|
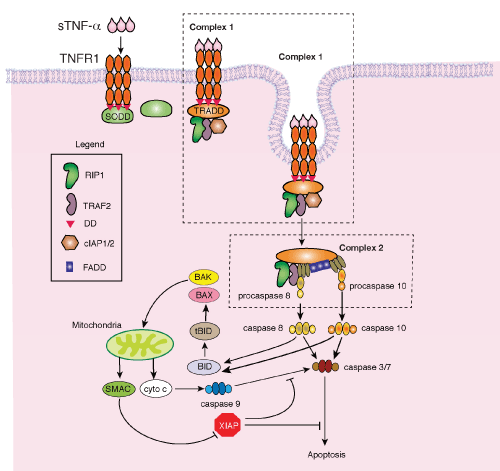
| Figure 2: The death pathway mediated by TNF-α. Soluble TNF-α binds to its cognate receptor, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) which is bound to silencer of death domain (SODD) via the TNFR1 death domain (DD). Binding of TNF-α to TNFR1 releases SODD, enabling the binding of TNFR1-associated death domain protein (TRADD), followed by the assembly of receptor-interacting protein-1 (RIP1), TNF receptor-associated factor-2 (TRAF2), and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-1 and -2 (cIAP 1/2) or Complex 1. Endocytosis of Complex 1 leads to the dissociation of cIAP 1/2 and the formation of Complex 2 which consists of TRADD, TRAF2, RIP1, Fas-associated death domain (FADD), and procaspases 8 and 10. Procaspase 8/10 cleaves BH3 interacting death domain (BID) into truncated BID (tBID), activating the mitochondrial death pathway. Procaspase 8/10 also activates caspase 3/7, leading to apoptosis. Additional abbreviations: BAX, Bcl-2-associated X protein; BAK, Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer; SMAC, second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases; cyto c, cytochrome c, XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis. |