 |
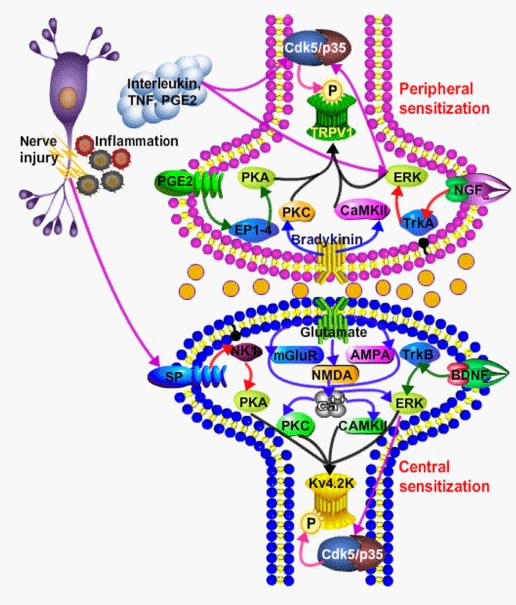
| Figure 2: Molecular involvement of Cdk5/p35 during pain signaling: At the site of tissue injury immune cells get activated and release inflammatory soup which includes but not limited to interleukins, TNF PGE2, and NGF. These cytokines activate receptors on nociceptor terminals including TNFR, NGFR (TrkA) and PGE2 leading to the activation of other kinases such as PKA, PKC, CaMK-II, ERK. This process leads to further activation of Cdk5/p35. Activated Cdk5 leads to phosphorylation of TRPV1 and activates TRPV1 ion channel, causing peripheral sensitization. The central sensitization occurs indirectly via release of glutamate and/or neurotrophins from peripheral neurons or directly by the release of the substance P. Overall this process leads to the activation of NMDA, AMPA, mGluR and TrkB receptors by corresponding ligands and further activating downstream kinases such as PKA, PKC, CaMK-II, ERK. This process further activates the Cdk5/p35 in postsynaptic dorsal horn neurons which modulates the activity of other ion channels by their by posttranslational modification. |