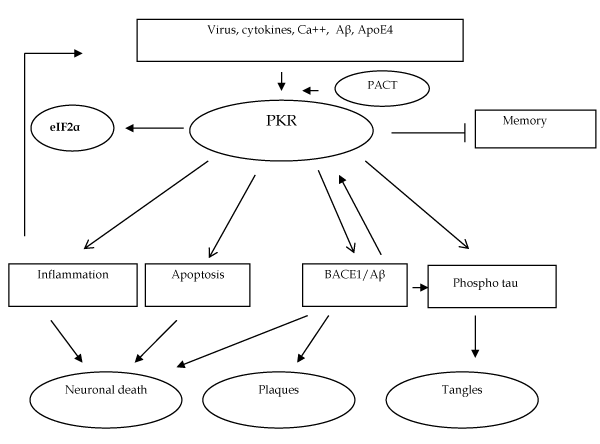
| Figure 1: PKR activation by inflammatory signals, ApoE4 expression or Aβ toxicity could trigger in AD brains the reduction of memory performance. In addition previous reports have shown that abnormal molecular signals leading to inflammation, neuronal death, Aβ production and tau phosphorylation could also be triggered by the activation of PKR as well as some other eiF2α kinases. Previous data have also demonstrated that the levels of phosphorylated PKR are increased in AD brains and in the CSF of AD patients. PKR is now a good candidate as putative diagnostic and prognostic biomarker as well as a valid pharmacological target to induce neuroprotection in AD patients. |