A Review on Analytical Methods for Estimation of Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form
Received: 02-Aug-2022 / Manuscript No. jabt-22-73537 / Editor assigned: 04-Aug-2022 / PreQC No. jabt-22-73537(PQ) / Reviewed: 18-Aug-2022 / QC No. jabt-22-73537 / Revised: 22-Aug-2022 / Manuscript No. jabt-22-73537(R) / Published Date: 29-Aug-2022
Abstract
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is a common condition that is characterized by having a higher amount of pressure in your blood vessels than normal. Hypertension (HT) is a very common disorder, particularly past middle age. It is not a disease in itself, but is an important risk factor for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. For improvement activity of hypertension, Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone newer combination in market,which is effective in Hypertension. This combination was developed to improve medication for Stage II Hypertension. Azelnidipine is Ca2+ channel blocker and chemically 3- [1- (Benzyldrylazetidin-3-yl] 5-isopropyl- 2- amino6methyl-4-(3- nitrophenyl)-1, 4- dihydropyridine-3,5dicarboxylate. Chlorthalidone is a diuretic used to treat hypertension or edema caused by heart failure, renal failure, hepatic cirrhosis, estrogen therapy, and other conditions and Chemically 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy- 3-oxo- 2H-isoindol-1-yl) benzenesulfonamide. This Review focuses on recent development in analytical method development for Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone, and there was no any method reported for this combination. It provides information about different analytical method development like UV spectrophotometry, HPLC, HPTLC, LC-MS methods reported for Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone for individual and other drug combination.
Keywords
Azelnidipine; Chlorthalidone; Analytical method; UV Spectrometry; HPLC; HPTLC; UFLC Hypertension
Introduction
Azelnidipine is dihydropyridine derivative and chemically 3-[1-(Benzyldrylazetidin-3-yl] 5-isopropyl-2- amino6methyl-4-(3- nitrophenyl)-1, 4-dihydropyridine-3,5dicarboxylate [1]. Azelnidipine category is Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. Azelnidipine calcium channel blocker. Azelnidipine inhibits trans-membrane Ca2+ influx through the voltagedependent channels of smooth muscles in vascular walls. It is a vasodilator that induces a gradual decrease in blood pressure in hypertension. When calcium channels are blocked, the vascular smooth muscle does not contract, resulting in relaxation of vascular smooth muscle walls and decreased blood pressure [1, 2]. It is used in Treatment of Hypertension which lowers the Blood Pressure due to Block calcium Channel and Decreases Blood Pressure and oral dose is 8 – 16 mg once daily [3-7]. It metabolized in hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and has no active metabolite product [8].
Chlorthalidone is 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2H-isoindol-1-yl) benzene sulfonamide. Chlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic used for the treatment of hypertension and for management of edema caused by conditions such as heart failure or renal impairment. Chlorthalidone improves blood pressure and swelling by preventing water absorption from the kidneys through inhibition of the Na+/Cl− symporter in the distal convoluted tubule cells in the kidney. The exact mechanism of chlorthalidone’s anti-hypertensive effect is under debate; however, it is thought that increased diuresis results in decreased plasma and extracellular fluid volume, decreased cardiac output and therefore overall reduction in blood pressure [9].
Physical and Chemical Property
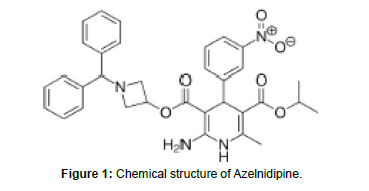
Azelnidipine is light yellow to yellow crystalline powder. IUPAC name is 3-[1- (Benzyldrylazetidin- 3-yl] 5-isopropyl- 2- amino6methyl- 4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1, 4- dihydropyridine-3,5dicarboxylate. Molecular formula of Azelnidipine is C₃₃H₃₄N₄O₆. Molecular weight is 582.646 g/mol. It is insoluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, soluble in ethyl acetate, freely soluble in acetone and in acetic acid [10].
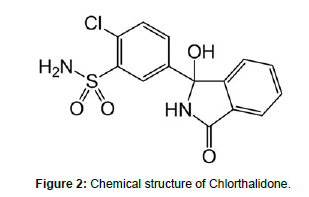
Chlorthalidone is White to Yellowish-White Crystalline Powder. IUPAC name is 2-chloro-5-(1- hydroxy-3-oxo-2H-isoindol-1- yl) benzene sulfonamide Molecular formula of Chlorthalidone is C14H11ClN2O4S .Molecular weight is 338.8 g/mol. Chlorthalidone is practically insoluble in water, in ether and in chloroform; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol. (Figure 1, 2)
Analytical Method Development
Analytical method development and validation assume fundamental part in the drug discovery, drug advancement and assembling the pharmaceutical products. It includes identification of the purity and toxicity of a drug substance. Analytical method development is the process of selecting an accurate assay procedure to determine the composition of a formulation. It is the process of proving that an analytical method is acceptable for use in laboratory to measure the concentration of subsequent samples Analytical methods should be used within GMP and GLP environments and must be developed using the protocols and acceptance criteria set out in the ICH guidelines Q2(R1). Analytical method development and Validation play important roles in the discovery, development, and manufacture of pharmaceuticals. The following Literature Survey reveals that there is no any singe method was reported for Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone Combination. However, UV Spectrophotometry, RP –HPLC, HPTLC, Stability indicating RP-HPLC methods, UFLC reported for Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone individual and along with other drugs. (Table 1-4)
| Method Type | Method Description |
|---|---|
| Liquid Chromatography (Indian Pharmacopoeia- 2018) | Column: Octadecylsilane Silica (25cm x 4.6 mm,5µm) Mobile phase:0.03 M potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate in water: Acetonitrile (50:50) v/v Wavelength: 256 nm Flow rate: 1.0 ml/min Injection volume :20 µ |
Method Type |
Method Description |
|---|---|
| UV Spectrophotometric method development and Validation for Determination of Azelnidipine in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. |
Model: Shimadzu 1800 UV Visible spectrophotometer Solvent: Methanol Wavelength (nm): 255nm Linearity: 2 - 14 µg/ ml |
| Simultaneous Determination of Azelnidipine and Olmesartan medoxomil by First Derivative Spectrophotometric Method. |
Model: Shimadzu – 1800 UV Visible Spectrophotometer Solvent: Methanol Method: 1. First Derivative Spectrophotometric Method Wavelength (nm): AZL - 217nm OLM- 239.4 nm Linearity: 4 - 32 µg/ ml |
| Spectrophotometric estimation of Azelnidipine in Bulk and Pharmaceutical dosage form by second order derivative methods. |
Model: Shimadzu 1800 UV Visible Spectrophotometer Solvent: Methanol Method: 1. Second Derivative Spectrophotometric Method Wavelength: 233.8 nm Linearity: 1 - 20 µg / ml |
| Method Development and Validation of Azelnidipine by RP- HPLC. | Column: C18 column (250 mm x 4.5 mm, 5 μm) Mobile Phase: Methanol: Water (75:25) v/v,0.1%glacial acetic acid. Flow rate: 1 mL/min Wavelength: 254nm Linearity: 10 - 50 μg/ml Retention Time: 6.13 min. |
| RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation of Azelnidipine. |
Column: C18 column (250 mm x 4.5 mm, 5 μm) Mobile Phase: Methanol: Water (80:20) v/v, Orthophosphoric acid (pH-3) Flow rate:1 mL/min. Wavelength:257 nm Linearity:20- 100μg/ml Retention Time: 6.5 min. |
| Simultaneous determination of Azelnidipine and two metabolites in Human Plasma using Liquid chromatography- tandem mass spectrometry | Column: Intersil ODS-3 C18 (2.1 mm × 150 mm,5μm) Mobile Phase: Methanol: Water: Acetic Acid (800:200:0.2) v/v Flow rate: 0.2ml/min. Wavelength: 256nm Linearity: 0.5- 40 mg/ml Retention Time: AZL –3.6min. M- 1(Aeromatizedform)-10.2min. M-2(Hydroxylated Form)- 6.8min. |
| Simultaneous Determination of Azelnidipine and Olmesartan Medoxomil in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms by UFLC Method. |
Column: ODS (250mm x 4.6mm, 5μm) Mobile Phase: Methanol: Water (85:15) v/v Flow Rate: 1.5ml/min. Wavelength: 255nm Linearity: 2-16 mg/ml Retention Time: AZL - 6.80 min. OLM -1.72 min |
| Stability Indicating Analytical Method Development and Validation for Estimation of Azelnidipine. |
UV Spectrophotometric m ethod: Solvent : Methanol: Water (80:20) v/v Methods: Method 1- Zero order Spectrophotometric method Method 2 -First order Derivative Spectrophotometric method Wavelength: Method 1 -257 nm Method 2- 242.6 nm Linearity: 2-10 μg/ml Method 3 – RP HPLC Method Column: ODS C18 (250mm×4.6mm.,5μm) Mobile phase: Sodium diabasic Phosphate Buffer: Acetonitrile: Methanol (10:50:40 )v/v/v, orthophosphoric acid (pH - 4.5) Flow rate: 1mL/min Wavelength: Method 3 - 256nm Linearity: 2-12 μg/ml Retention Time : 6.1 min. |
| Validated Stability- Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Azelnidipine and Olmesartan in Their Combined Dosage Form. |
Column: Hypersil GOLD C18 (150 mm × 4.6mm, 5 µm) Mobile Phase: Methanol: Acetonitrile: Water (40:40:20) v/v/v Flow rate :0.5 mL/min Wavelength :260 nm Linearity: AZL – 2 - 48 μg/ml OLM- 2.5 - 60 μg/ml Retention Time: AZL -8.56min. OLM - 3.04 min |
| Validation and Forced StabilityIndicating HPTLC Method for Determination of Azelnidipine. | Stationary Phase: Silica gel 60 F254 (20cm × 10cm, 0.2mm) Mobile Phase: Chloroform: Ethyl acetate: methanol 6.5:3.5: 0.1 (v/v/v) Wavelengtz: 255nm Linearity:300-800ng/band Rf Value :0.59,0.60 |
| Sensitive Analysis of Azelnidipine and Related Derivative in Human Plasma by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography- Tandam Mass Spectrometry. | Column: C18 (50 mm × 2.1 mm.,1.7 µm) Mobile Phase: A (20 mM Ammonium acetate aqueous solution) B (0.1 % formic acid in Acetonitrile) Flow Rate: 0.5 mL/min Linearity: 0.01-10 mg/ml Retention Time: AZL -1.38 min. IS -1.26 min |
Method Type |
Method Description |
|---|---|
| Liquid Chromatography (Indian Pharmacopoeia -2018) |
Column:C8 column (250 × 4.6 mm; ‘5 μm particle size) Mobile phase A consisted of buffer solution (diammonium hydrogen orthophosphate (10 mM, pH 5.5)) and methanol at a 65: 35 ratio (v/v), and mobile phase B consisted of buffer solution and methanol at a 50: 50 ratio (v/v). Wavelength: 220 nm Flow rate: 1.4 ml/min Injection volume :20 µL |
Method Type |
Method Description |
|---|---|
| A Validated RP-HPLC Stability Method for the Estimation of Chlorthalidone and Its Process-Related Impurities in an API and Tablet Formulation | Column:C8 (250 ×4.6 mm,' 5 µm) Flowrate:1.4 mL/min Wavelength:220 nm Mobile phase: A consisted of buffer solution [diammonium hydrogen orthophosphate (10 mM,pH 5.5)] and methanol at a 65:35 ratio w/v Mobile phase B: A consisted of buffer solution and methanol at a 50:50 ratio w/v |
| Development and validation of HPTLC method for simultaneous determination of telmisartan and chlorthalidone in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form | Mobile phase: Acetonitrile: Toluene: Glacial acetic acid (7.5:2.5:0.05 v/v/v) Wavelength:242 nm Rf value for telmisartan and chlorthalidone :0.26 ± 0.02 and 0.67 ±0.02 Concentration range :400-2400 ng/spot and 125-750 ng/spot (n=6) % recovery=100.03 and 100.026 |
| “Simultaneous Estimation of Atenolol and Chlorthalidone as Bulk and in Tablet dosage Form Using UV- spectrophotometry”. | Absorbance maxima of atenolol and Chlorthalidone :225 nm and 284 nm Concentration range of atenolol is 10-60 μg/ ml and chlorthalidone is 30-140 μg/ ml. |
| “A Reversed- Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Method for Determination of Chlorthalidone in Pharmaceutical Formulation”. |
Column: C18 column Solvent: mixture of Acetonitrile, Methanol, and 50mM dihydrogen phosphate in the ratio of 05:30:70 v/v pH:3.5 Mobile phase: orthophosphoric acid Wavelength: 220 nm. The calibration was found to be linear in the range of 0.1to3.2 μg/ ml. |
| Stability indicating RP – HPLC method development and validation for simultaneous estimation of amlodipine and chlorthalidone in bulk and tablet dosage form (P. H. Sakpal * and A. R. Chabukswar) |
mobile phase as a mixture of 0.1% formic acid: methanol: acetonitrile in the ratio of (50:5:45 v/v) pH :3 was adjusted with orthophosphoric acid. C18 column (5 µm, 25 cm × 4.6 mm) flow rate of 1.0 ml per min. Wavelength: λmax 266 nm Retention time: 6.32 min and 5.32 min Calibration curve determined at respective retention time is found to be 2.5-7.5 μg/ml and 06-18 μg/ml regression coefficient of 0.9990 and 0.9940 |
| “Development and Validation of a Reversed – Phase High-Performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of amiloride hydrochloride, atenolol, hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone in their combined mixtures”. |
The method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 2 ternary mixtures containing amiloride hydrochloride, atenolol, hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone using Cyanopropyl column, the mobile phase consisted of 10mM KH2PO4 Buffer pH 4.5 and Methanol in the ratio of 75:25 % v/v, at the flow rate 1 ml/min. Uv detector was operate 275 nm. Calibration graphs were linear in the concentration ranges of 2-10μg/ml, 20-200 μg/ ml, 10-100 μg/ ml and 5-50 μg/ ml for amiloride hydrochloride, atenolol, hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone, respectively. |
| “Development and Validation of RP-HPLC method for Simultaneous Estimation of Atenolol and Chlorthalidone from Pharmaceutical Formulation”. | mobile phase: Methanol- Potassium dihydrogen Phosphate buffer (50:50v/v adjusted to pH 3.4) Flow rate: 0.5ml/ min Wavelength: 240 nm. Retention time: Atenolol was 3.2 min and for Chlorthalidone 5.0 min. Atenolol and Chlorthalidone. Concentration range of 50-150 μg/ ml. Correlation coefficient for Atenolol and Chlorthalidone was 0.9996. |
| “RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Amlodipine, Valsartan, Telmisartan, Hydrochlorothiazide and Chlorthalidone: Application to Commercially available Drug Products”. | The separation was achieved on Cosmosil PAQ 4.6×150 mm and particle size:5 μm flow rate of 1ml /min] Mobile phase: consisted of 0.05M Sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer and acetonitrile Wavelength: 220 nm. |
Conclusion
This article gives an idea about improved activity of Azelnidipine and chlorthalidone from other drugs. The presented review provides information about the various methods available in the literature for the determination of Azelndipine and chlorthalidone. The different analytical methods are reported for the individual and other combination like UV Spectroscopy, HPLC, LC-MS, and HPTLC. This article also present with Pharmacological action, chemical structure, solubility, etc. of Azelnidipine and chlorthalidone. The given Literature review focus that there is not a single method reported for Azelnidipine and chlorthalidone Combination. This Article also suggests that reported methods for Azelnidipine and chlorthalidone for individual and other combinations. This review will help in future to develop the analytical method for this new combination and also gives the knowledge about its characteristics of both drugs.
References
- Ellison, Norig (2002) Goodman and Gilman’s The pharmacological basis of therapeutics; 10th Edn; Medical publishing division 94: 1377.
- Tripathi KD (2013) Essentials of Medical Pharmacology; 6th ed., New Delhi, Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd 271-275.
- Beckett AH, Stenlake JB (2002) Practical pharmaceutical chemistry; 4th ed., New Delhi, CBS publisher and distributors 279-300.
- Chatwal GR, Anand SK (2002) Instrumental methods of chemical analysis; 5th ed., Mumbai Himalaya publishing house 2149-2184.
- Sethi PD (2006) High Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantitative Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulations; 4th Edn, 11-97.
- Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Crouch SR (2017) Principles of instrumental analysis; 6th ed., Delhi, Cengage learning, 2017; 806-835.
- Validation of analytical procedures: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1); ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline, 2005: 4-13.
- Drug Profile, “Azelnidipine”, December, 2020.
- Drug Profile, “chlorthalidone”, December, 2020.
- The Indian Pharmacopoeia, Government of India, Ministry of Health and Family welfare; 7th ed., The Indian pharmacopeia commission, Ghaziabad, 2018; II: 1304-1305, 3319-3320.
Citation: Patel KB, Barot RV (2022) A Review on Analytical Methods for Estimation of Azelnidipine and Chlorthalidone in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. J Anal Bioanal Tech 13: 473.
Copyright: © 2022 Patel KB, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Usage
- Total views: 1788
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Apr 07, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1463
- PDF downloads: 325