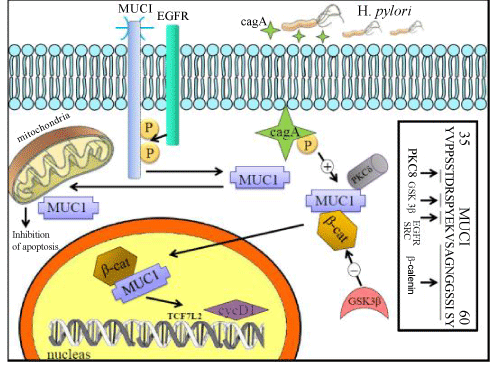
MUC1 is phosphorylated by EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases. Under normal conditions, the cytoplasmic tail of MUC1 cycles from the cell membrane to endosomes and then back to the cell membrane. When overexpressed, MUC1 activates the wnt-β-catenin pathway. MUC1 competes with E-cadherin for binding to β-catenin. CagA and PKC-δ promote MUC1 binding to β-catenin, whereas GSK3β blocks MUC1 binding to β-catenin leading to β-catenin degradation. Persistence of the MUC1-β-catenin complex facilitates cycling to the nucleus where MUC1-β-catenin binds TCF7L2 on the cyclin-D1 promoter, coactivates cyclin-D1 and interacts with other transcription factors such as STAT1/3, NF κB RelA, and ERα. Transport of MUC1 to the mitochondria leads to inhibition of apoptosis.