A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Employment Status of Mothers and Acute Malnutrition among Under Five Children in Ethiopia
Received: 28-May-2021 / Accepted Date: 11-Jun-2021 / Published Date: 18-Jun-2021 DOI: 10.4172/2572-4983.1000216
Abstract
The objective of this meta-analysis was to determine the association between Employment status of mothers and acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia.Using data from 11 studies in Ethiopia we performed a meta- analysis with a specific focus on acute malnutrition among under five children.
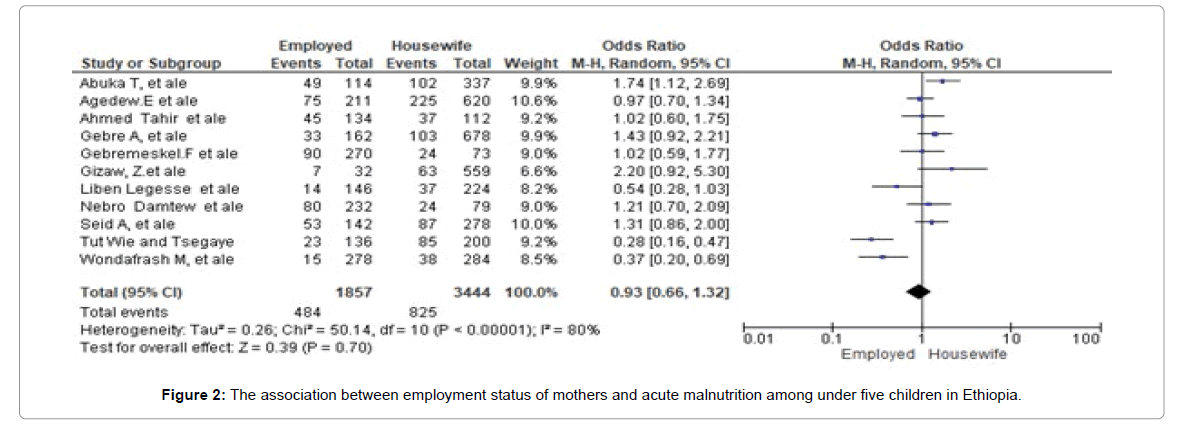
We applied a random effects analytic model and calculated a pooled odds ratio.Electronic databases were searched on reference manager software and quality assessment of the included studies was performed. using assessment of risk of bias tool. The funnel plot shows that there is no publication bias as Egger Regression p value is 0.882 and Begg and Mazumdar p-value is 0.815. The odds ratios for all studies revealed no statistically significant association of Acute Malnutrition among under five children with employed mothers compared to house wife mothers OR MH, Random, 95% CI, 0.93, (0.66, 1.32) Heterogeneity Tau²=0.26; Chi²=50.14, DF=10 (P<0.00001); I²=80% Test for overall effect: Z=0.39 (P=0.70) A total of 5301 under five children included in our systematic review and meta-analysis. The proportion of acute malnutrition among employed mothers is 26.1% (484) and among house wife mothers is 24% (825). Our findings suggest that employment status of mothers has not statistically significant association with acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia.
Keywords: Acute malnutrition ; Employment ; Children ; Electronic databases
Introduction
Acute malnutrition is a recent and severe weight loss (wasting) as a result of acute food shortage and/or illness and is measured by weight for height or Mid Upper Arm Circumference (MUAC) [1].
Malnutrition is associated with more than half of all child mortality worldwide [2].
Malnutrition is a serious problem in the world; currently, 195 million under-five children are affected by malnutrition globally; 55 million of them suffer from acute malnutrition and around 26 million under-five children are severely acute malnourished. Among the total under-five children suffering from malnutrition, 90% lives in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Every year, 3.5 million children die of malnutrition- related causes in the world [3,4]. Hence, it is at third level in the world of the disease burden in this age group [5].
In sub-Saharan Africa, the prevalence of stunting is declining but remains over 30% [6]. Among sub-Saharan countries, the prevalence of wasting in Ethiopia is 10%, and the prevalence of stunting is 38% [7].
Many studies in developing countries including Ethiopia showed that household characteristics like income [8-12], less access to health service, [9-11], household head [9-11], lack of toilet, [13,14] mothers’ education, [15,16], paternal education [17], hand washing, [18-20], household food insecurity [21,20], poor exclusive breast feeding [21,22] and number of under-five children or family size [23,24], has explained the occurrence of acute malnutrition.
The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to determine the association between Employment status of mothers and acute malnutrition in children in Ethiopia.
Thus, this finding will be used as a source of information on the association between employment status of mothers and acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia (Table 1).
| S. No. | Article | Mother occupation / Employment status | Acute malnutrition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| yes | No | |||
| 1 | Tut Wie and Tsegaye | Housewife/Unemployed | 85 | 115 |
| Employed /Others | 23 | 113 | ||
| 2 | Gebremeskel. F et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 24 | 49 |
| Employed /Others | 90 | 180 | ||
| 3 | Gizaw, Z. et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 63 | 496 |
| Employed /Others | 7 | 25 | ||
| 4 | Ahmed Tahir et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 37 | 75 |
| Employed /Others | 45 | 89 | ||
| 5 | Nebro Damtew et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 24 | 55 |
| Employed /Others | 80 | 152 | ||
| 6 | Abuka T, et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 102 | 235 |
| Employed /Others | 49 | 65 | ||
| 7 | Liben Legesse et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 37 | 187 |
| Employed /Others | 14 | 132 | ||
| 8 | Wondafrash M, et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 38 | 246 |
| Employed /Others | 15 | 263 | ||
| 9 | Gebre A, et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 103 | 575 |
| Employed /Others | 33 | 129 | ||
| 10 | Seid A, et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 87 | 191 |
| Employed /Others | 53 | 89 | ||
| 11 | Agedew.E et al. | Housewife/Unemployed | 225 | 395 |
| Employed /Others | 75 | 136 |
Table 1: Employment status of mothers and acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia.
Methodology
Electronic databases were searched on reference manager software and quality assessment of the included studies was performed. Using assessment of risk of bias tool.
A meta-analysis was applied to determine the effect of mother’s employment status on acute malnutrition among fewer than five children in Ethiopia.
Words used to search related literatures on the topic were ‘Acute Malnutrition’, ‘Employment status of mothers in Ethiopia, Determinants of Acute Malnutrition in Ethiopia’ were used.
Study selection
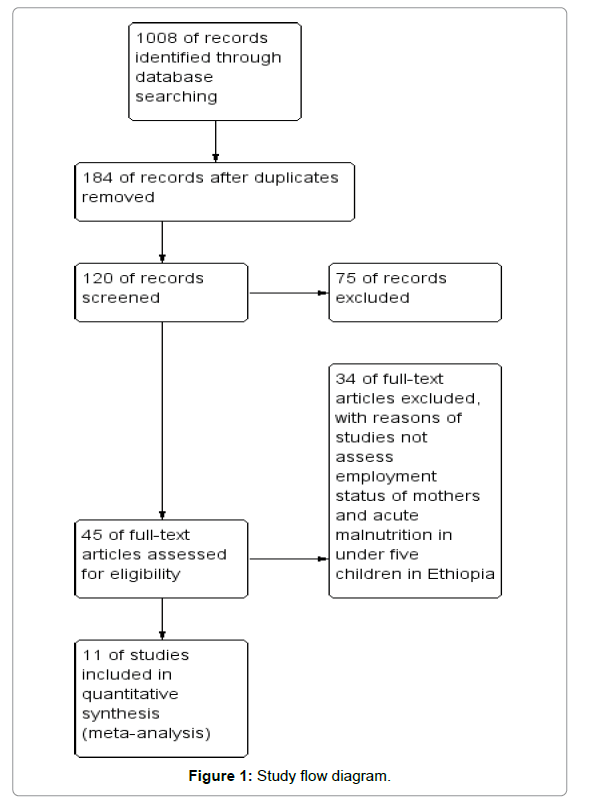
The PRISMA statement [25] for the reporting of systematic reviews recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration was followed while conducting this meta-analysis (Figure 1).
The first searching of databases results in 1008 articles.
After removing duplicates, we have got 184 studies on acute malnutrition among fewer than five children in Ethiopia.
Forty five [26] full-text articles assessed for eligibility and 11 studies met the inclusion criteria.
The rest were excluded due to studies not assess employment status of mothers and acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia.
Results
Using data from 11 studies in Ethiopia we performed a meta- analysis with a specific focus on acute malnutrition among under five children.
We applied a random effects analytic model and calculated a pooled odds ratio.
The meta-analysis is done using RevMan software version 5.3 and meta essential software.
When we see the employment status of mothers, 35% (1857) employed mothers and 65% (3444) house wife mothers were included in this study.
The proportion of acute malnutrition among employed mothers is 26.1% (484) and among house wife mothers is 24% (825).
Meta-analysis
The odds ratios for all studies revealed no statistically significant association of Acute Malnutrition among under five children with employed mothers compared to house wife mothers.
OR MH, Random, 95% CI, 0.93, (0.66, 1.32)
Heterogeneity Tau²=0.26; Chi²=50.14, DF=10 (P<0.00001); I²=80%
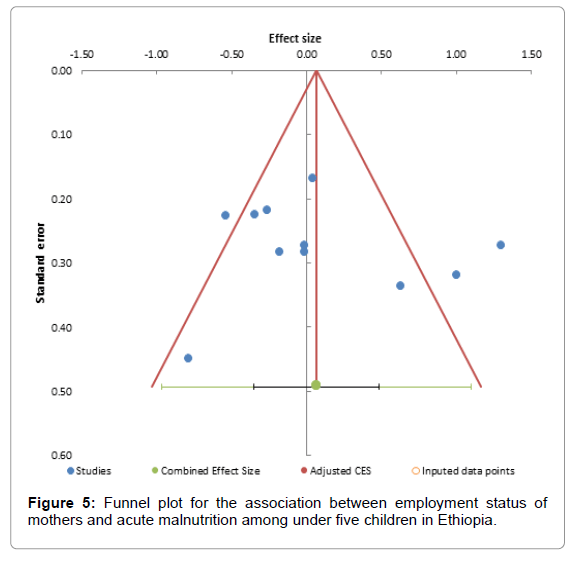
Test for overall effect: Z=0.39 (P=0.70) (Figures 2-5).
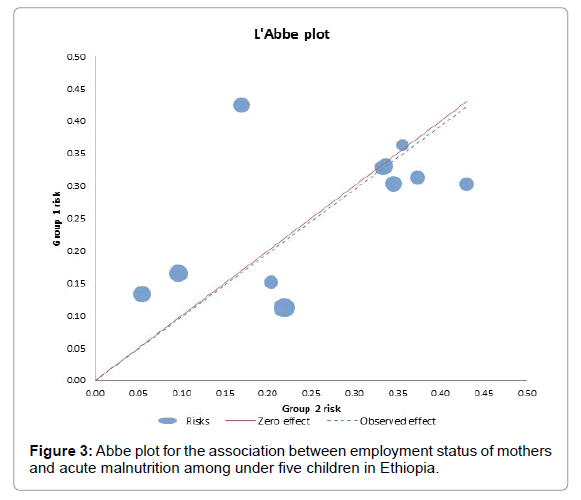
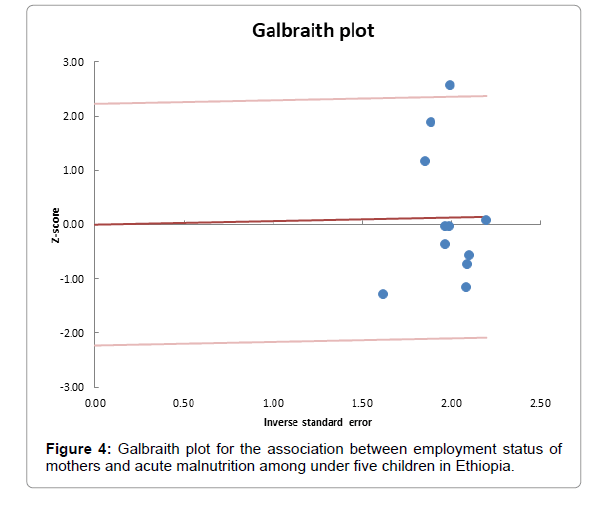
The Abbe plot shows that 3 studies are above zero effect and the rest below zero effect. Galbraith plot shows that 95% of the studies are within the range of two-color lines and there is no outlier of effect size.
The funnel plot shows that there is no publication bias as Egger Regression p value is 0.882 and Begg and Mazumdar p value is 0.815 (Table 2).
| Egger regression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | SE | CI LL | CI UL | |
| Intercept | 0.81 | 5.28 | -10.97 | 12.58 |
| Slope | -0.34 | 2.67 | -6.28 | 5.6 |
| t test | 0.15 | |||
| p-value | 0.882 | |||
| Begg and Mazumdar | ||||
| ?x-y | 3 | |||
| Kendall's Tau a | 0.05 | |||
| Z | 0.23 | |||
| P | 0.815 | |||
Table 2: The funnel plot shows that there is no publication bias as Egger regression p value is 0.882, Begg and Mazumdar p-value is 0.815.
Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis show that there is no statistical significant association between employment status of mothers and acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia and this finding is similar with previous studies Wolayta Sodo Town [26], Konso, Southern Ethiopia, [27], Afar Region, Northeast Ethiopia [28], Karat Town Public Health Facilities, Southern Ethiopia [29], Hadaleala district, Afar region, northeast Ethiopia [30], analysis of the 2016 Ethiopia demographic and health survey [31] two Public Hospitals, North West Ethiopia [32].
The explanation for our finding may be majority of mothers have maternal leave and children get the same care by employed and house wife mothers.
This finding is not similar with previous studies Gedeo Zone, Ethiopia [33] Ethiopia [34].Ekpoma, Edo-Nigeria [35], Mazowe District of Zimbabwe [36], Adama Town, Central Ethiopia. [37], in Tanzania [38], in Addis Ababa [39], Chapel Hilly, Job Arket Paper [40], in Nghean Vietnam [41], in Aydyn, a western city of Turkey [42-44].
The explanation for the observed differences in the findings of our study and other previous studies may be difference in sample size and geographic variations.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that employment status of mothers has not statistical significant association with acute malnutrition among under five children in Ethiopia.
Authors’ Contributions
Kaleab Tesfaye Tegegne, ElenI Tesfaye Tegegne and Mekibib Kassa Tessema was responsible for conceptualization, project administration, software, supervision, and development of the original drafting of the manuscript.
Kaleab Tesfaye Tegegne,, ElenI Tesfaye Tegegne and Mekibib Kassa Tessema were participated in quality assessment of articles, methodology, validation, and screening of research papers.
All authors contributed with data analysis, critically revised the paper, and agreed to be accountable for their contribution.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the primary authors of the included articles.
References
- Stevenson DK, Dennery PA, Hintz SR. (2001) Understanding newborn jaundice. J Perinatol. 21: 21-39.
- Vinod BK, Stark AR, Lazzeroni LC, Poland R, Gourley GR, et al. (2013) Predischarge screening for severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia identifies infants who need phototherapy. Â J Pediatr 162: 477-482.
- Myatt M, Khara TCS, Collins S (2009) A review of methods to detect cases of severely malnourished children in the community for their admis-sion into community-based therapeutic care programs. Food Nutr Bull. 27: 7–23.
- United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition (2004) 5thReport on the World NutritionSituation:Nutrition for Improved development Outcomes.
- Alemayehu M, Tinsae F, Haileslassie K. Nutritional status and associated factors among under-five children, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Int J Nutr Food Sci 2014; 3: 6
- UNICEF, children and the millennium development goals (2007) Progress for children a report card on nutrition 2007.
- Dereje N (2014) Determinants of severe acute malnutrition among under-five children in Shashogo Woreda, Southern Ethiopia: A community based matched case control study. Int J Res 1: 339-364
- UNICEF (2019) Levels and trends in child malnutrition, United Nations Children’sfund (UNICEF), World Health Organization, International Bank forReconstruction and Development/The World Bank. Levels and trends inchild malnutrition: key findings of the 2019 edition of the joint childmalnutrition estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; 2019
- Central statistical agency (2016) [Ethiopia] and ICF, Ethiopiademographic and health survey, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and Calverton,Maryland, USA.
- Tariku A, Bikis GA, Woldie H, Wassie MM, Worku AG (2017) Child wasting is a severe public health problem in the predominantly rural population of Ethiopia: A community based cross–sectional study. Archives of Public Health. 1; 75: 26.
- Egata G, Berhane Y, Worku A (2014) Predictors of acuteundernutrition among children aged 6 to 36 months in east rural Ethiopia: A community based nested case-control study. BMC Pediatrics. 1;14: 91.
- Gelu A, Edris M, Derso T, Abebe Z (2018) Undernutrition and associated factors among children aged 6–59 months living in slum areas of Gondar city, northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. Pediat Heal, Med Therap. 9:81.
- Fentaw R, Bogale A, Abebaw D (2013) Prevalence of child malnutrition in agro-pastoral households in Afar Regional State of Ethiopia. Nutrition Research and Practice. 1; 7:122-31.
-  Pravana NK, Piryani S, Chaurasiya SP, Kawan R, Thapa RK, et al (2017). Determinants of severe acute malnutrition among children under 5 years of age in Nepal: A community-based case–control study. BMJ Open; 7:e017084.
- Wubante AA. (2017) Â Determinants of infant nutritional status in Dabat district, North Gondar, Ethiopia: A case control study. PloS One. 27; 12: e0174624.
- Cooten MH, Bilal SM, Gebremedhin S, Spigt M (2018). The association between acute malnutrition and water, sanitation, and hygiene among children aged 6–59 months in rural Ethiopia. Matern Child Nutr. 15: e12631.
- Gone T, Lemango F, Eliso E, Yohannes S, Yohannes T (2017) The association between malaria and malnutrition among under-five children in Shashogo District, Southern Ethiopia: a case-control study. Infectious Diseases of Poverty. 2017 Dec 1;6: 9
- Fava FP, Upton J, Banerjee RR, Taye M, Mude AG (2018) Pre-feasibility study for Index-Based Livestock Insurance in Niger. Int Livestock Res Insti. 03: 4903-6613.
- Tut G, Tsegaye D (2020) Determinants of Acute Malnutrition Among Children Aged 6–59 Months Visiting Public Health Facilities in Gambella Town, SouthwestEthiopia Nutrition and Dietary Supplements. Nut Diet Suppl. 12: 147–156
- Seid A, Seyoum B, Mesfin F (2017) Determinants of acute malnutrition among children aged 6–59 months in Public Health Facilities of Pastoralist Community, Afar Region, Northeast Ethiopia: a case control study. J Nutr Metab. 7265972.
- Ambadekar NN, Zodpey SP (2017) Risk factors for severe acute malnutrition in under-five children: A case-control study in a rural part of India. Public Health. 1;142:136-43
- Abitew DB, Yalew AW, Bezabih AM, Bazzano AN, (2020) Predictors of relapse of acute malnutrition following exit from community-based management program in Amhara region,Northwest Ethiopia: An unmatched case-control study. PLos-One 15: e02315
- Burza S, Mahajan R, Marino E, Sunyoto T, Shandilya C, et al. (2016) Seasonal effect and long-term nutritional status following exit from community-based management of severe acute malnutrition program inBihar, India. Eur J Clin Nutr. 70: 437-44.
- Ambadekar NN, Zodpey SP (2017) Risk factors for severe acute malnutrition in under-five children: a case-control study in a rural part of India. Public Health 15; 54: 817-824.
- Awoke A, Ayana M, Gualu T (2018) Determinants of severe acute malnutrition among under five children in rural Enebsie Sarmidr District, East Gojjam Zone, North West Ethiopia, 2016. BMC Nut. 1; 4: 4
- Â Costa ME, Trumble B, Kaplan H, Gurven MD (2018) Child nutritional status among births exceeding ideal family size in a high fertility population. Matern Child Nutr 14: e12625.
- A Liberati, DG Altman, J Tetzlaff, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, et al. (2009) “The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration,â€. The British Med J 339: b2700 18
- Eshete H, Abebe Y, Loha E, Gebru T, Tesheme T (2017) Nutritional Status and Effect of Maternal Employment among Children Aged 6-59 Months in Wolayta Sodo Town, Southern Ethiopia: A Cross-sectional Study. Ethiop J Health Sci 27: 155.
- Agedew E (2016) Determinant of Severe Acute Malnutrition among Children Aged 6-59 Months in Konso, Southern Ethiopia: Case Control Study. Qual Prim Care 24: 181-186
- Seid A, Seyoum B, Mesfin F. (2017) Determinants of Acute Malnutrition among Children Aged 6-59 Months in Public Health Facilities of Pastoralist Community, Afar Region, Northeast Ethiopia: A Case Control Study. J Nutr Metab. 2017: 7265972.
- Miskir A, Godana W, Girma M, Miskel FG (2017) Determinants of Acute Malnutrition among Under-Five Children in Karat Town Public Health Facilities, Southern Ethiopia: A Case Control Study Qual Prim Care 25: 242-252
- Gizaw Z, Woldu W, Bitew BD (2018) Acute malnutrition among children aged 6–59 months of the nomadic population in Hadaleala district, Afar region, northeast Ethiopia. Ital J Pediatr 44: 21.
- Amare ZY, Ahmed ME, Mehari AB (2019) Determinants of nutritional status among children under age 5 in Ethiopia: further analysis of the 2016 Ethiopia demographic and health survey. Global Health 15: 62.
- Seid A, Seyoum B, Mesfin (2017) Determinants of Severe Acute Malnutrition among Children age 6-59 Months Old in Two 2Public Hospitals, North West Ethiopia: a Case Control Study. J Nut Met. 2017: 7265972.
- Abuka T, Jembere D, Tsegaw D (2017) Determinants for Acute Malnutrition among Under-Five Children at Public Health Facilities in Gedeo Zone, Ethiopia: A Case-Control Study. Pediatr Ther 7: 317.
- Tesfaye M (2009) Bayesian approach to identify predictors of childrennutritional status in Ethiopia. AAU Inst Rep. 2009: 06.
- Ozor MO, Omuemu VO (2014) Maternal determinants of undernutrition among under five year children in Ekpoma, Edo-Nigeria. Int J Public Health Res 2: 20-24.
- Radebe BZ, Brady P, Siziya S, Todd H (1996) Maternal risk factors forchildhood malnutrition in the Mazowe District of Zimbabwe. Cent Afr J Med 42: 240-244.
- Wondafrash M, Admassu B, Bayissa ZB, Geremew F (2017) Comparative Study on Nutritional Status of under Five Children with Employment Status of Mothers in Adama Town, Central Ethiopia. Matern Pediatr Nutr 3: 117.
- Hannah Ross-Suits Maternal Autonomy as a Protective Factor in ChildNutritional Outcome in Tanzania 2010.
- Zenbere B (2001) The effect of maternal employment on nutritional status ofchildren in Addis Ababa. Ethiopian J Pub Heal Nut. 4:1.
- Hubbard MN (2008) The Effect of Mothers' Employment and Child CareDecisions on the Body Mass Status of Young Children, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hilly, Job Arket Paper. 1-43.
- .Hein NN, Kam S (2007) Nutritional Status and the Characteristics Related toMalnutrition in Children Under Five Years of Age in Nghean, Vietnam. J Prev Med Public Health 41: 232-40.
- Ergin F, Okyay P, Atasoylu G (2007) Nutritional status and risk factors ofchronic malnutrition in children under five years of age in Aydyn, a western city of Turkey. Turk J Pediatr 49: 283-289.
Citation: Tegegne KT, Tegegne ET, Tessema MK (2021) A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Employment Status of Mothers and Acute Malnutrition among Under Five Children in Ethiopia. Neonat Pediatr Med 7:216. DOI: 10.4172/2572-4983.1000216
Copyright: © 2021 Tegegne KT, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Conferences
42nd Global Conference on Nursing Care & Patient Safety
Toronto, CanadaRecommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2921
- [From(publication date): 0-2021 - Apr 25, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 2089
- PDF downloads: 832