A Case of Glucocorticoid-Induced Multifocal Osteonecrosis
Received: 21-Jan-2015 / Accepted Date: 23-Feb-2015 / Published Date: 01-Mar-2015 DOI: 10.4172/2165-7025.1000250
Keywords: Glucocorticoids; Osteonecrosis; Avascular necrosis
361000Introduction
There is a well-known relevance between the development of osteonecrosis and steroid administration. Glucocorticoid use is the most common cause of secondary osteoporosis and can lead to nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Multifocal or multiple osteonecrosis, defined by the involvement of 3 or more anatomic sites, is unusual, being observed in only 3%-10% of patients diagnosed with osteonecrosis [1]. We present a case of multifocal osteonecrosis in a woman receiving Methylprednisolone 16 mg 2×1 treatment for 10 months for symptom control of hyperthyroidism. She was investigated for knee pain, which could have been attributed to her primary disease, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed bone infarcts within the hip and shoulder. This case highlights the importance of investigating musculoskeletal pain in patients with hyperthyroidism receiving corticosteroids.
Case Presentation
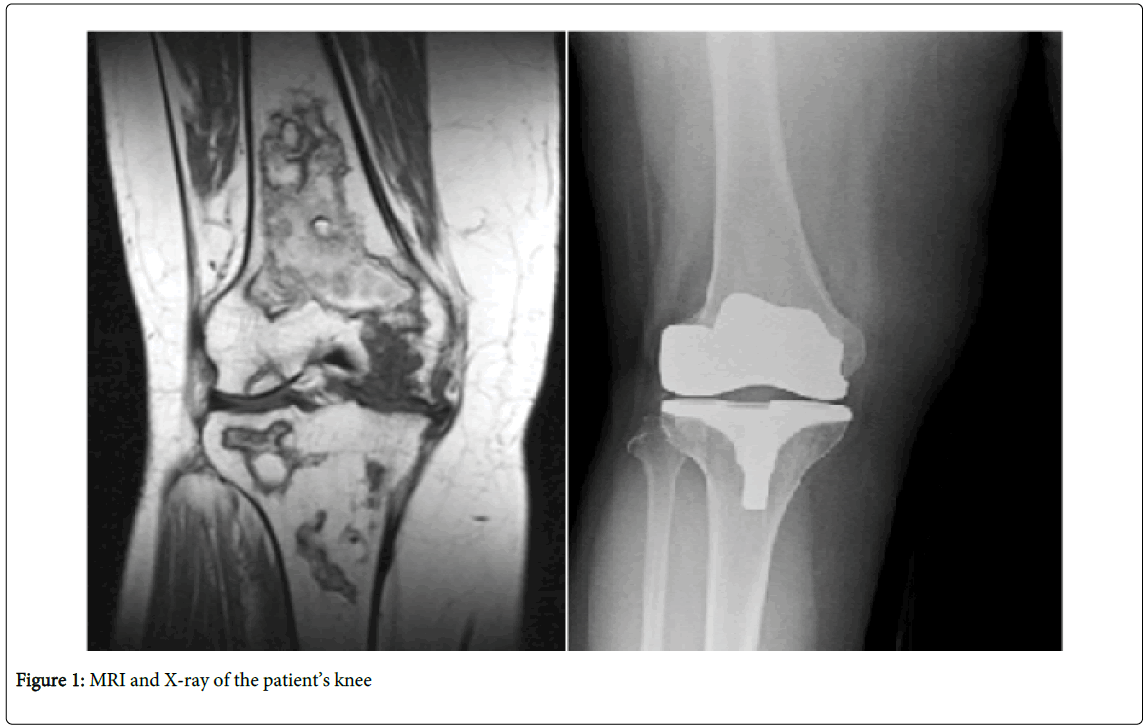
We present a 55 years-old female, who entered menopause after a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingooophorectomy eight years ago. She was diagnosed with hyperthyroidism when she was 50 and underwent total thyroidectomy three years ago. She was on Methylprednisolone 16 mg 2×1 treatment for 10 months (9 months before the surgery and 1 month after the surgery). She had an magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) because of bilateral knee pain 1 year after her thyroidectomy. Osteonecrosis was detected and knee replacement surgery was advised. The patient did not accept surgery at that time, but a year later she underwent right total knee replacement because of severe knee pain (Figure 1).
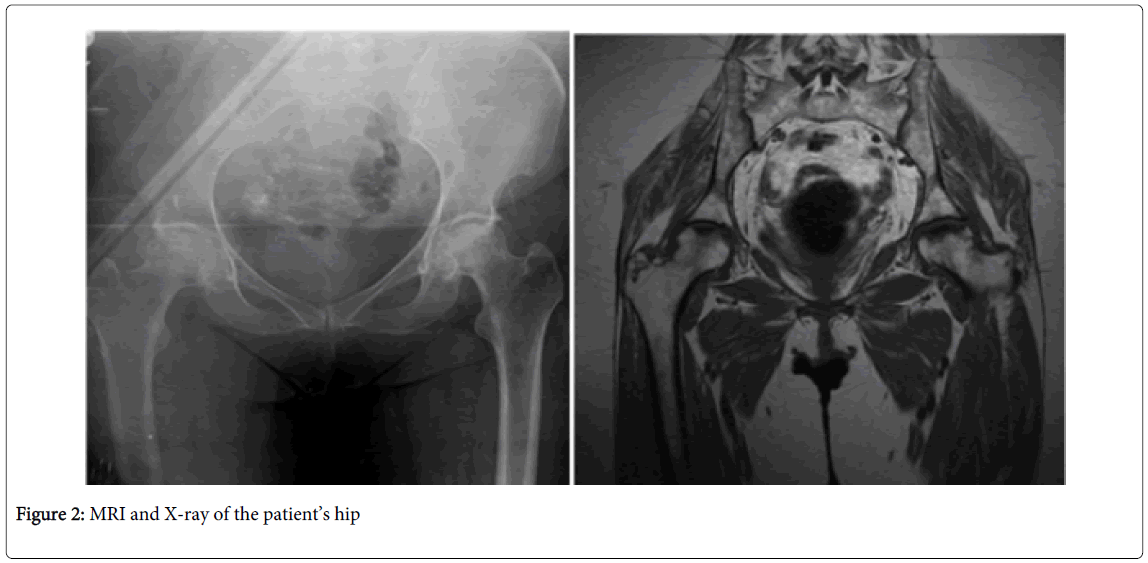
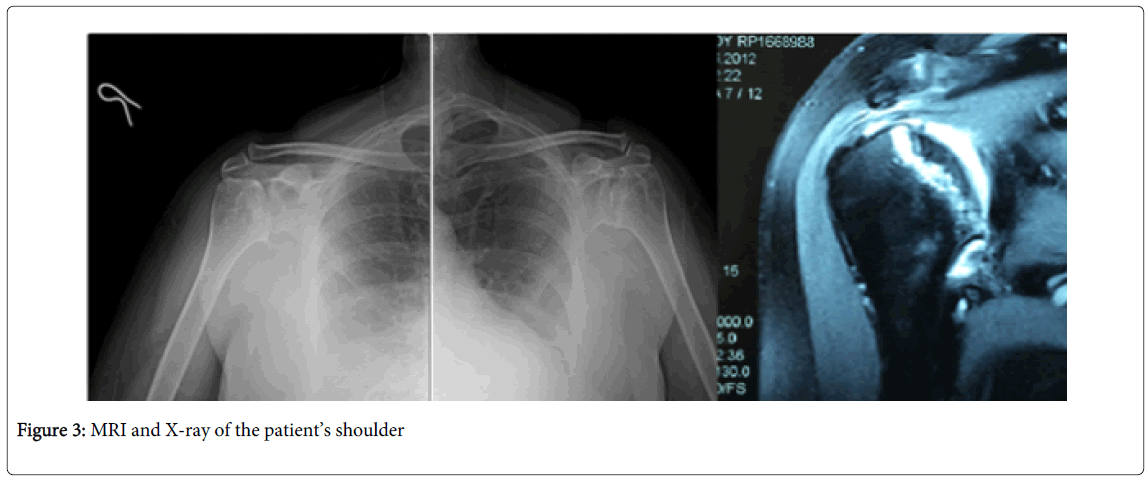
For the last 4 years she has been suffering from bilateral hip and shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. Her MRI taken before the knee replacement surgery shows osteonecrosis in both her hip and shoulder joints (Figures 2 and 3). Hip and sholder range of motion improved with physical therapy. Pain is also relieved and under control with analgesic drugs.
She is on Alendronat 70 mg treatment for osteoporosis for the last three years and her recent bone mineral density (BMD) scores are; femoral neck t score: -2.3, femoral total t score:-2.9, lumbar1-4 t score:-3.5
Discussion
Glucocorticoid use is the most common cause of secondary osteoporosis and can lead to nontraumatic osteonecrosis. In patients receiving long-term therapy, glucocorticoids may cause fractures in 30 to 50% and osteonecrosis in 9 to 40% [2,3]. The risk in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis increases with higher doses and prolonged treatment [4,5].
The exact mechanism by which glucocorticoids induce avascular necrosis is not well understood. A study suggested that glucocorticoids cause damage in venous endothelial cells, leading to stasis, decreased arterial perfusion, increased intraosseous pressure and finally, infarction of the bone [6] Glucocorticoids directly effect osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes. The adverse effects of glucocorticoids are primarily created by decreasing the production of both osteoblasts and osteoclasts and increasing the apoptosis of osteoblasts while prolonging the lifespan of osteoclasts [7-9].
Glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis mostly affects the femoral head, but it can also occur in any skeletal site such as the knee, shoulder, ankle and the hand. The most common symptom is pain, which is generally insidious in onset, and increased by activity and exercise. With time, the pain may occur at rest and affects function and range of motion of the affected joints [10].
Persistent hip, knee or shoulder pain, especially with joint movement, tenderness or decreased range of motion, needs MRI verification [4,5]. MRI is the most sensitive modality in picking up early stage of avascular necrosis [10]. The subchondral crescent sign on radiographic examination is pathognomonic for osteonecrosis but this is a late sign and MRI can show extensive osteonecrosis before any change in the shape of the femoral head or appearance of a fracture crescent [10].
At present, it is still controversial to recommend universal screening for asymptomatic AVN in long-term GC users. Physicians should have a high index of suspicion for persistent pain at typical sites after GC use. Initial treatment includes bed rest or partial weight bearing activities. There is not enough evidence to support the routine use of bisphosphonates in GC-induced AVN [11]. Nonsteroidal or other analgesics can also be used . If conservative management fails, additional therapeutic options, that include core decompression, joint replacement, and osteotomy can be used [12] Advanced stages of AVN usually requires arthroplasty. Therefore, early diagnosis is crucial in the management of AVN [11].
Bone loss in glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis is biphasic, with a relatively rapid decrease in BMD of 6–12% within the first year, and a slower annual loss of about 3% for as long as the glucocorticoids are administered [3]. However, the relative risk of fracture increases by as much as 75% within the first 3 months after initiation of glucocorticoid treatment and this usually occurs before a significant decrease in BMD. There is also a remarkable decrease in fracture risk within the first 3 months after the glucocorticoids are discontinued, well before any increase in BMD [13]. An increase in vertebral and hip fractures occurs with as little as 2.5 to 7.5 mg/day of prednisolone (equivalent to 3.1 to 9.3 mg of prednisone). In a cohort study of patients aged 18 to 64 years taking glucocorticoids for a range of disorders, the combination of higher dose, longer duration and continuous use had the biggest effect on the occurrence of fractures. Continuous treatment for more than 90 days with 10 mg/day of prednisone was associated with a 7-fold increase in hip fractures and a 17-fold increase in vertebral fractures [14].
Conclusion
Multifocal or multiple osteonecrosis, defined by the involvement of 3 or more anatomic sites, is unusual, being observed in only 3%-10% of patients diagnosed with osteonecrosis [1]. Our literature search did not reveal any cases of glucocorticoid induced multifocal osteonecrosis because of the use of steroids to control symptomatic hyperthyroidism. The relationship between steroid use and osteonecrosis and osteoporosis has been known for many years. It also has to be kept in mind that, multifocal osteonecrosis can develop even long time after cessation of steroids. Physicians should have a high index of suspicion for persistent pain at typical sites after commencement of glucocorticoids. Patients should be evaluated for steroid induced osteoporosis and osteonecrosis.
References
- Gomez-Puerta JA, Peris P, Reverter JC, Espinosa G, Martinez-Ferrer A, et al.(2013) High prevalence of prothrombotic abnormalities in multifocal osteonecrosis: description of a series and review of the literature. Medicine 92: 295-304.
- Weinstein RS (2011) Clinical practice. Glucocorticoid-induced bone disease.N Engl J Med 365: 62-70.
- Weinstein RS (2012) Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and osteonecrosis.EndocrinolMetabClin North Am 41: 595-611.
- Drescher W, Schlieper G, Floege J, Eitner F (2011) Steroid-related osteonecrosis--an update.Nephrol Dial Transplant 26: 2728-2731.
- Weinstein RS (2012) Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis.Endocrine 41: 183-190.
- Nishimura T, Matsumoto T, Nishino M, Tomita K (1997) Histopathologic study of veins in steroid treated rabbits.ClinOrthopRelat Res : 37-42.
- Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Parfitt AM, Manolagas SC (1998) Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by glucocorticoids. Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone.J Clin Invest 102: 274-282.
- O'Brien CA, Jia D, Plotkin LI, Bellido T, Powers CC, et al. (2004) Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoblasts and osteocytes to induce their apoptosis and reduce bone formation and strength.Endocrinology 145: 1835-1841.
- Jia D, O'Brien CA, Stewart SA, Manolagas SC, Weinstein RS (2006) Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoclasts to increase their life span and reduce bone density.Endocrinology 147: 5592-5599.
- Chan KL, Mok CC (2012) Glucocorticoid-induced avascular bone necrosis: diagnosis and management.Open Orthop J 6: 449-457.
- Patt H, Bandgar T, Lila A, Shah N (2013) Management issues with exogenous steroid therapy.Indian J EndocrinolMetab 17: S612-617.
- Moghadam-Kia S, Werth VP (2010) Prevention and treatment of systemic glucocorticoid side effects.Int J Dermatol 49: 239-248.
- Van Staa TP, Laan RF, Barton IP, Cohen S, Reid DM, et al. (2003) Bone density threshold and other predictors of vertebral fracture in patients receiving oral glucocorticoid therapy.Arthritis Rheum 48: 3224-3229.
- Steinbuch M, Youket TE, Cohen S (2004) Oral glucocorticoid use is associated with an increased risk of fracture.OsteoporosInt 15: 323-328.
Citation: Sahbaz T, Javadov A, Diraçoglu D (2015) A Case of Glucocorticoid-Induced Multifocal Osteonecrosis. J Nov Physiother 5:250. DOI: 10.4172/2165-7025.1000250
Copyright: © 2015 Sahbaz T, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 14541
- [From(publication date): 4-2015 - Mar 31, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 9985
- PDF downloads: 4556