 |
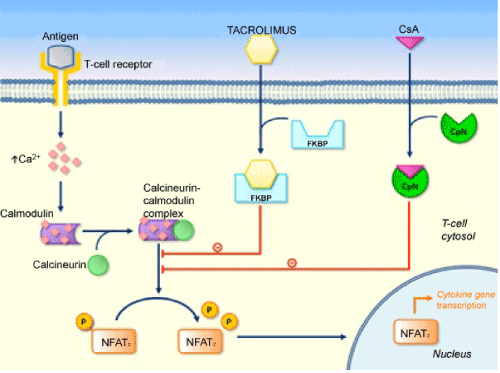
| Figure 1: Mechanism of action of tacrolimus and cyclosporine A. Tacrolimus binds to the immunophilin FKBP12, forming the FKBP12-tacrolimus complex, responsible for inhibiting calcineurin, a serine-threonine phosphatise involved in T lymphocyte activation. CsA binds cyclophilin (CpN) to induce calcineurin inhibition. Inhibition of calcineurin prevents dephosphorylation of nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT), resulting in decreased expression of cytokines such as IL-2, thereby suppressing T cell activation and proliferation. |