 |
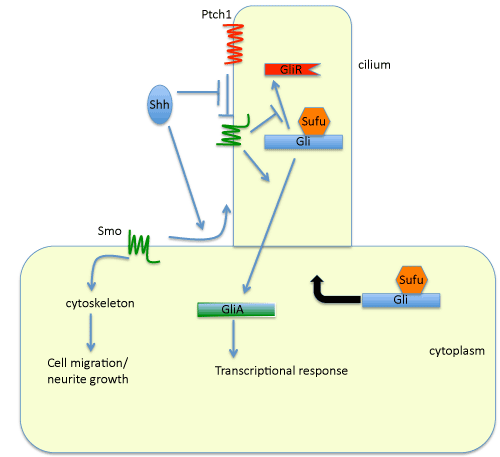
| Figure 1: The primary cilium and the Hh signaling. The interaction between Shh and Ptch1 leads to the ciliary localization of Smo, which is otherwise inhibited by Ptch1. A Gli-Sufu complex is also localized to the cilium and this localization is enhanced by Shh. It is believed that Gli proteins are proteolytically processed inside or at the base of the cilium in the absence of Shh. In the presence of Shh, activated Smo promotes the dissociation of Gli proteins from Sufu and turns Gli proteins into transcriptional activators. Smo outside the cilium appears to regulate cell migration and neurite growth in response to Shh. |