HIV Testing Among Californians Aged 50-64, 2010
Received: 07-Apr-2013 / Accepted Date: 23-Jul-2013 / Published Date: 26-Jul-2013 DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000129
Abstract
Testing is critical for the prevention and care for the spread of HIV-1 among older adults, aged 50-64. The overarching goal of the research question was to determine some of the reasons adults age 50 and older were not routinely tested for HIV in California in 2010. Secondary data analysis directed from the 2010 edition of the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) formed the basis for this project. The surveyed 5,544 adult populations were between ages 50-64 years living in California who completed the core module. The risk and demographic characteristics of the age 50-64 population were obtained from the survey. Data analysis examined whether adults age 50 and older were ever tested for HIV in California. SAS 9.3 statistical software was used for categorical data, by chi-square tests. In addition, geospatial representation of the population of interest and adjusted/multiple logistic regression analyses were performed and how this varies by several demographic and other risk factors/covariates. The outcome of interest, ever tested for HIV group, contained ~30% of the sample of ages 50-64 years. The likelihood of ever tested for HIV was greater for: (a) females (OR=1.82; 95%CI=1.71-1.93) as compared to Males; (b) Attended College (OR=1.58; 95%CI=1.15- 2.16) and Graduated College (OR=1.83; 95%CI=1.33-2.51) compared to attended high school (c) Black, non-Hispanic (OR=1.85; 95%CI=1.33-2.59) compared to White, non-Hispanic; (d) Less than $15,000 (OR=1.78; 95%CI=1.39-2.29) and $25,000-$35,000 (OR=1.37; 95%CI=1.03-1.82) and (e) Low risk groups (OR=3.58; 95%CI=2.05-6.25) compared to high risk groups. The likelihood of ever tested for HIV group was less likely to: Hispanics (OR=0. 61; 95%CI: 0.45-0.82). Currently there is a growing need for continual analysis, appropriate health education and health promotion efforts to increase HIV testing and to promote disease prevention among 50-64 years adults; a group that perceive themselves as low-risk for HIV infection in California.
Keywords: HIV; Age 50-64; California
160393Abbreviations
PDLWHA: Persons Diagnosed and Living With HIV/AIDS; BRFSS: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System; NABS: National AIDS Behavioral Surveys; HBM: Health Belief Model
Introduction
Testing for HIV is primarily aimed for those persons diagnosed and living with HIV/AIDS (PDLWHA), aged 25 to 44 years old. Consequently, prevention strategies and testing marketed younger populations, in spite of 10% of AIDS cases occurred among persons aged 50 and older [1]. As of 2005, the proportions of AIDS diagnosed in those 50 and older had increased to 19.2% [2]. Testing of HIV among those aged 50-64 years has developed into major public health precedence in California.
Undiagnosed HIV infection or deferral in testing for HIV has severe health implications among those 50 and older. These HIVrelated health implications, among individuals 50 and older, are due to the difficulty of assessment, diagnosis, and death [1,3]. Absence of health coverage further confounds the HIV epidemic, mostly in areas where proportions of HIV/AIDS infection are higher among older adults. California adult population (19-64 years) is ranked second highest for cumulative AIDS diagnosis in the United States and 26% of adults are uninsured [4].
The amplified HIV incidence amongst those 50-64 are stigma and discrimination that discourages health-seeking behaviour, inadequate condom use, inability to communicate diagnoses to possible sexual associates, and lack of knowledge about HIV/AIDS [5]. Also, older adults considered HIV as a concern for younger adults among clinicians, HIV/AIDS assessment is less reserved for adults age 50 and older despite routine testing guidelines and clinical presentation. In addition, one-third of those who died, occurred within was within 90 days of HIV testing [2]. If earlier testing for HIV among these elderly had occurred, disease trajectory may have been different particularly since newly diagnosed HIV infection progression to AIDS occurs most rapidly in the elderly when compared to those younger.
Based on data collected by National AIDS Behavioural Surveys, adults of ages 50-75 years reported sexual behaviour as the highest risk for exposure, blood transfusions as the lowest, and no condom use at 92% during anal or vaginal sex [6]. Additionally, older adults were least likely to get tested and delayed diagnosis of HIV disease due to lack of knowledge of partners’ risk behaviours, delayed reporting of symptoms and low income [7].
The theoretical framework of the Health Belief Model (HBM) is a reference for why those ages 50-64 are at increased risk for contracting HIV/AIDS. According to the HBM, personal belief and perception influence one’s behaviour to protect their health. If there is a perception of seriousness, susceptibility, benefits of protecting one’s health and no barriers to do so one is more likely to be motivated and incorporate positive behaviours and self-efficacy [8].
The purpose of this research is to address the needs of adults 50-64 for HIV testing. In 1993, the HIV guidelines were updated to include vital care, hospitals, and clinics in promoting standard HIV care during health preventions. This practice would potentially increase consciousness of safer sex practices, risk behaviours, and reduction of HIV testing obstacles among ages 50-64 [7]. Nonetheless, the amount of HIV screening for those ages 50 and older is of limited proportion in California. The main hypothesis is that adults age 50 and older are not routinely tested for HIV in California.
Methods
The Behavioural Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) formed the basis for this project. The weighted cross-sectional phone assessment design is currently used in BRFSS dataset was an assembled survey with more than 300 optional, core, and derived fields for individuals who resided in the 50 states and territories [9]. The exact core questions the team used consisted of health insurance, HIV/AIDS risks, and demographic variables [9]. From this data set, inhabitants in the state of California and ages 50-64 were used. The HIV test offering was the outcome of interest.
Sample and Data Collection
The surveyed adult populations were between ages 50-64 years living in California who completed the core module. This population was chosen because the question from the codebook only collected data up to the age of 64. Eligibility criteria excluded locations, such as skilled nursing institutions, military housing, hospitals, college dorms, and correctional facilities.
The risk and demographic characteristics of the age 50-64 population were obtained from the BRFSS survey. The outcome of interest and exposure were derived from adults aged 50-64 that had been tested at some point in their history for HIV, recoded to account for small cell counts in the sub-groups. The BRFSS questions used were health insurance coverage, participants’ sex, race/ethnicity, education, and risk of HIV. In addition, the survey used weights that were generalized to the general population. The BRFSS random telephone survey offered a rich source of information in that it reported data for 2010 to develop a probability sample of homes with telephones in each state [10].
Data Analyses
The 2010 BRFSS dataset was analyzed with SAS 9.3. The data set was generalized and corrected for non-response using statistical weights [9]. Therefore, the resulting dataset was used to conduct this quantitative analysis in addressing some of the descriptive reasons; adults age 50 and older are not routinely tested for HIV in California. The sample size of the data set of participants of ages 50-64 in California was 5,554. The SAS 9.3 was used because of the software’s ability to support statistical analyses for categorical data, using Chi-Square (χ2) Test Statistics. In addition, geospatial representation of the population of interest and weighted adjusted/multiple logistic regression analyses was performed and how this varied by several demographic and other risk factors.
Results
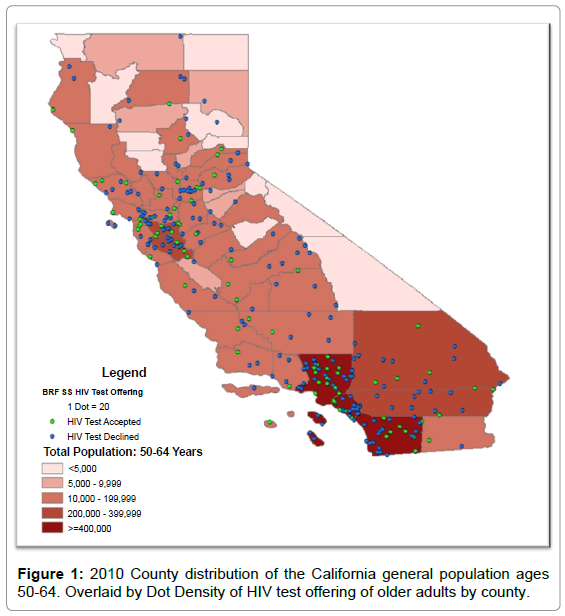
In 2010, 17,778 individuals aged 18-99 years were residents of the state of California. From that sample from California (as shown in Figure 1), 5,544 adults, identified as those tested for HIV, aged 50-64 years responded to the BRFSS survey. The outcome of interest, ever tested for HIV group, contained ~30% of the sample of ages 50-64 years. Table 1 shows, the Chi-square test results of comparisons of subcohorts of those with and without the outcome of interest, HIV testing, revealed the “ever tested for HIV group” had significant values of all variables but health insurance. The ever tested group had the following characteristics: (a) female (55%); (b) completed a college degree or higher (48%), had some college (28%), completed high school (14%), or did not complete high school (9%); (c) White, non-Hispanic (71%), Hispanic (16%), Unknown (8%), and Black, non-Hispanic (6%); (d) Higher income levels (~58%) and (e) Low risk groups (97%). The findings from Table 1 and 2 show there were significant differences in the distribution of HIV tests by sex, education, race/ethnicity, income, and HIV risk groups.
| Characteristics | HIV/AIDS Tested | Not Tested | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percent | Number | Percent | P value | ||
| Total | 1657 | 100 | 3887 | 100 | ||
| Income Group | Less than $15,000 | 301 | 18 | 493 | 13 | |
| $15,000-$25,000 | 174 | 11 | 401 | 10 | ||
| $25,000-$35,000 | 147 | 9 | 294 | 8 | ||
| $35,000-$50,000 | 140 | 8 | 399 | 10 | ||
| $50,000 or more. | 833 | 50 | 1993 | 51 | ||
| Unknown | 62 | 4 | 307 | 8 | <.0001 | |
| Insurance | Health Insurance | 1464 | 88 | 3411 | 88 | |
| No Health Insurance | 193 | 12 | 476 | 12 | 0.5312 | |
| HIV Risk | High Risk | 55 | 3 | 28 | 1 | |
| Low Risk | 1602 | 97 | 3859 | 99 | <.0001 | |
| Race/Ethnicity | White, Non-Hispanic | 1169 | 71 | 2704 | 70 | |
| Black, Non-Hispanic | 96 | 6 | 113 | 3 | ||
| Hispanic | 266 | 16 | 720 | 18 | ||
| Other/Unknown | 126 | 8 | 350 | 9 | <.0001 | |
| Sex/Gender | Male | 743 | 45 | 1523 | 39 | |
| Female | 914 | 55 | 2364 | 61 | <.0001 | |
| Education | Less than High school | 152 | 9 | 402 | 10 | |
| High School Graduate | 224 | 13 | 760 | 20 | ||
| Some College | 374 | 28 | 1055 | 27 | ||
| College Graduate | 802 | 48 | 1670 | 43 | <.0001 | |
Table 1: Characteristics of HIV testing status of persons living in California and have of an current age 50 or above, (n=5,544), 2010.
| HIV/AIDS Tested | Not Tested | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | N=1657 | N=3887 | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | |||
| Sex/Gender | |||||||
| Male | 743 | 45% | 1523 | 39% | 1.00 | ||
| Female | 914 | 55% | 2367 | 61% | 1.19 | 1.03 | 1.38 |
| Education Level | |||||||
| Attended High School | 152 | 9% | 402 | 10% | 1.00 | ||
| Graduated High School | 224 | 14% | 760 | 20% | 0.92 | 0.66 | 1.28 |
| Attended College | 479 | 29% | 1055 | 27% | 1.58 | 1.15 | 2.16 |
| Graduated College | 807 | 49% | 1670 | 43% | 1.83 | 1.33 | 2.51 |
| Race/Ethnicity | |||||||
| White. Non-Hispanic | 1169 | 71% | 2704 | 70% | 1.00 | ||
| Black, Non-Hispanic | 96 | 6% | 113 | 3% | 1.85 | 1.33 | 2.59 |
| Hispanic | 87 | 5% | 270 | 7% | 0.61 | 0.45 | 0.82 |
| All other Races | 305 | 18% | 800 | 21% | 1.01 | 0.83 | 1.24 |
| Income Groups | |||||||
| $50,000 or more | 833 | 50% | 1993 | 51% | 1.00 | ||
| Less than $15,000 | 301 | 18% | 493 | 13% | 1.78 | 1.39 | 2.29 |
| $15,000-$25,000 | 236 | 14% | 708 | 18% | 0.93 | 0.75 | 1.17 |
| $25,000-$35,000 | 147 | 9% | 294 | 8% | 1.37 | 1.03 | 1.82 |
| $35,000-$50,000 | 140 | 8% | 399 | 10% | 0.95 | 0.72 | 1.26 |
| High Risk of HIV/AIDS | |||||||
| Yes | 55 | 3% | 28 | 1% | 1.00 | ||
| No | 1602 | 97% | 3859 | 99% | 3.58 | 2.05 | 6.25 |
Table 2: Weighted Logistic Region Table of HIV/AIDS in California, 2010.
The likelihood of ever tested for HIV was greater for: (a) females (OR=1.82; 95%CI=1.71-1.93) as compared to Males; (b) Attended College (OR=1.58; 95%CI=1.15-2.16) and Graduated College (OR=1.83; 95%CI=1.33-2.51) compared to attended high school (c) Black, non-Hispanic (OR=1.85; 95%CI=1.33-2.59) compared to White, non-Hispanic; (d) Less than $15,000 (OR=1.78; 95%CI=1.39-2.29) and $25,000-$35,000 (OR=1.37; 95%CI=1.03-1.82) and (e) Low risk groups (OR=3.58; 95%CI=2.05-6.25) compared to high risk groups. The likelihood of ever tested for HIV group was less likely to: Hispanics (OR=0. 61; 95%CI: 0.45-0.82).
Discussion
From our research of the 2010 BRFSS data set, it was determined that roughly 30% of the population in California that admitted to HIV testing was adults aged 50-64. This is consistent with extrapolated finding with 18-49 years old adults, where nearly 40% (25% men and 15% women) were sexually active and expected to transmit HIV, yet are not tested [10]. Most individuals (84%) who reported no recent HIV test perceived the risk as low or none [10] this is consistent with our data in that only 3% of people perceived as high risk are actually HIV tested. In addition, the amount of older adults living in California who tested for HIV was 55% female. The findings were also consistent with Emlet and Farkas in that older adults living in California who are tested for HIV are more likely to be female than male [3].
There are several limitations in this study that are addressed. First, the targeted audience for the BFRSS is households with landline telephones, excluding those households that only had a cell phone [9]. This presented an expected bias in data collection [10]. Another limitation in the data analysis was that the questions in the survey tool tended to capture nominal data that were qualitative in nature. When this situation occurs, it becomes highly possible for people not to report accurately on very specific questions, such as HIV risk, which has a reported frequency of 1% [9]. A final limitation it that there might be some people who do not want to be interviewed, limiting the sample size.
In conclusion, future research needs to disclose the seriousness of health implications for those older than 50 when risks are not acknowledged or not investigated due to unawareness, an oversight or limited access. Finally, increased awareness of sexual activity risk behaviours among the 50 and older population are necessary to target the misperceptions and lack of knowledge for older adults.
References
- Mack K, Bland S (1999) HIV testing behaviors and attitudes regarding HIV/AIDS of adults aged 50-64. Gerontologist 39: 687-694.
- Longo B, Camoni L, Boros S, Suligoi B (2008) Increasing proportion of AIDS diagnoses among older adults in Italy. AIDS patient care STDS22: 365-371.
- Emlet CA, Farkas KJ (2001) A descriptive analysis of older adults with HIV/AIDS in California. Health Soc Work 26: 226-234.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2008) Persons aged 50 and older.
- Stall R, Catania J (1994) AIDS risk behaviors among late middle aged and elderly Americans: The national AIDS behavior surveys. Arch Intern Med 154: 57-63.
- Bassett IV, Walensky RP (2010) Integrating HIV screenings into routine health care in resource limited settings.Clin Infect Dis 50: S77-S84.
- Painter JE, Borba CP, Hynes M, Mays D, Glanz K (2008) The use of theory in health behavior research from 2000 to 2005: A systemic review. Ann Behav Med 35: 358-362.
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (2011) Behavioral risk factor surveillance system [Data file and code book].
- Takahashi TA, Johnson KM, Bradley KA (2005) A population-based study of HIV testing practices and perceptions in 4 U.S. states. J Gen Intern Med 20: 618-622.
Citation: Geyer N, Parham M, Wallace LS, Washington W Jr (2013) HIV Testing Among Californians Aged 50-64, 2010. Epidemiol 3:129. DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000129
Copyright: © 2013 Geyer N, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 15247
- [From(publication date): 8-2013 - Oct 08, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 10477
- PDF downloads: 4770