 |
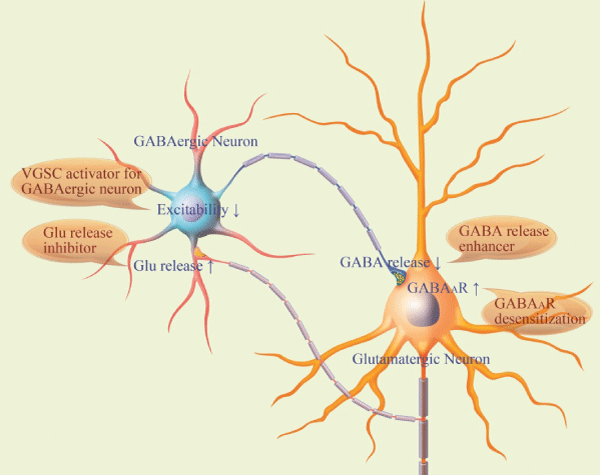
| Figure 2: Pathophysiology in prelimbic cortical GABAergic and glutamatergic cells from depression mice and therapeutic strategies. The excitability of GABAergic neurons and the release of their axonal GABA decrease. Their reception from glutamate (Glu) release and innervation from glutamatergic neurons rise. The incompatibility among the subcellular compartments of GABAergic neurons reduces their efficiency to coordinate their downstream nerve cells. In glutamatergic neurons, their responses to GABAergic input increase. These alternations impair the interaction between GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. The therapeutic strategies stated in shadow symbols will be to reduce Glu release from excitatory neuron and GABAAR responsiveness in excitatory neuron as well as to elevate GABA release from inhibitory neuron and voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) activity in inhibitory neuron. |