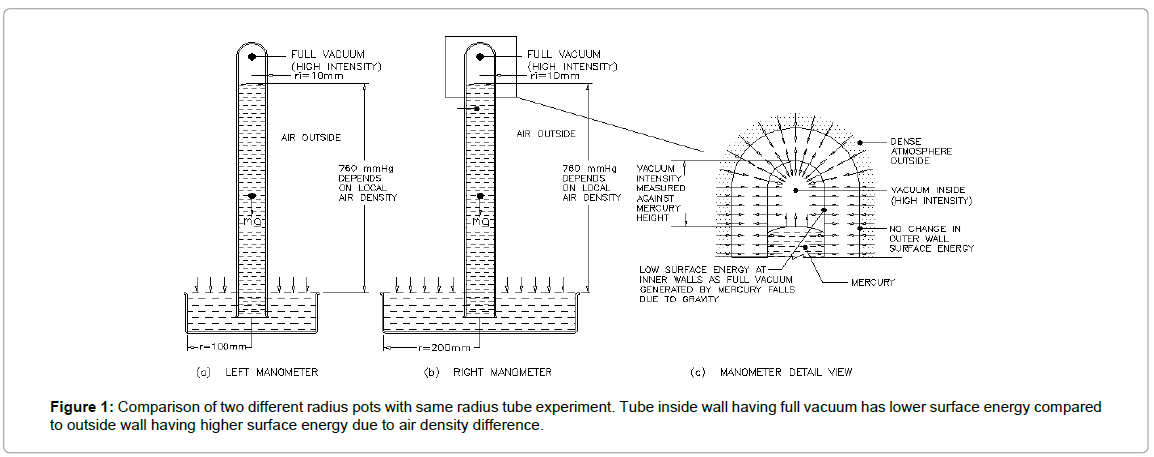
Galileo had observed that water is not rising in an exhausted tube to a height greater than thirty-three feet, but he was not able to offer a satisfactory explanation of the phenomenon. He believed that there is something in a suction side that balances the weight of water [1]. In 1643 Torricelli had demonstrated that the height at which the water stood depends upon nothing but its (let’s say mercury) weight as compared with the weight of air vertical column outside. Here, it is noted that tube was filled with mercury and raised against gravity was by Torricelli. So, work was already done by himself and not by the atmosphere. To elaborate more, refer to the Figure 1. Here, two different radius pots with same radius tube experiment demonstrated. If the atmosphere has pressure to raise mercury against gravity, Mercury in right tube (pot radius 200 mm) must rise higher than the left side tube (pot radius 100 mm). But this is not the case, So, Torricelli’s argument is wrong on why mercury shows 760 mmHg reading every time on Earth surface.
Literature Review
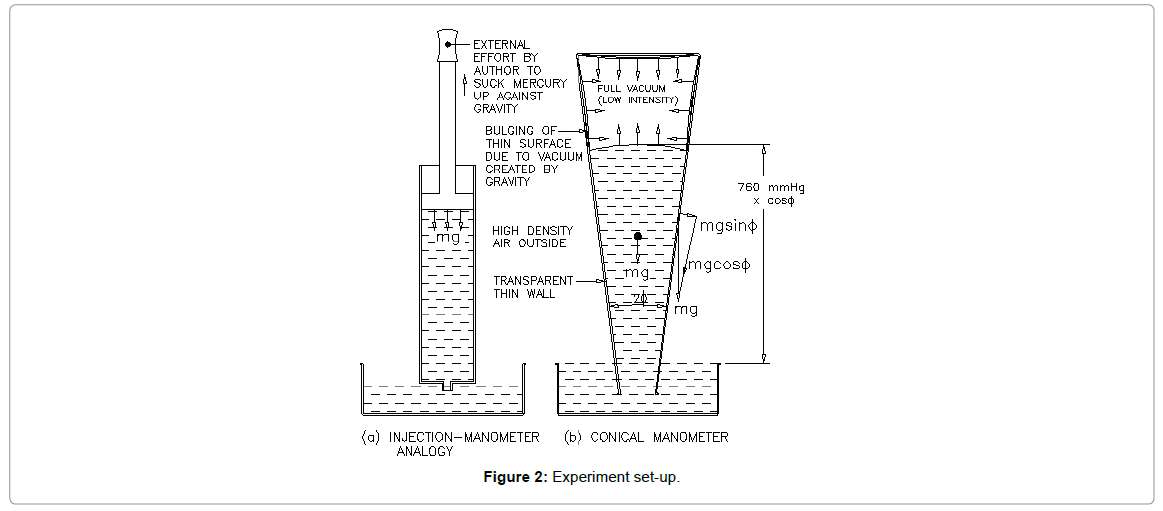
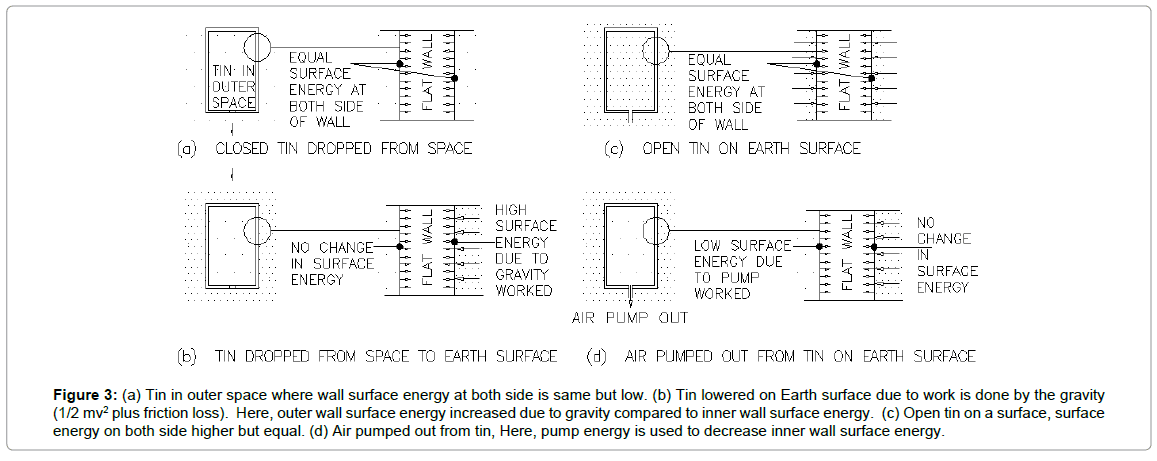
Let us consider different situations where mercury manometer is elevated/lowered against Earth’s sea level. Firstly put two manometers as per Figure 1. Here, left-hand side mercury manometer pot has less exposed surface area compared to right-hand side manometer pot. So, as per Torricelli’s principle, the force exerted by the atmosphere on right side pot is more. It means it has to raise more mercury than left side against gravity if atmosphere has a pressure to do work. Here, mercury is raised against gravity by the author by taking closed end up to invert the filled tube. So, work already done to elevate mercury against gravity. It is same analogy as injection fill up by efforts taken to create a vacuum at back side ass per Figure 2a. If the tube is of bigger dia and long enough mercury drops due to gravity that creates a vacuum on top of the tube tries to suck in all direction that holds mercury up against gravity. Another experiment can be done with the conical transparent manometer. Here Mercury level will be less compared to standard as per Figure 2b. Which reduces inner wall surface energy. To be in equilibrium with tube outer wall in all surfaces, inner wall surface tries to suck direction. Here, it is clearly visible that walls bulge inside due to gravity works to lower mercury level [2]. Now, consider manometer kept on Mt. Everest. Here, mercury will rise low compared to sea level. That is because tube wall faces have less surface energy difference. Here, inside wall having full vacuum has lower surface energy compared to outside wall having low density atmosphere. A lab experiment can be demonstrated by creating partial pressure in the closed container and putting manometer inside it. Here, vacuum intensity inside the tube is less. Now, consider a tin closed in outer space (Figure 3a). Here, both side molecule densities are very less and same. Once it is released, Earth gravity takes it to dense atmosphere (Figure 3b). Here, gravitational energy is used to increase the tin outer wall surface energy by taking tin to higher density air. To be in equilibrium between inner and outer wall surface, the outer wall gets crushed to have a concave surface (reduced surface energy). Now consider open tin is kept at sea level on Earth (Figure 3c). Here wall both side surface energy is higher and equal. When air is pumped out from tin, pump works to reduce inside wall surface energy (Figure 3d). So, it gets crushed inside to have a convex surface (surface energy increases) to get equilibrium with outer wall. Now consider the tin with atmospheric air inside and lowered in water. Here, tin is lowered against buoyancy of fluid in support of gravity by the author. So, surface energy increases at outside wall by outside water is a result of external work done by the author.
Figure 3: (a) Tin in outer space where wall surface energy at both side is same but low. (b) Tin lowered on Earth surface due to work is done by the gravity (1/2 mv2 plus friction loss). Here, outer wall surface energy increased due to gravity compared to inner wall surface energy. (c) Open tin on a surface, surface energy on both side higher but equal. (d) Air pumped out from tin, Here, pump energy is used to decrease inner wall surface energy..
Discussion
Consider an equilibrium state of the atmosphere with gravity and assume there is no wind currents and convection to provide a constant mixing of the atmosphere. Also, it should be agreed that the atmosphere tries to be in homogeneous state to have uniform molecule quantity everywhere in the universe. or it can be said that molecules want to be equally distributed everywhere in space. It is agreed that gravity attracts all gas//air molecules with same acceleration but with different force based on their mass. Carbon dioxide is heavy air molecule so; gravity causes it to be attracted more so, it is positioned/settled towards Earth’s surface. Whereas Hydrogen is the least mass molecule so, it is least attracted towards Earth’s gravity and it is positioned/settled away from the surface. That is because light molecules collision with heavy molecules keeps light molecules away from gravitating object. Now, consider two planets Earth & Venus atmosphere for example. It is observed that Earth and Venus both have nearly same gravity. Venus mass is nearly similar to Earth's mass. But the mass of 250 km thick atmosphere on Venus is 4.8 × 10^20 kg, whereas the mass of 100 km thick Earth's atmosphere is 5 × 10^18 kg. That means Venus atmosphere has 100 times more mass than Earth’s atmosphere mass. But, as per above explanation gravity causes/attracts atmosphere, so, both should have nearly same atmospheric conditions as gravity uses energy to hold the atmosphere. The explanation I that, Venus most surface is currently covered with heavy elements which are exposed due to volcano eruptions. That caused high absolute gravity which is utilized for constantly attracting the molecules. Whereas on Earth no such heavy eruptions exist. That is why on Venus, atmosphere is denser and expanded high compared to Earth.
Now, put the manometer on Venus surface. Due to Venus atmosphere is so dense compared to Earth's atmosphere, the author need to take huge effort to elevate filled mercury tube up. Here, mercury will keep showing very high level compared to Earth’s surface level. That is because tube wall faces have very high surface energy difference. Here, inside wall having a full vacuum which balances mercury column against gravity has very low surface energy compared to outside wall.
Now, examine the siphon pipe experiment [3,4]. Here, to create initial siphon, vacuum is applied by author against gravity to raise water level up and lowered below enough to overcome pipe/fluid frictional losses to start flow. Also, it is concluded that neither atmosphere nor molecular cohesion causing siphon effect. It is vacuum that is caused by gravity at lower side which propagates continuously at every cross section of pipe which creates continuous flow of liquid.
Now, examine the Casimir phenomenon which was first predicted in 1948 by the Dutch theoretical physicist Hendrik Casimir. The force between the two perfect parallel planes is known as the Casimir force which is attractive in nature. The force is proportional to the crosssection area of the two planes and increases 16 times as distance between the plane decreases half [5]. Here, this is same as gravity formula derived in cause of gravity [2]. So, Casimir effect is nothing but gravity (vacuum suck) caused due to two objects surface energy. Here, it depends on experimental objects shape, surface roughness, flatness, material etc.
Conclusion
It is clear that atmosphere possessed by universe objects has no energy to push or pull until external efforts taken to create density difference by creating isolating wall. Also, it is concluded that full vacuum intensity depends on how much efforts taken to act against gravity or external work done to create vacuum.
Acknowledgements
I am thankful to journals/scientists who have posted their data for freely accessible on the internet. The paper is developed by author own as an individual and not taken any financial or technical support from Organization/Institution/Govt. body.
References
- Galileo G (2011) Dialogues concerning two new sciences. Online Library of Liberty 6:27
- Prajapati RS (2017) Cause of gravity: Disruption of intermolecular bonds. Journals of Earth Science and Climate Change 7:30.
- Stephen H, Som G (2014) Exploring the boundary between a siphon and barometer in a hypobaric chamber. Scientific Reports 5:4.
- Hughes SW (2010) A practical example of a siphon at work. Physics Education 45:162-166.
- Astrid L (2008) The Casimir effect: A force from nothing. IOP Publishing 6: 0953-8585.
Citation: Rajendra SP (2018) Atmosphere Has No Energy as It is Balanced Between Gravity and Full Vacuum Universe: A Mini Review. J Earth Sci Clim Change 9: 461. DOI: 10.4172/2157-7617.1000461
Copyright: © 2018 Rajendra SP. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.