Antimetastatic Mechanisms of Bisdioxopiperazine Compound Study, A Gateway to Success
Received: 15-Aug-2017 / Accepted Date: 20-Aug-2017 / Published Date: 30-Aug-2017
Abstract
Neoplasm metastasis is the causality of 90% cancer patient’s mortality. Bisdioxopiperazine compounds (Biz compounds) are a series of synthetic agents that are firstly discovered to exhibit antimetastatic efficacy to animal tumor models. In order to completely overcome neoplasm metastasis in clinics, antimetastatic therapeutic study for Biz compounds is of great clinical significance. This editorial highlights these researches from new perspective.
Keywords: Bisdioxopiperazine compounds; Probimane; Razoxane; MST-16; Antimetastatic drugs; Neoplasm metastasis; Drug combinations, Drug development
418078Background
Cancer is one of the deadliest diseases that cause the 7-10 millions deaths annually worldwide [1-2]. Neoplasm metastasis is prime factor for patient’s deaths (approximately 90% of cancer mortality). Therapeutic benefits in late-staged or aged cancer patients are especially poor and useless [3-4]. Clinical anticancer drug therapies currently in use are mainly focusing on primary tumor growth rather than specifically targeting pathologic courses of metastases. It nevertheless needs changing mindset into other types of drug targets and personalized cancer therapy in clinics [4-7]. One of them is the revisiting of Biz compound study [8-9].
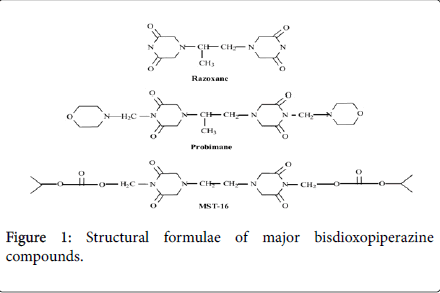
Inventions of Biz Compounds
Biz compounds are a series of synthetic agents that are firstly discovered to exhibit antimetastatic efficacy to animal tumor model. In order to completely overcome neoplasm metastasis in clinics, antimetastatic therapeutic study for Biz compounds is of great clinical significance. Since Biz compounds are unique agents in their pharmacological mechanisms of action of metastases inhibition and are conservative anticancer and antimetastatic activities between Biz compounds, further medicinal chemistry or pharmacological studies seems indispensable [8-10]. The structural formulae of the major Biz compounds are represented in Figure 1.
Current Discoveries
Biz compounds are the earliest anticancer agents found to especially inhibit spontaneous neoplasm metastases [12-14]. Due to these earliest discoveries on neoplasm metastasis inhibition, Biz compounds are widely noticed for cancer metastasis treatment study. So far, a lot of new anticancer activity and mechanisms of Biz compounds have been found [15-31]. Accordingly, it is proposed that anticancer and antimetastatic mechanisms of Biz compounds can be a medical gateway for completely understanding into neoplasm metastasis pathogenesis and their therapeutics in clinics.
Discussion
The major drawback of Biz compounds is low antimetastatic efficacy in clinical trials. Most of past discoveries are come from experimental data. In addition, the debate of high risk of carcinogenesis from Biz compound treatments is difficult to conclude [32-33]. Since there is no definite pathway of anti-metastatic drug developments, we thus suggest that Biz compounds should be carefully studies for both experimental investigations and clinical applications in cancer treatments. Today, we are in front of widely therapeutic failure in cancer metastasis treatments [4-5]. To change this scenario, new generation of pharmacologic/medical researches for Biz compounds, such as personalized cancer treatments [34] are urgently needed.
Summary
In summary, we address and highlight the different inhibitions against metastases in vivo and molecular mechanisms in vitro of Biz compounds, especially relating to the inhibitions of tumor metastasis including pathways of angiogenesis, topoisomerase II, calmodulin, sialic acid, fibrinogen, cell-movements and so on [12-31]. These kinds of researches might be an avenue for the successes of neoplasm metastasis treatments.
References
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A(2017) Cancer stastistics. CA-Cancer J Clin67:7-30.
- Ali I, Enein AY.H, Imran, Rahis-ud-din,Saleem K, et al. (2011) Social aspects of cancer genesis. Cancer Ther8:6-14.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Wu HY (2013)Cancer metastases treatments. Curr Drug ther8:24-29.
- Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell147:275-292.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Zhu H, Ding J,Xu B, et al.(2017)Anticancer drug development, getting out from bottleneck. Med Chem7: 739-744
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Chen EH, Nagendra SY, Bin XU,et al.(2017) Anticancer drug development, system updating and global participations. Curr Drug ther12:37-45.
- Lu DY, Lu TR(2010) Anticancer activities and mechanisms of bisdioxopiperazine compounds probimane and MST-16.Anticancer Agents Med Chem10:78-91.
- Lu DY, Lu TR (2010) Antimetastatic activities and mechanisms of bisdioxopiperazine compounds. Anticancer Agents Med Chem10:564-570.
- Herman EH, Witiak DT, Hellmann K,Waravdekar VS, Properties of ICRF-159 and related Bis(dioxopiperazine) compounds. AdvPharmacolChemother. Garattini S, Goldin A, Hawking F, Kopin IJ (Edsn) Academy Press,New York.
- Hellmann K, Burrage K (1969) Control of malignant metastases by ICRF-159. Nature 224:273-275.
- James SE, Salsbury AJ(1974) Effect of (±)-1,2-bis(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-yl) propane nontumor blood vessels and its relationship to the antimetastatic effect in the Lewis lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 34:839-842
- Lu DY, Xu B, Ding J(2004) Anti-tumor effects of two bisdioxopiperazines against two experimental lung cancer models in vivo. BMC Pharmacol4:32.
- Okamoto T, Nishimura Y, Yamada S, Itoh T, Mori A,et al.(2000) Long-term administration of oral low-dose topoisomerase II inhibitors, MST-16 and VP- 16, for refractory or relapsed non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Acta. Haematol104:128-130.
- Bakowski MT ICRF 159, (+/-) 1, 2-di (3, 5-dioxopiperazin-1-yl) propane NSC-129, 943; razoxane. Cancer Treat Rev 3: 95-107.
- O’connell MJ (1976) Randomized clinical trial comparing two dose regimens of ICRF-159 in refractory malignant lymphomas. Cancer Treat Rep 64:1355-1358
- Lu DY, Wu FG, Shen ZM,Lu RT,Wu HY, et al. (2010) Different spontaneous pulmonary metastasis inhibitions against Lewis lung carcinoma in mice by Bisdioxopiperazine compounds of different treatment schedules. Sci Pharm78:13-20.
- Lu DY, Chen RT, Lu TR, Wu HY, Qu RX,et al. (2010) The absorption, distribution and excretion of 14C-probimane in mice bearing Lewis lung carcinoma. Sci Pharm 78:445-450.
- Lu DY, Huang M, Xu CH, Yang WY, Hu CX, et al. (2005) Anti-proliferative effects, cell cycle G2/M phase arrest and blocking of chromosome segregation by probimane and MST-16 in human tumor cell lines, BMC Pharmacology 5: 11.
- Lu DY, Huang M, Xu CH, Zhu H , Xu B, et al. (2006) Medicinal chemistry of probimane and MST-16: comparison of anticancer effects between bisdioxopiperazines. Med Chem 2: 369-375.
- Lu DY, Chen EH, Cao JY,Xu BJ, Ding J,et al. (2007)The antiproliferative effects of probimane and razoxane on tumor cells are concomitant with inhibition of hemolysis and calmodulin (CaM) action and a new CaM-ATPase acting model. Res J Biol Science 2:127-133.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Ding J (2010) Cell manifestation of bisdioxopiperazines treatment of human tumor cells lines in culture. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 10: 657-660.
- Hellmann K(2003) Dynamics of tumor angiogenesis: effect of razoxane- induced growth rate slowdown. ClinExp Metastasis20:95-102.
- Lu DY, Chi J, Lin LP, Huang M, Xu B, et al. (2004) Effect of anticancer drugs on the binding of 125I-fibrinogen to two leukemia cell lines in vitro. J. Int. Med. Res 32: 488-491.
- Lu DY, Xu J, Lu TR,Wu HY, Xu B,et al. (2013) Inhibitions of some antineoplastic drugs on serum sialic acid levels in mice bearing tumors. Sci Pharm 81:223-231.
- Lu DY, Liang G, Zhang MJ,Xu B(1994) Serum contents of sialic acids in mice bearing different tumors. Chin. Sci. Bull 39:1220-1223.
- Yang KZ (1990) Short-term results of malignant lymphoma treated with probimane. Chin J Cancer9:192-193.
- Lu DY, Chen EH, Cao JY (2001) Comparison between probimane and razoxane on inhibiting calmodulin activity of rabbit erythrocyte membrane. Chin J PharmacolToxicol15: 76-78.
- Lu DY, Chen EH, Cao JY (1991)The inhibition of probimane on lipoxidation of rabbit and human erythrocytes. J Shanghai University 7:301-304.
- Hellmann K, Rhomberg W. Radiotherapeutic enhancement by razoxane. Cancer Treat Rev 18, 225-240.
- Vuong MC, Hasegawa LS , Eastmond DA (2013) A comparative study of the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of ICRF-154 and bimolane, two catalytic inhibitors of topoisomerase II. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 750: 63-71.
- Barry EV, Vrooman LM, Dahlberg SE, Neuberg DS, Asselin BL, et al. (2008) Absence of secondary malignant neoplasms in children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with dexrazoxane. J ClinOncol 26: 1106-1111.
- Lu DY (2014) Personalized cancer chemotherapy, an effective way for enhancing outcomes in clinics Woodhead Publishing, Elsevier, UK.
Citation: Lu DY, Ding J, Chen RT, Xu H, Yarla NS, et al. (2017) Antimetastatic Mechanisms of Bisdioxopiperazine Compound Study, A Gateway to Success. J Cell Mol Pharmacol 1: e101.
Copyright: © 2017 Lu DY, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Usage
- Total views: 3395
- [From(publication date): 0-2017 - Jul 09, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 2497
- PDF downloads: 898