 |
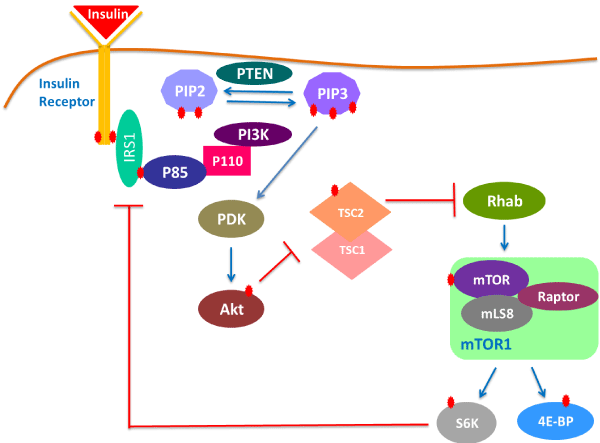
| Figure 3: Insulin signalling activate mTOR/PI3K pathway. Insulin and insulin like growth factor corroborating with insulin receptor that will phosphorylate insulin receptor substrate IRS1. In turn IRS1 corporate with p85 and p110 to activate the PI3K. Once the PI3K has phosphorylated, the 4,5-phosphatidylinositolbiphosphate (PIP2) produces phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3), which plays a role in the activation of PDK. PDK in turn activates the pathway in phosphorylating Akt that plays a critical role in inhibiting TSC1/TSC2 which inhibits Rheb. By this mechanism Rheb is now active and can activate mTOR1. MTOR1 which will activate the 4EBP1 and S6K. Negative regulation of the pathway is by PTEN and TSC1/ TSC2. PETN negatively regulates the 4,5-biphosphate (PIP2) and produces phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) while, TSC1/TSC2 regulates the Rheb mechanism. In addition the negative regulator for this pathway is also mediated by S6K which can block the insulin signalling by inhibiting the IRS [16]. |