Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
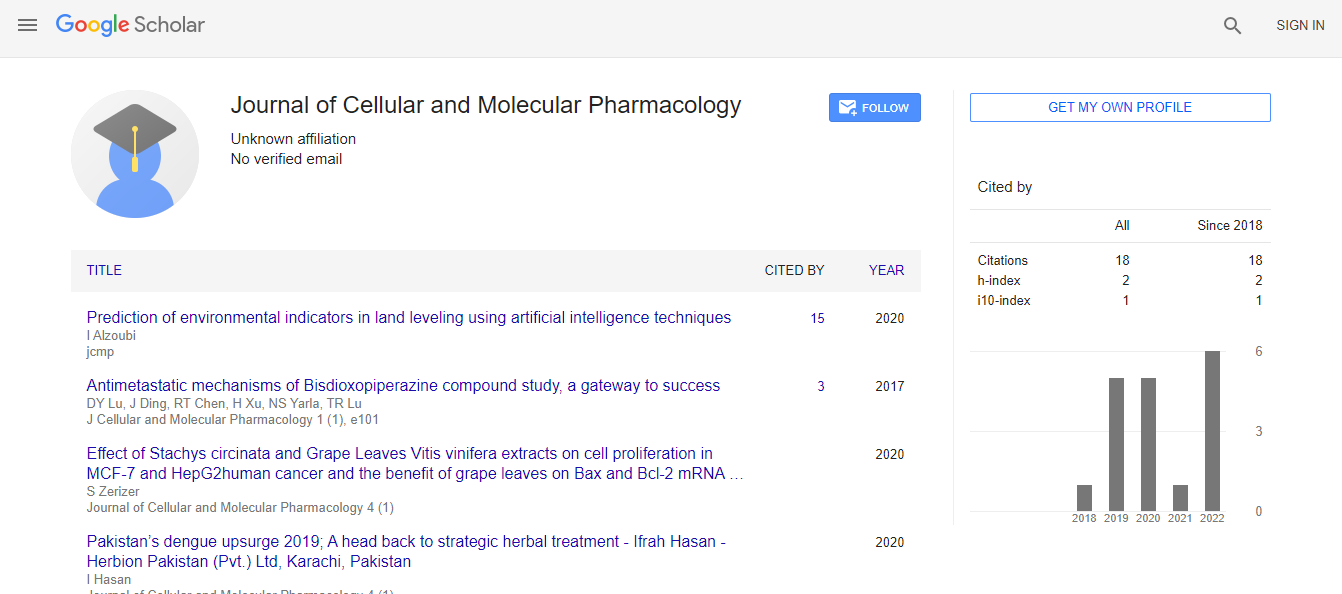
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 23
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology received 23 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Editorial Board
Submit Manuscript
Submit manuscript at or send as an e-mail attachment to the Editorial Office at pharmaj@omicsscholars.com
If you are interested in publishing with us or have any questions, please feel free to contact us directly on WhatsApp .
Table of Contents
About the Journal
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology aims to promote clinical and translational research on drug design, development and delivery that can effectively address the disorders and challenges at the cellular and molecular level, which may turn chronic if unattended at the formative stages.
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology caters to the diversified needs of pharmacists, chemists and druggists, oncologists, radiologists, immunologists, endocrinologists, and hematologists.
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology focuses on a broad spectrum of topics related to this field, including but not limited to clinical and translational research, xenobiotic metabolism, Antibiotic and Anticancer drug action, toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics, pharmacogenomics and pharmacoproteomics, radiopharmacology, pharmacological agents on gene regulation, drug design and discovery, drug metabolism, drug-drug interactions, immunopharmacology, cell signaling, transduction pathway analysis, cancer metastasis, hematopoiesis, Angiogenesis, cell differentiation, apoptosis, biomarkers, and metabonomics.
The Journal aims to publish the most reliable and complete source of information on discoveries and current developments in the form of research articles, review articles, case reports and short communication. All articles are peer reviewed and published under the guidance of our Editorial Board members on an open access platform.
Transduction pathway analysis
Signal transduction is the action by which a actinic or concrete arresting is transmitted through a corpuscle as a alternation of atomic events, a lot of frequently protein phosphorylation catalysed by protein kinases, which ultimately after-effects in a cellular responsE and aswell complex in the adjustment of abounding important cellular processes such as corpuscle survival, adverse and apoptosis. Kinase signaling networks are about characterized by assorted kinases abiding in cascades absolute nodes with acknowledgment loops, and crosstalk amid pathways. There are lot of broadly advised pathways is the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) which contains the after kinases Akt and mTOR (mammalian ambition of rapamycin). Genetic mutations consistent in aberrant activation of the PI3K are in a top amount of animal cancers. Therefore, inhibitors targeting PI3K and added apparatus in the alleyway are abeyant drugs for blight therapy.
Related Journals: Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling,Journal of Molecular Signaling,Journal of Receptor and Signal Transduction Research, Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling, Current Signal Transduction Therapy ,Current Cancer Drug Targets, Current Protocols in Stem Cell Biology, International Journal of Stem Cells,Journal of Stem Cells ,Journal of Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine, Cellular Signalling ,Journal of Receptor, Ligand and Channel Research, Drug Testing and Analysis, Journal of Cell Signaling
Preclinical and clinical drug development
In biologic development, preclinical development studies are to actuate the safe dosage for first-in-man abstraction and appraise a product's assurance profile. Products may cover new medical devices, drugs, gene analysis solutions and analytic tools. On average, alone one in every 5,000 compounds that enters biologic analysis to the date of preclinical development becomes an accustomed drug. We accept accumulated a array of solutions to advice you get through preclinical development faster and with a bigger able admixture that can bear the rigors of analytic development and analytic trials. Current actual continued and abundantly cher biologic analysis and development action is actual inefficient, with abrasion amount spanning from abounding bags of new actinic structures, through a scattering of accurate biologic leads, to individual acknowledged new biologic launches, accomplished in boilerplate afterwards 13 years, with circuitous amount estimates from hundreds of bags to over one billion US dollars
Related Journals: Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development ,Assay and Drug Development Technologies , Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development , Drug Development Research,International Journal of Drug Development and Research ,Journal of Developing Drugs , Journal of Clinical Case Reports , Journal of Clinical Trials , Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacodynamics • American Journal of Drug Discovery and Development • Current Drug Discovery Technologies , Current Drug Targets ,Drug Design, Development and Therapy, Clinical Pharmacology & Biopharmaceutics
Immunopharmacology
An allowed arrangement is a arrangement of biological structures and processes aural an animal that protects adjoin ache by anecdotic and killing bacilli and bump cells. Immunopharmacology acquired into the preclinical science of immunotherapy and, by 1979, two texts had congenital the name into their titles. They attempted to abode the accessible definitions of the acreage and included circadian nucleotide pharmacology, deepening pharmacology, immunosuppressive analysis and immunotherapy. In the aforementioned year three journals: Immunopharmacology, the account of immunopharmacology, the International Account of Immunopbarmacology were launched, establishing the aspect as a audible annex of science. International Immunopharmacology is the primary car for the advertisement of aboriginal analysis affidavit pertinent to the overlapping areas of immunology, pharmacology, cytokine biology, immunotherapy, immunopathology and immunotoxicology
Related Journals: The Journal of Interferon Research , The Journal of Immunotherapy ,The International Journal of Immunotherapy , The Journal of Immunology, Journal of Molecular Immunology , Immunochemistry & Immunopathology: Open Access , Clinical & Cellular Immunology Open Access ,Immunome Research Open Access, Journal of Immune Research , Clinical & Experimental Pharmacology Open Access , Clinical Pharmacology & Biopharmaceutics Open Access , International Journal of Immunopharmacology , Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology , International Immunopharmacology, Immunological Disorders & Immunotherapy
Drug-drug Intereactions
A Biologic alternation is an alternation amid a biologic and some added substance, such as addition biologic or an assertive blazon of food, which prevents the biologic from alive correctly. An alternation can either access or abatement the capability and/or the ancillary furnishings of a drug, or it can actualize a new ancillary aftereffect not ahead apparent afore or drug-drug alternation is a modification of the aftereffect of a biologic if administered with addition drug. The aftereffect may be an access or a abatement in the activity of either substance, or it may be an adverse aftereffect that is not commonly associated with either drug. The accurate alternation may be the aftereffect of a chemical-physical abhorrence of the two drugs or a change in the amount of assimilation or the abundance captivated in the body, the bounden adeptness of either drug, or an about-face in the adeptness of receptor sites and corpuscle membranes to bind either drug. Most adverse drug-drug interactions are either pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic in nature.
Related Journals: Side Effects of Drugs Annual, Current Drug Safety, Drug and Alcohol Dependence , Adverse Drug Reaction Bulletin ,Biopharmaceutics and Drug Disposition , Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions , Drug Target Insights ,Drug, Healthcare and Patient Safety ,Drugs in R and D , Inflammation and Allergy - Drug Targets,Journal of Drug Metabolism & Toxicology , Journal of Drug Abuse , Journal of Drugs and Toxins , Journal of Addiction Research & Therapy, Advances in Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety
Drug receptor-effective coupling
Receptors are macromolecules complex in actinic signaling and aural cells; they may be amid on the corpuscle apparent film or aural the cytoplasm, Several actinic armament may aftereffect in a acting bounden of the biologic to the receptor. About any band could be complex with the drug-receptor interaction. Covalent bonds would be actual bound and about irreversible. Since by analogue the drug-receptor alternation is reversible, covalent band accumulation is rather attenuate except in a rather baneful situation. Since abounding drugs accommodate acerbic or amine anatomic groups which are ionized at physiological pH, ionic bonds are formed by the allure of adverse accuse in the receptor site. Polar-polar interactions as in hydrogen bonding are a added addendum of the allure of adverse charges. The drug-receptor acknowledgment is about a barter of the hydrogen band amid a biologic molecule, surrounding water, and the receptor site. Finally berserk bonds are formed amid non-polar hydrocarbon groups on the biologic and those in the receptor site. These bonds are not actual specific but the interactions do action to exclude baptize molecules. Repulsive armament which abatement the adherence of the drug-receptor alternation cover abhorrence of like accuse and steric hindrance. Steric albatross refers to assertive 3-dimensional appearance area abhorrence occurs amid electron clouds, adamant actinic bonds, or beefy alkyl groups.
Related Journals: Journal of Receptor and Signal Transduction Research,Journal of Receptor, Ligand and Channel Research , Cardiovascular and Hematological Disorders - Drug Targets , Current Drug Targets , Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics, Drugs in R and D, Therapeutics, Pharmacology and Clinical Toxicology , Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ,Advances in Pharmacology , Journal of Receptor, Ligand and Channel Research ,Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Biomembranes ,Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids ,Cell Membranes and Free Radical Research , Current Protein and Peptide Science ,Protein & Cell ,Basic and clinical Pharmacology,Journal of Pharmacokinetics & Experimental Therapeutics
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly focused on treatment is one of the real modalities of restorative treatment (pharmacotherapy) for disease, others being hormonal treatment and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a type of atomic pharmaceutical, targeted therapy obstructs the development of malignancy cells by meddling with particular focused on particles required for carcinogenesis and tumor growth,[1] instead of by just meddling with all quickly separating cells (e.g. with customary chemotherapy). Since most operators for focused treatment are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic treatment is now and then synonymous with focused treatment when utilized as a part of the setting of growth treatment (and subsequently recognized from chemotherapy, that is, cytotoxic treatment). Be that as it may, the modalities can be joined; counter acting agent medicate conjugates consolidate biologic and cytotoxic components into one focused on treatment.
Related Journals: Journal of OncoTargets and Therapy, Cancer Cell, The Journal of Targeted Therapies in Cancer, Nature Reviews Cancer, Journal of Clinical Oncology ,Journal of the National Cancer Institute, Cancer Research ,Clinical Cancer Research, Seminars in Cancer Biology, Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, Chemotherapy
Biosensors
A biosensor is associate degree analytical device, used for the detection of associate degree analyse, that mixes a biological part with a chemistry detector. The sensitive biological part (e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc.) may be a biologically derived material or biomimetic part that interacts (binds or recognizes) with the analyse beneath study. The biologically sensitive components can even be created by biological engineering. The electrical device or the detector part (works during a chemistry way; optical, electricity, chemical science, etc.) transforms the signal ensuing from the interaction of the analyse with the biological part into another signal (i.e., transduces) that may be a lot of simply measured and quantified. The biosensor reader device with the associated physics or signal processors that are primarily accountable for the show of the ends up in a easy approach. This generally accounts for the foremost valuable a part of the sensing element device, but it's potential to come up with a user friendly show that has electrical device and sensitive part (holographic sensor). The readers are typically custom-designed and made to suit the various operating principles of biosensors.
Related Journals: Journal of Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research, Biosensors - Research and Reviews, Austin Journal of Biosensors & Bioelectronics ,Bioengineering Journals, Biomedical Science Journals, Biosensors Journal, Data Communication Journals, Network Sensor Journals, Biosensors Journal
Pathophysiological adaptation
Pathophysiological adaptation in cell biology and pathophysiology, cellular adaptation refers to changes made by a cell in response to adverse environmental changes. The adaptation may be physiological (normal) or pathological (abnormal). Type of adaptations included is atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, dysplasia, and metaplasia.
Related Journals: International Journal of Cell Biology , Journal of Cellular & Molecular Pathology, The Journal of Physiology , Developmental Cell, Trends in Biochemical Sciences, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, Perspectives in Cancer Research , Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, Virus Adaptation and Treatment, Motricite Cerebrale Readaptation Neurologie du Developpement, Journal of Thrombosis and Circulation
Metabolomics of Drug Action
Metabolomics is that the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites. Specifically, metabolomics is that the "systematic study of the distinctive chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule matter profiles. The metabolome represents the gathering of all metabolites in an exceedingly biological cell, tissue, organ or organism, that area unit the tip merchandise of cellular processes. The action of medicine on the physical body is named pharmacodynamics, and what the body will with the drug is named materia medica. The medications that enter the human tend to stimulate sure receptors, particle channels, act on enzymes or transporter proteins. As a result, they cause the physical body to react in an exceedingly specific method. Metabolites of foreign substances like medication area unit termed xenometabolites.
Related Journals: Adverse Drug Reactions and Toxicological Reviews, Adverse Drug Reaction Bulletin, Letters in Drug Design and Discovery, Recent Patents on CNS Drug Discovery, Recent Patents on Endocrine, Metabolic and Immune Drug Discovery, Side Effects of Drugs Annual ,Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, Journal of Drug Metabolism & Toxicology , Advances in Pharmacoepidemiology & Drug Safety , Journal of Developing Drugs, Journal of Pharmaceutics & Drug Delivery Research, Advances in Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety
Experimental therapeutics
Experimental therapeutics is the development of treatment strategies to give more accurate and effective treatment to human disease with less toxicity. Research in experimental therapeutics integrates assorted disciplines in adjustment to understand the disease from the molecular to organismal levels and again strives to administer this ability to analyse and validate targets, ascertain and advance interventions or drugs to dispense these targets, and ultimately drive preclinical and analytic studies to reach the goal of personalized medicine.
Related Journals: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Pharmacology & Therapeutics , Clinical Therapeutics , American Journal of Therapeutics, Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics , Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics, Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics , American Journal of Therapeutics, International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics
Chemotherapy of intracellular infection
The viability of the chemotherapy of intracellular infection relies upon a viable participation between the antibodies and the host. Antibiotics must not just infiltrate inside the cells and target the infected cell parts, additionally express their action in the relating environment. Macrophages and non-phagocytic cells help in the intracellular pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, their efficacy against intracellular pathogens. The topics related to Chemotherapy of intracellular infection are clinical toxicology, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, drug interactions, and indications for chemotherapy of intracellular infection.
Related journal: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, Chemotherapy ,Antiviral Chemistry and Chemotherapy, Journal of Chemotherapy, Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, Supplement , Japanese Journal of Cancer and Chemotherapy, Biotherapy, Cancer chemotherapy and biological response modifiers , Japanese Journal of Chemotherapy, Antiviral Chemistry and Chemotherapy, Supplement, Infection and Chemotherapy ,Antibiotics and chemotherapy, Anti-infective Drugs and Chemotherapy, Chinese Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Translational Research
Translational research helps in finding out the basic science to enhance human health and well-being. In a medical research context, it aims to "translate" findings in fundamental research into medical practice and meaningful health outcomes. Translational research implements a "bench-to-bedside", from laboratory experiments through clinical trials to point-of-care patient applications, model, harnessing knowledge from basic sciences to produce new drugs, devices, and treatment options for patients. The translational research point of interest is to produce promising new treatment that can be used with practical applications, that can then be used clinically or are able to be commercialized.
Related Journals: American Journal of Translational Research, Applied and Translational Genomics
Anticancer Drug Action
The available anticancer drugs have distinctly different mechanisms of ac tion which may vary at different drug concentrations and in their effects on different types of normal and neoplas tic cells. While not selectively lethal to cancer cells, as such, in many instances these drugs produce more extensive injury and death to certain neoplastic cells than to the normal tissues, pre sumably because of quantitatively al tered metabolic processes in the cancer cell. These selective anticancer effects, thus far, are difficult to anticipate in the individual patient, or to define in terms of demonstrable biochemical dif ferences in the cancer cells. In the great majority of cases, also, initially responsive cancers recur in a form re sistant to the previously effective agent. Despite the many unsolved problems, there is a great deal of in formation on how anticancer drugs act at the cellular level to inhibit the growth of, or to destroy, susceptible cells.
Related journals- Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs, Chemical Research in Toxicology, Anti-cancer Drugs, Journal of Cancer therapy, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Journal of Nutrition, Cancer Treatment Reports, Coordination Chemistry Reviews
Translational Research
Translational research helps in finding out the basic science to enhance human health and well-being. In a medical research context, it aims to "translate" findings in fundamental research into medical practice and meaningful health outcomes. Translational research implements a "bench-to-bedside", from laboratory experiments through clinical trials to point-of-care patient applications, model, harnessing knowledge from basic sciences to produce new drugs, devices, and treatment options for patients. The translational research point of interest is to produce promising new treatment that can be used with practical applications, that can then be used clinically or are able to be commercialized.
Related Journals: American Journal of Translational Research, Applied and Translational Genomics, Clinical and Translational Oncology, Clinical and Translational Science, Drug Delivery and Translational Research, Experimental and Translational Stroke Medicine, Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, Journal of Experimental Stroke and Translational Medicine, Journal of Translational Medicine, Stem cells translational medicine
Structure-Based Drug Design
Structure-based drug design is the design and optimization of a chemical structure with the goal of identifying a compound suitable for clinical testing — a drug candidate. It is based on knowledge of the drug’s three-dimensional structure and how its shape and charge cause it to interact with its biological target, ultimately eliciting a medical effect. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a bio molecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. Drug design or rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. Drug design involves the design of small molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the bio molecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Related Journals: Chemical Biology and Drug Design, Current Computer-Aided Drug Design, Drug Design, Development and Therapy, International Journal of Computational Biology and Drug Design, Letters in Drug Design and Discovery, Current Drug Delivery, Current Drug Discovery Technologies, Current Drug Metabolism 9. Current Drug Safety
Drug Metabolism
To eliminated the pharmaceutical substances from the body in a more easier biotransformation takes place and this entire process is called Drug metabolism.The majority of metabolic processes that involve drugs occur in the liver, as the enzymes that facilitate the reactions are concentrated there. The purpose of metabolism in the body is usually to change the chemical structure of the substance, to increase the ease with which it can be excreted from the body.
Drugs metabolism involves various reactions such as Oxidation, Reduction, Hydrolysis, Hydration, Conjugation, Condensation, Isomerization.
Related Journals: Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms, Drug Discovery Today: Disease Models, Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies, Drug Discovery World, Drug Invention Today, Drug Metabolism and Disposition, Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions, Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics, Drug Metabolism Letters.
Toxicokinetics And Toxicodynamics
Pharmacokinetics helps to determine the relationship between the systemic exposure of a compound in experimental animals and its toxicity. It is used in environmental risk assessments in order to determine the potential effects of releasing chemicals into the environment. It can be used to establishing relationships between exposures in toxicology experiments in animals and the corresponding exposures in humans. Toxicodynamics, termed pharmacodynamics in pharmacology, describes the dynamic interactions of a toxicant with a biological target and its biological effects.
Related Journals: Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics, European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, International Journal of Chemical Kinetics, Isokinetics and Exercise Science, Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, Review of Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics, International Edition, Cognitive Neurodynamics, Developmental Dynamics
Xenobiotic Metabolism
The principal classes of xenobiotics of medical relevance are drugs, chemical carcinogens, naturally occurring compounds in plant foods, and various compounds that have found their way into our environment by one route or another, such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), insecticides and other pesticides. Metabolism of xenobiotics include two phases:
- Phase 1, e.g, hydroxylation. the major reaction involved is hydroxylation, catalyzed by members of a class of enzymes referred to as monooxygenases or cytochrome P450s isoforms .
The other reaction include reduction and hydrolysis, which perform by same enzymes species.
- Phase 2, conjugation (e.g. glucronic acid). the hydroxylated or other compounds produced in phase 1 are converted by specific enzymes to various polar metabolites by conjugation with glucuronic acid, sulfate, acetate, glutathione, or certain amino acids, or by methylation.
overall purpose of the two phases of metabolism of xenobiotics is to increase their water solubility (polarity) and thus excretion from the body.
Related journals- Journal of Chemical Education, Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, Journal of Cheminformatics, Toxicological Sciences, Food and Chemical Toxicology, Hepatology, Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, Chemical sciences, Chemical Research in Toxicology, Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapautics, Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, Cancer Research, Pharmacogenetics and Genomics.
Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacoproteomics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of how genes affect a person’s response to drugs. This relatively new field combines pharmacology (the science of drugs) and genomics (the study of genes and their functions) to develop effective, safe medications and doses that will be tailored to a person’s genetic makeup. Pharmacogenomics allows us to identify sources of an individual’s profile of drug response and predict the best possible treatment option for this individual. The use of genomic information has opened new possibilities in drug discovery and development. Pharmacoproteomics is the use of proteomic technologies in drug discovery and development. Along with pharmacogenomics and pharmacogenetics, pharmacoproteomics will play an important role in the development of personalized medicines in several ways. Proteomic technologies are contributing to molecular diagnostics, which is a basis of personalized medicine. Pharmacoproteomics is a more functional representation of patient-to-patient variation than that provided by genotyping.
Related Journals: Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, Applied and Translational Genomics, BMC Genomics, BMC Medical Genomics, Cancer Genomics and Proteomics, Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, Current Chemical Genomics, Current Genomics, Current Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine
Bio-medicine Development
Biomedicine has createed a boom today and is hyped to create the futuristic and more precise health solutions in the coming years? After the US, the Europeans too have shown keen interest in this field and have invested hugely in research in this field. The major interest is to evolve better cures for genetic disorders, gerontology and multiple sclerosis amongst the rest. Biomedicine has been evolving since the last 100 years and the last 2 decades have seen its popularity rate doubled. The major difference between the existing branches of medicine and biomedicine is that whereas the present branches work more on practical applications, biomedicine derives its solution through research and theoretical approach. This branch relies more on theory, keen observations and studying the history of the disease, the medicines recommended, their effectiveness and finally the result. This mode of research is the spine of biomedicine from where evolves the most natural and effective solution.
Related journals- Molecular Cell, Nucleic acids research, Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, Journal of Biomedical Informatics, Reproductive BioMedicine Online, The new England journal of Medicine, Journal of Animal science, Journal of Biomedical Science, Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal, Biomedical Sciences, Biochemical Engineering Journal, Biochemical Medicine, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, Biochemical Medicine and Metabolic Biology.
Cytotoxicity Assays
Cytotoxicity Assays are experimental techniques used to evaluate the toxicity of substances on cells. These assays measure the extent to which a chemical, drug, or other agent can damage or kill cells.
Common methods include assessing cell viability, proliferation, and morphology. By analyzing parameters such as cell membrane integrity, metabolic activity, and apoptotic or necrotic cell death.
Nanoparticle Drug Delivery
Nanoparticle Drug Delivery involves using nanoscale particles to transport and release therapeutic agents precisely to targeted sites within the body.
These nanoparticles, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers in size, can be engineered to improve the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of drugs. They can also be designed to release their payload in a controlled manner, enhancing the efficacy of treatments while minimizing side effects.
Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Molecular Dynamics Simulations are computational techniques used to study the movement and interactions of molecules over time.
By applying the principles of classical mechanics, these simulations model the behavior of atoms and molecules in a system, allowing researchers to observe dynamic processes at the atomic level.
Biotransformation
Biotransformation is the process by which living organisms, particularly enzymes in the liver, chemically alter substances, including drugs, toxins, and endogenous compounds.
This transformation typically involves converting lipophilic compounds into more hydrophilic metabolites to facilitate their excretion from the body. Biotransformation encompasses two main phases: Phase I reactions and Phase II reactions.
Cellular Homeostasis
Cellular Homeostasis is the process by which cells maintain a stable internal environment, essential for their survival and function.
This balance is achieved through tightly regulated mechanisms that control factors like pH, ion concentrations, temperature, and nutrient availability. Cellular homeostasis involves various cellular processes, including metabolism, signal transduction, and transport across cell membranes.
Journal Highlights
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.
Recently Published Articles
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in ATLL: from Basic Biology to Preclinical Study
Jalal naghinezhad -
Exploring the Role of Protein Biomarkers in Traumatic Brain Injury: Preclinical and Clinical Highlights
Khadga Raj, Riya Dogra, Vir Vikram and Shamsher Singh -
CSBC 2018: The logic of bioactive small molecules: Looking for new drugs for refractory diseases- Makoto Ubukata- Hokkaido University, Japan
Makoto Ubukata -
Bioinformatics 2018: Modeling and dynamics studies of cytochrome bd oxidase in staphylococcus aureus & escherichia coli- Camina Jhonser- Suntech Business Solutions Limited, UAE
Camina Jhonser -
Pharmaconference 2018 : In vitro regenerative function of Silymarin in preparation of hematopoietic progenitor cells - Minoo Shahidi - Iran University of Medical Sciences
Asma Irshad -
Pharmaconference 2018: In vitro antimicrobial analysis of Green Matrix Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles- Asma Irshad- University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Faisalabad-Pakistan
Asma Irshad

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi