A Preliminary Study on Various Types of 4-Aminoquinolines for Pre or Post-Exposure Prophylaxis and for Treatment in Severe Covid-19
Received: 20-Jun-2020 / Accepted Date: 31-Jul-2020 / Published Date: 07-Aug-2020 DOI: 10.4172/2161-0711.1000690
Abstract
Background: LiveWell Initiative LWI is a self-funded nonprofit social enterprise which thrives on innovation.
The organization has, for 5 years, supervised MPH and DrPH Practicums for the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Harvard University, Boston USA. It also supervises PhD thesis at University of Helsinki, Finland. At the inception of COVID-19, LWI designed and compiled three (3) sets of study protocols in response to the COVID-19 response in Africa with a goal to arriving at a practical and affordable solution to the pandemic using 4-Aminoquinolines.
Method: A concurrent cohort/descriptive study of observation in patients exposed to HCQ/CQ Prophylaxis and Treatment with HCQ/CQ and Quinine with categorization as specified as Not critically ill, critically ill but not on a ventilator and critically ill on a ventilator. One hundred and twenty-three (123) subjects were categorized into shelter-in-place, self-quarantine and self-isolation (Not critically ill, critically ill but not on a ventilator and critically ill on a ventilator). The 4-Aminoquinolines were administered with macrolide and zinc sulphate as appropriate for a defined duration and doses.
Results: The preliminary study of the 123 subjects covering all categories listed above resulted in 100% positive outcomes; Nil death, Nil relapse in Symptomatic persons and Total recovery with no relapse after 6 weeks lockdown, and asymptomatic persons post-prophylaxis, after 6 weeks lockdown. The results have been gathered principally from Clinician Reported Outcomes with a few Patient Reported Outcomes.
Conclusion: These repurposed drugs with unique strengths- Chloroquine and its analogue Hydroxychloroquine as well Quinine, hold away in the treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: 4-Aminoquinolines; Zinc Sulphate; COVID-19; Ventilator; Pandemic; Repurposing; Ionophore
Introduction
Stated Coronavirus to be an enveloped [1], positive single-strand RNA virus which belongs to the Orthocoronavirinae subfamily, as the name, it possesses the characteristic “ crown-like ” spikes on their surfaces [2]. Stated that alongside SARS-CoV, bat SARS-like CoV and others, it also falls into the genus beta-coronavirus.
COVID-19 enters the cell by using the S spike on its surface to bind onto an ACE2 receptor through a process of glycolysis. Once in the cell, the virus RNA uses the host cell ribosome to synthesise more RNA and protein. The protein is used to form the virus the capsule that protects the genetic material RNA. After making a million copies of itself using the host ribosome, it then assembles new viral particles and leaves the cell to find a new host. The immune system which is a complex interconnection of molecular interactions across the cell, nucleus and cytoplasm, Sometimes overreacts because of its weakened and dysfunctional state during the process of infection, releasing cytokines than required resulting in a cytokine storm. As of present, there is yet to be an ideal treatment for COVID-19, the treatment is mainly supportive.
The 3 sets of Protocols designed by Live Well Initiative have undergone professional debates among physicians, researchers and pharmacists for Hypothesis Testing over 5 weeks. Thereafter the team presented a Global Webinar on Apri 15th 2020 at which the Panelists were the Country Rep WHO Nigeria Dr Fiona Braka, The FIP Vice President, EMROPHARM Secretary-General, AFRO Lead at FIP, UN Ambassador of Goodwill Dr Corinne Shenouda and A Clinician at Mayo Clinic, Dr Michael Leise. The webinar series was thereafter taken along with the Nigeria National COVID-19 THINKTANK and a third webinar was held with the medical community in Nigeria, hosted by GSK. The Study Protocols are currently undergoing random Physician- Patient Trials at the discretion of Prescribing Clinicians and Clinical Researchers, they are as recommended in a compilation of recent findings by LiveWell Initiative LWI on COVID-19. LiveWell Initiative LWI, a nonprofit organization, takes no liability for damage from the use of the above-suggested STUDY PROTOCOLS FOR COVID-19 RESPONSE IN AFRICA. It is a Study Protocol designed to ‘evolve’ as an African Solution to COVID-19 Response.
This document is not intended for non-physicians, non-researchers or non-pharmacists. It is strictly meant for research, as we look towards a cure for the Pandemic. The outcomes of the empirical data are encouraging, as there has been 100% recovery from COVID-19 on 11 patients at an Isolation Center in Oyo State Nigeria; and a patient in faraway Canada recovered under the ventilator, with the protocols. The Study is to be scaled through prospective partnership or collaboration. This is also an open call for partnerships to scathe COVID-19REPONSE IN AFRICA and the DIASPORA.
Material and Methods
Some key facts:
• There is a dose-response relationship
• Those on HCQ/CQ prophylaxis are less likely to develop SARSCoV- 2 infection, compared to those who were not on it
• This does not, however, belie the need for PPEs and must not confer an undue sense of overprotection
Inclusion Criteria
• Shelter-in-place: are a healthy individual who chose to stay at home just to limit the spread of the virus
• Self-quarantine: are those that must have come in contact with someone who tested positive for coronavirus. They may be immune active or immunocompromised
• Asymptomatic healthcare workers working in non-COVID hospitals/non-COVID areas
• Asymptomatic healthcare workers involved in containment and treatment of COVID-19
• Asymptomatic frontline workers,
• Asymptomatic household contacts of laboratory-confirmed cases.
• Self-isolated: Those who tested positive for COVID-19
• Symptomatic Self-isolated persons
• Symptomatic Hospital isolated persons
• Symptomatic critically ill persons
Exclusion Criteria
• The drug is contraindicated in persons with a known case of 1. Retinopathy, 2. Hypersensitivity to HCQ or 4-aminoquinoline compounds 3. G6PD deficiency 4. Pre-existing cardiomyopathy and cardiac rhythm disorders
• The drug is not recommended for prophylaxis in children under 15 years of age and in pregnancy and lactation.
Doses
Shelter-in-place: 1.5G Chloroquine, 1.2G Hydroxychloroquine and 0.7G azithromycin Maximum.
• Chloroquine 500mg daily for three days
• Hydroxychloroquine 400mg daily for three days
• Azithromycin 250mg daily for three days
Self-Quarantine: 2.5G Chloroquine, 2.0G Hydroxychloroquine; and 1.5-2G Azithromycin Maximum.
• Chloroquine 500mg 12 hourly stat, then 500mg daily for three days
• Hydroxychloroquine 400mg 12 hourly stat, then 400mg daily for seven days
• Azithromycin 250mg daily for five to seven days
Self-Isolation: 1.8G Quinine; 1.5-2G Azithromycin Maximum.
• (Not critically ill)
• Quinine 600mg 8 hourly for five days
• Azithromycin 500mg daily for seven days
• Zinc sulphate 220mg daily for seven days
• (Critically ill)
• Quinine Intravenous with Dextrose saline 8 hourly for five days
• Azithromycin 500mg intravenously
• Zinc sulphate 220mg daily for seven days
• Generous fluid
Treatment doses below 4G sustained due to the ionophoric effect of zinc on Chloroquine, which makes lower doses of Chloroquine more efficacious due to enhanced tissue binding affinity and uptake by the viral cell. Other mechanisms of action of HCQ/CQ offer additiona protection to the host. HCQ/CQ will alter the pH in the ACE2 Receptor thus making it difficult for the virus to penetrate the host cell. In addition, it breks the polymerase chain, and , in advanced COVID-19 exhibits its Haemozoin inhibitor action, thus disabling the virus from engulfing food vacuoles of deris and dead blood cells. Quinine, highly soluble and crosses the blood brain barrier; penetrating in advanced COVID-19 patients into the alveoli and dislodging the viruses. Thus the usefulness of the 4-Aminoquinolines end to end, in COBVID-19.
Use beyond 7 weeks:
For its use beyond 7 weeks on weekly dosage with strict monitoring of clinical and ECG parameters which would also ensure that the therapy is given under supervision. This is ideally for IPT Intermittent Prophylactic Therapy post-recovery, as the virus is still shed through the bowels after recovery. Foor further research we recommend the bowel infiltrates of the virus for possible vaccine development as it is believed to be the attenuated virus.
Safety as a major concern
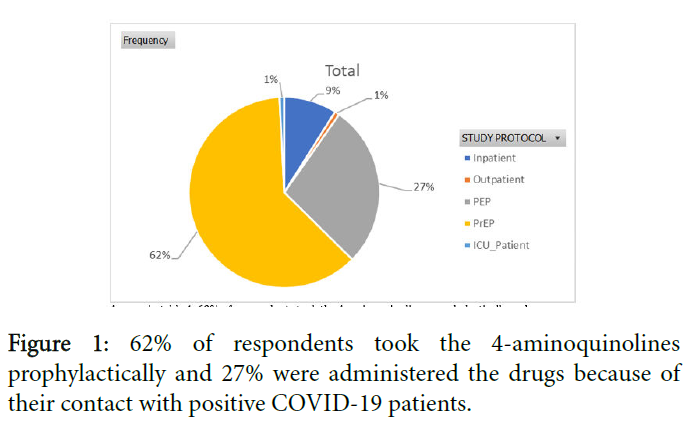
The safety of Chloroquine or Hydroxychloroquine is premised on the use of a dose below 4G Cumulative Total loading dose. This is carefully titrated at LWI. As long as HCQ/CQ is used at therapeutic concentrations it remains a very safe drug with a broad therapeutic margin. Even Quinine, used in advanced COVID-19, remains very safe with no requirements for TDM within the specified therapeutic concentrations where side effects are sef limiting, and, reversible; namely reversible ototoxicity Figure 1.
Affordable, replicable, scalable
• The remedy is affordable, scalable and replicable for all low-income economies.
• It is hereby strongly recommended.
Results and Discussion
Outcomes of preliminary study: A preliminary study of 123 subjects covering all categories listed above resulted in 100% positive outcomes; Nil death, Nil relapse in Symptomatic persons and Total recovery with no relapse after 6 weeks lockdown, and asymptomatic persons Tables 1-6.
| Resource | CLASSIFICATION | PrEP | PEP | Age | Gender | Outpatient | Inpatient | Critical Care | Outcome | Lab. Test for covid – pcr test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic Non-COVID-19 Tested non- exposed |
Asymptomatic Non-covid-19 tested exposed |
|||||||||
| F.A. | HCW | 20 | 8 | 18-35 | 24 m | - | - | - | ASYMPT (28) | Nil Tested |
| 36-55 | 4 f | |||||||||
| K. O | HCW | - | 1 | 36-55 | 1 f | - | - | - | SYMPT (1) | Nil Tested |
| F. O | FHCW | 20 | 2 | 18-35 | 22 m | - | - | - | ASYMPT (20) | Nil Tested |
| 36-55 | *Security men | SYMPT (2) | ||||||||
| J.M | FHCW | 5 | 15 | 18-35 | 14 m | - | - | - | ASYMPT (20) | Nil Tested |
| 36-55 | 6 f | |||||||||
| R.B. | >55yrs | 2 | - | >55yrs | 1m | - | - | - | ASYMPT (2) | Nil tested |
| 1f | ||||||||||
| A.P. | FHCW | 22 | 2 | 18-35 | 13 m | - | - | - | ASYMPT (22) | Nil Tested |
| 36-55 | 11 f | SYMPT (2) | ||||||||
| U.U. | HCW | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | ASYMPT (1) | Nil tested | |
| B.B. | HCW | 4 | 2 | 18-35 | 2 m | - | - | - | ASYMPT (4) | Nil Tested |
| 36-55 | 4 f | SYMPT (2) | ||||||||
| B.A. | HCW | 1 | - | 36-55 | 1f | - | - | - | ASYMPT (1) | Nil Tested |
| S.S (proxy) | HCW | - | 1 | >55yrs | 1 f | - | - | - | SYMPT (1) | Nil Tested |
| JESS | YOUTH | - | 1* | 18-35 | 1 f | - | - | - | SYMPT (1) | Online Tested |
| Y.A. | >55yrS | 1 | 2* | 36-55 | 3f | - | - | - | ASYMPT (1) | Online tested |
| SYMPT (2) | ||||||||||
| NURSE, UK | FHCW | - | - | 36-55 | 1f | I | - | - | SYMPT (1) | Lab. Tested +ve |
| OYO STATE ISOLATION CENTER | C-19 PATIENTS/ FHCW | - | - | - | 11 | - | SYMPT (11) | Lab. Tested +ve | ||
| VENTILATOR - PATIENT, CANADA | PATIENT’s FAMILY | - | - | >55yrs | 1f | - | - | 1 | SYMPT (1) | Lab. Tested +ve |
| TOTAL | 76 | 34 | 1 | 11 | 1 | |||||
| GRAND TOTAL | 123 |
*2 persons exposed after pep, online tested, awaiting laboratory testin. Outcomes are mostly clinician reported outcomes with a few patient reported outcomes, namely fhcw frontline healthcare workers and hcw healthcare workers.
Table 1: Outcomes of preliminary study.
| Study Protocol | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inpatient | 11 |
| Outpatient | 1 |
| PEP | 34 |
| PrEP | 76 |
| ICU_Patient (Treated on Quinine i.v.) | 1 |
| Grand Total | 123 |
Table 2: Designation of respondents.
| Age (Years) | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 18-35 | 65 |
| 36-55 | 55 |
| >55 | 3 |
| Grand Total | 123 |
Table 3: Age of respondents.
| Gender | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Male | 76 |
| Female | 34 |
| Grand Total | 123 |
Table 4: Gender of respondents.
| Classification | Laboratory tested (n) | Non-tested (n) | Online tested - awaiting laboratory testing (2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PrEP | NIL | 75 | 1 |
| PEP | NIL | 31 | 3 |
| OutPatient (U.K. Nurse) | 1 | - | - |
| Inpatient / Isolation Center (Oyo State Isolation Center) | 11 | - | - |
| Critical Care / Ventilator Patient (Canada) *treated on Quinine Injection i.v. | 1 | - | - |
| TOTAL | 13 | 106 | 4 |
Table 5: laboratory testing for covid-19.
| Symptoms & testing stratification | Number (n) | Comments - AFTER |
|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic, online tested, awaiting laboratory test | 3 | General Public – Awaiting Laboratory Test for 3 weeks but now symptom-free |
| Symptomatic not laboratory tested | 8 | 4 Frontline Workers, 4 Frontline Healthcare Workers. No Symptoms |
| Symptomatic, laboratory tested positive | 13 | 1 inpatient in Canada, 1 Self Quarantined HCW in the UK, 11 Isolation Center inpatients in Nigeria. No Symptoms. |
| Total | 24 | COVID-19 Free 100% NIL mortality NIL morbidity |
Table 6: Symptom outcomes assessment before and after use of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for covid-19 prophylaxis.
Discussion
As of present, there is yet to be a validated and consensus treatment for COVID-19, the treatment is mainly supportive. However, the repurposed drugs with unique strengths- Chloroquine and its analogue Hydroxychloroquine as well as Quinine, from time immemorial have been largely touted as possessing an antiinflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, hence its use in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and other rheumatism [3]. As the mechanisms of action of the 4-aminoquinolines are been further elucidated, it is been believed to distort the ACE2 receptor by altering the glycan attachment thereby preventing the attachment of SARS-COV2. It is also believed to decrease the pH of the cell thereby inhibiting viral replication, altering the viral particle assemblage and stopping cytokine storm [4-6]. Researchers have even reported both prophylactic and therapeutic advantages of CQ for SARS-CoV infection [7]. However, other researchers have reported in a retrospective study with no defined administration time that no evidence in the use of Hydroxychloroquine either with or without azithromycin reduced the risk of a mechanical ventilator in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 [8,9] in an open-label non-randomized clinical trial concluded that Hydroxychloroquine showed a significant association with viral load reduction/disappearance in COVID-19 patients and its effect is reinforced by azithromycin. In a randomized controlled trial in china of 62 patients who were positive for COVID-19 and hospitalized, Chen reported that 31 patients received Hydroxychloroquine 400mg per day and the remaining 32 received a placebo, Chen concluded pneumonia improved in 81% compared to 55% control [10].
The LWI Study Protocols have undergone Hypothesis Testing among Physicians, Researchers, Pharmacists and Clinicians, with online debates on several professional health platforms. The results in this preliminary study are based on preliminary data gathered from Physician-Patient recommendations of Prophylaxis using the 4- Aminoquinolines in COVID-19 Treatment and Prophylaxis. It also recognises some self-medicating individuals who took advantage of the non-prescription remedy.
The LWI Study Protocols are currently being used in Kaduna State, Bauchi State, and some other States in Nigeria. The unique thing about the Study Protocols, the 4-Aminoquinolines offer an end to end care in COVID-19, from CQ/HCQ in Pre and Post Exposure to Mild and Moderate COVID-19 and escalating into QUININE I.V. for Critical Care in COVID-19.
Conclusion
CQ and HCQ Prophylaxis works as none of the 110 clients placed on prophylaxis has progressed into COVID-19 in 6 weeks Post- Lockdown; none of them is symptomatic.
CQ/HCQ is relevant for Ambulatory care as the Laboratory Tested Positive Healthcare Worker on Self Quarantine who was treated with CQ is fully recovered, up to 6 weeks post-lockdown with no relapse, and having tested negative twice post-treatment.
CQ/HCQ is also relevant for Inpatient care as the 11 Laboratory Tested Positive Patients placed on admission at the COVID-19 Isolation Center who were treated with CQ are all fully recovered, up to 6 weeks post-lockdown with no relapse, and having tested negative twice post-treatment.
Quinine works in advanced COVID-19 as the Single Laboratory Tested Positive client on the ventilator, has fully recovered after Treatment with I.V. Quinine and is still symptom-free 6 weeks postlockdown.
References
- Perlman S (2020) Another decade, another coronavirus. N Engl J Med 382: 760-762.
- Bai Y, Yao L, Wei T, Tian F, Jin DY, et al. (2020) Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID-19. JAMA 323: 1406-1407.
- Gordon C, Amissah-Arthur MB, Gayed M, Brown S, Bruce LN, et al. (2018) The British Society for Rheumatology guideline for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Rheumatology 57: e1-e45.
- Akpovwa H (2016) Chloroquine could be used for the treatment of filoviral infections and other viral infections that emerge or emerged from viruses requiring an acidic pH for infectivity. Cell Biochem Funct 34:191-196.
- Keyaerts E, Vijgen L, Maes P, Neyts J, Ranst MV (2004) In vitro inhibition of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus by chloroquine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323: 264-268.
- Vincent MJ, Bergeron E, Benjannet S, Â Erickson BR, Rollin PE, et al. (2005) Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread. Virol J 2: 69.
- Al-Bari MA (2015) Chloroquine analogues in drug discovery: New directions of uses, mechanisms of actions and toxic manifestations from malaria to multifarious diseases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 70: 1608-1621.
- Joseph M, Siddharth N, Felip P, Tammy C, James H, S, et al. (2020) Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19. Med.
- Gautret P, Lagier J, Parola P, Hoang V, Meddeb L, et al. (2020) Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents 56: 105949.
- Chen Z, Hu J, Zhang Z, Jiang S, Han S, et al. (2020) Efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in patients with COVID-19: Results of a randomized clinical trial. MedRxiv 18: 26.
Citation: Bright B, Ali W, Fajimi N, Adesope T, Tairu S, et al. (2020) A Preliminary Study on Various Types of 4-Aminoquinolines for Pre or Post- Exposure Prophylaxis and for Treatment in Severe Covid-19. J Community Med Health Educ 10: 690. DOI: 10.4172/2161-0711.1000690
Copyright: © 2020 Bright B, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 1947
- [From(publication date): 0-2020 - Apr 07, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1221
- PDF downloads: 726