Make the best use of Scientific Research and information from our 700+ peer reviewed, Open Access Journals that operates with the help of 50,000+ Editorial Board Members and esteemed reviewers and 1000+ Scientific associations in Medical, Clinical, Pharmaceutical, Engineering, Technology and Management Fields.
Meet Inspiring Speakers and Experts at our 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events with over 600+ Conferences, 1200+ Symposiums and 1200+ Workshops on Medical, Pharma, Engineering, Science, Technology and Business
Editorial Open Access
Approach Bias in Obesity Management: A Proposed Solution
| Reza Rastmanesh1*, Pedro Carrera-Bastos2, Roberto Catanzaro3, Archana Kumari4 and Francesco Marotta5 | |
| 1Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, National Nutrition and Food Technology Research Institute, Tehran, Iran | |
| 2Center for Primary Health Care Research, Faculty of Medicine, Lund University, Malmö, Sweden | |
| 3Dept of Gastroenterology-Internal Medicine, University of Catania, Italy | |
| 4Université du Québec, Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique, Centre Eau, Terre and Environnement, Québec, Canada | |
| 5ReGenera Research Group for Aging Intervention, Milano, Italy | |
| Corresponding Author : | Reza Rastmanesh Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences National Nutrition and Food Technology Research Institute Tehran, Iran Tel: +98-22357484 Fax: +98-22360660 E-mail: rezar@sbmu.ac.ir |
| Received January 09, 2012; Accepted January 11, 2012; Published January 13, 2012 | |
| Citation: Rastmanesh R, Carrera-Bastos P, Catanzaro R, Kumari A, Marotta F (2012) Approach Bias in Obesity Management: A Proposed Solution. J Obes Weig los Ther 2:e102. doi:10.4172/2165-7904.1000e102 | |
| Copyright: © 2012 Rastmanesh R, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Obesity & Weight Loss Therapy
| There is no argument that caloric manipulation holds an indisputable importance in weight loss management programs. The scientific community, however, would agree that mounting evidence on other non-calorie related weight lowering potentials of foods have not been used as much as they merit in current obesity clinical trials. For example, intestinal microbiota balance manipulation has been proposed as an auxiliary method to weight loss diets in addition to calorie restriction or manipulation [1]. In planning a diet, imagine that we just focus on calorie content of, let us say an apple and forget about its high satiety index or its high polyphenol content that might help weight loss irrespective of caloric considerations. |
| In a recent review, Feinman and Fine discuss that “A calorie is a calorie” violates the second law of thermodynamics and that some diets have metabolic advantages over some other isocaloric diets [2]. One could argue that multiple factors, such as interactions between nutrients-hormones [3], nutrients-neurotransmitters [4], nutrientspersonalities [5,6], nutrients-appetite [7,8] and an enormous number of other influential connections, has not been taken into account in the second law of thermodynamics. Consequently, considering that these parameters would promise great auxiliary advantages in obesity management, especially if dietary regimens are planned based on a deep knowledge of unique nutritional properties that some foods, fruits, vegetables or herbs have. Different nutrients, foods, and herbs have different effects on thermoregulation, absorption, intestinal microbiota, anabolism, catabolism etc and we are only focusing on caloric contents of foods or caloric balance of diets. |
| We have produced a huge amount of data and information, yet the process of translation of this information into applicable diets has been sadly slow. For instance, despite a solid literature body of evidence, there is still a rather limited use of “aging” markers in clinical practice. It would be then advisable for physicians and health professionals to routinely rely on markers of systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, i.e. overall cellular aging factors and which are now available and feasible at the doctor’s desk (CAF-panel, Natrix, Reggio Emilia, Italy) as dietary-response predictors as recently presented (C. Conti, Personal communication, International Age-Management Symposium, Sept 30-Oct 3, 2011, Warshaw, Poland). The recent evidence also suggests that in addition to the marked decreases in body weight associated, a calorie-restricted diet may contribute to the redistribution of fats within the body. This is also what we observed in concomitance with improved cellular membrane potential by using a novel body composition analytical device (Phosa, Rilevo, Piacenza, Italy) [9]. The calorie has been the pivot of dietary regimens and management programs traditionally, and this has leaded to an approach bias in nutrition intervention policies globally. An integrated discipline is urgently needed to translate data and information to produce feasible, sensible and applicable understanding of results obtained from obesity clinical trials. Building the bridges to bioinformatics in nutrition research should be the most urgent action in the coming decade and so let us call for a scientific discussion to investigate the possibility and requirements of establishing such a new discipline, in coming proceedings and congresses of nutrition. For example, on the nutrigenetics viewpoint, recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified several single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with fasting glucose and insulin concentrations in individuals free of diabetes. Indeed, a meta-analysis of data from 14 cohorts comprising about 48,000 caucasians studying the interactions of whole-grain intake with loci previously associated in GWAS with fasting glucose and/or insulin concentrations confirmed such beneficial association and a potential interaction between variation in GCKR and whole-grain intake in influencing fasting insulin concentrations with a smaller reduction in fasting insulin concentrations in those with the insulin-raising allele [10]. In this regard, pilot ongoing studies targeting specific metabolic pro-inflammatory polymorphisms clusters (Metabolic panel, NextGenomics, Prato, Italy) are preliminarly proving to be useful predictor to help hysicians identifying those subjects with a more consistent clinical response (Marotta F, Personal communication- Study in progress, International Symposium on “Innovations in agemanagement medicine”, Dec. 2-3, 2011, Warshaw, Poland). |
References
- Rastmanesh R (2011) High polyphenol, low probiotic diet for weight loss because of intestinal microbiota interaction. Chem Biol Interact 189: 1-8
- Feinman RD, Fine EJ (2004) "A calorie is a calorie" violates the second law of thermodynamics. Nutr J 3: 9
- Gerozissis K (2008) Brain insulin, energy and glucose homeostasis; genes, environment and metabolic pathologies. Eur J Pharmacol 585: 38-49.
- Szekely M, Petervari E, Balasko M (2010) Thermoregulation, energy balance, regulatory peptides: recent developments. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2: 1009-1046.
- Garland T Jr, Schutz H, Chappell MA, Keeney BK, Meek TH, et al. (2011) The biological control of voluntary exercise, spontaneous physical activity and daily energy expenditure in relation to obesity: human and rodent perspectives. J Exp Biol 214: 206-229.
- Webb IC, Baltazar RM, Lehman MN, Coolen LM (2009) Bidirectional interactions between the circadian and reward systems: is restricted food access a unique zeitgeber? Eur J Neurosci 30: 1739-1748.
- Leidy HJ, Mattes RD, Campbell WW (2007) Effects of acute and chronic protein intake on metabolism, appetite, and ghrelin during weight loss. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15: 1215-1225.
- Strubbe JH, Van DG (2002) The temporal organization of ingestive behaviour and its interaction with regulation of energy balance. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26: 485-498.
- Mariani G, Dellaglio F, Marotta F (2010) A novel bioengineering clinical device testing cellular homeostatic potentials to customize and monitor nutritional-related age-management interventional strategies. Rejuvenation Res 13: 256-259.
- Nettleton JA, McKeown NM, Kanoni S, Lemaitre RN, Hivert MF, et al.(2010) Interactions of dietary whole-grain intake with fasting glucose- and insulin-related genetic loci in individuals of European descent: a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies. Diabetes Care 33: 2684-2691.
Figures at a glance
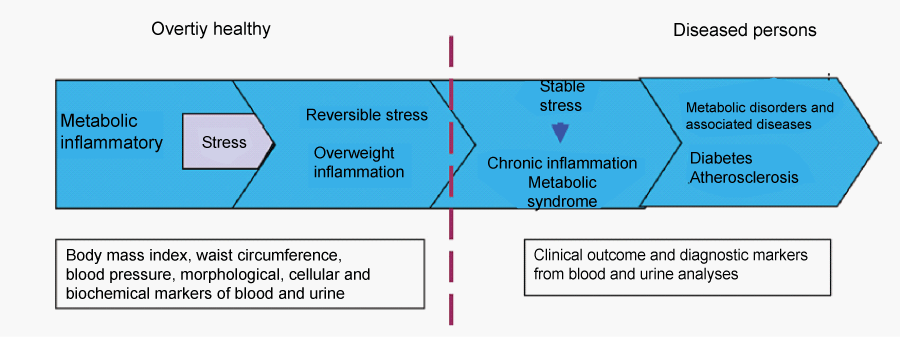 |
| Figure 1 |
Post your comment
Relevant Topics
- Android Obesity
- Anti Obesity Medication
- Bariatric Surgery
- Best Ways to Lose Weight
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Child Obesity Statistics
- Comorbidities of Obesity
- Diabetes and Obesity
- Diabetic Diet
- Diet
- Etiology of Obesity
- Exogenous Obesity
- Fat Burning Foods
- Gastric By-pass Surgery
- Genetics of Obesity
- Global Obesity Statistics
- Gynoid Obesity
- Junk Food and Childhood Obesity
- Obesity
- Obesity and Cancer
- Obesity and Nutrition
- Obesity and Sleep Apnea
- Obesity Complications
- Obesity in Pregnancy
- Obesity in United States
- Visceral Obesity
- Weight Loss
- Weight Loss Clinics
- Weight Loss Supplements
- Weight Management Programs
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 6440
- [From(publication date):
January-2012 - Jul 15, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 1854
- PDF downloads : 4586
