Clinical images Open Access
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Administrating Oral Paracetamol Suspension in Sprague Dawley Rats
Maryam IU, Aliya S, Thant Z, Swethadri JKM, Nordin S and Atif AB*Department of Medicine, Molecular Medicine, Biomedical Center, Malaysia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Atif Amin Baig
Molecular Medicine, Biomedical Center
Faculty of Medicine, Malaysia
Tel: +6096275587
E-mail: atifamin@unisza.edu.my
Received Date: April 27, 2015; Accepted Date: April 29, 2015; Published Date: April 30, 2015
Citation: Maryam IU, Aliya S, Thant Z, Swethadri JKM, Nordin S, et, al. (2015) Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Administrating Oral Paracetamol Suspension in Sprague Dawley Rats. Interdiscip J Microinflammation 3:I105. doi: 10.4172/2381-8727.1000I105
Copyright: © 2015 Atif AB, This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Inflammation, Cancer and Integrative Therapy
Clinical Image
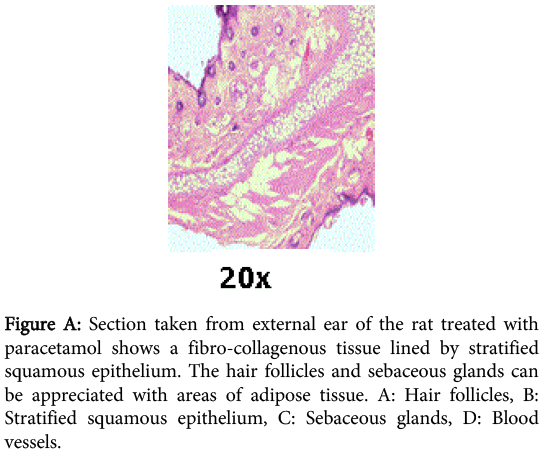
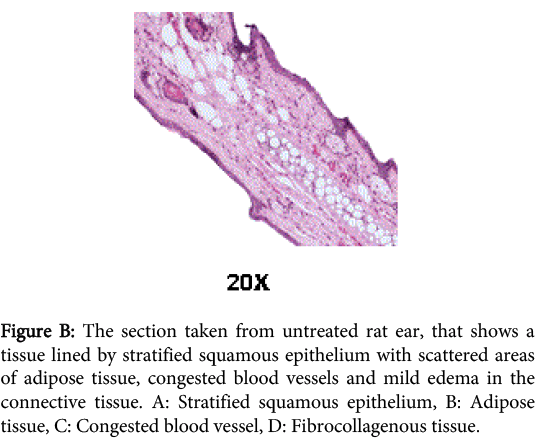
The anti edenic effect of paracetamol was observed in two groups of rats; untreated (n=11) and treated with oral paracetamol (15 mg/kg) for total of 21 days. The ear edema was induced using croton oil. The comparative analysis was recorded as a mean of difference between the weights of the ears (mean weight of edema, g) and percentage edema inhibition (89% for paracetamol). The paracetamol suspension was found to decrease edema and congestion beside its analgesic effects in our rat groups.
Figure 1: Section taken from external ear of the rat treated with paracetamol shows a fibro-collagenous tissue lined by stratified squamous epithelium. The hair follicles and sebaceous glands can be appreciated with areas of adipose tissue. A: Hair follicles, B: Stratified squamous epithelium, C: Sebaceous glands, D: Blood vessels.
Figure 2: The section taken from untreated rat ear, that shows a tissue lined by stratified squamous epithelium with scattered areas of adipose tissue, congested blood vessels and mild edema in the connective tissue. A: Stratified squamous epithelium, B: Adipose tissue, C: Congested blood vessel, D: Fibrocollagenous tissue.
Relevant Topics
Recommended Journals
- Journal of Lung Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
- Advances in Cancer Prevention
- Breast Cancer: Current Research
- Cancer Surgery
- Immunology: Current Research
- Current Trend in Gynecologic Oncology
- Journal of Cancer Diagnosis
- Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer and Stromal Tumors
- Cervical Cancer: Open Access
- Journal of Mucosal Immunology Research
- Journal of Oncology Research and Treatment
- Journal of Orthopedic Oncology
- Journal of Prostate Cancer
- Research and Reviews on Pathogens
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 12474
- [From(publication date):
July-2016 - Nov 21, 2024] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 11640
- PDF downloads : 834